Syllabus :GS 3/Economy
In News
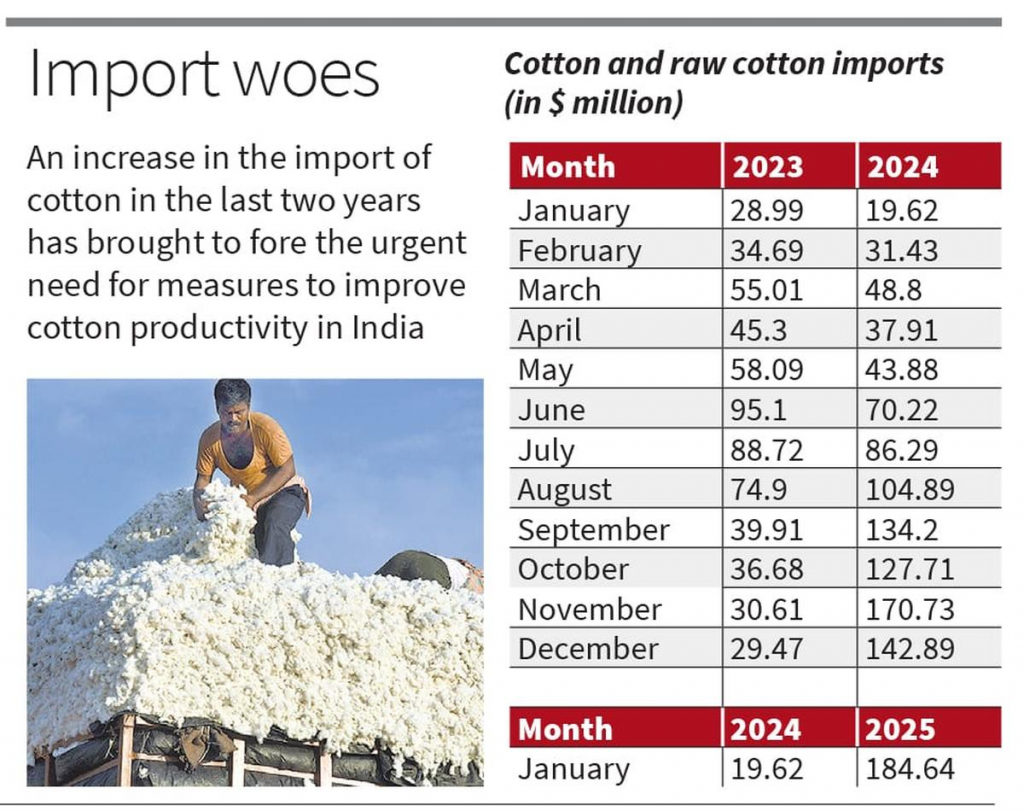
- India’s cotton imports have significantly increased in recent months, with imports reaching $104 million in August 2024 and rising to $184.64 million in January 2025, compared to $19.62 million in January 2024.
Reasons for High Cotton Imports
- Global cotton prices are weak, making imports more attractive.
- Indian cotton prices are higher than those of key exporters like Brazil, U.S., Australia, and Africa.
- Example: Indian cotton costs 80-85 cents per pound, while Brazilian cotton is 60-65 cents per pound.
- Export demand for garments & home textiles is rising (over 60% of India’s textile exports are cotton-based).
- Mills imported cotton despite an 11% duty as international prices were lower.
Key Facts About Cotton Cultivation
- About Cotton:
- One of India’s most important commercial crops, contributing 25% of global cotton production.
- Known as “White-Gold” due to its economic importance.
- Growing Conditions:
- Cotton is chiefly a tropical and sub-tropical crop. It requires uniformly high temperatures (21°C to 30°C) and grows well within the average annual rainfall range of 50-100 cm.
- Most of the irrigated areas under cotton are in Punjab, Haryana, Gujarat, and Rajasthan.
- Grows in varied soil types: Alluvial soils (Northern region), Black clayey soils (Central region), Mixed black and red soils (Southern region).
- India’s Cotton Scenario:
- India is the only country in the world that grows all four species of cotton. These species are:
- Gossypium arboreum (Asian Cotton),
- Gossypium herbaceum (Asian Cotton),
- Gossypium barbadense (Egyptian cotton), and
- Gossypium hirsutum (American Upland cotton).
- It is a crucial fiber and cash crop in India, significantly contributing to both the industrial and agricultural economy.
- It provides the primary raw material for the cotton textile industry.
- Gujarat, Maharashtra and Telangana are the major cotton producing states which produce about 65% of cotton production in the country.
- India is the only country in the world that grows all four species of cotton. These species are:
- Hybrid & Bt Cotton:
- Hybrid Cotton: Cross of two parent strains with different genetic traits, often formed through natural cross-pollination.
- Bt Cotton: Genetically modified, pest-resistant variety designed to combat bollworms.
Importance of Cotton
- The importance of cotton crop is as follows:
- Economic Significance: Cotton is a major cash crop in India, providing livelihoods to millions of farmers and supporting the country’s large textile industry.
- Global Position: India is the largest producer of cotton globally, playing a crucial role in the international cotton market.
- Textile Industry Backbone: Cotton is the primary raw material for the textile industry, which is a significant contributor to India’s GDP and export earnings.
- Employment Generation: The cotton industry, from farming to textiles, creates employment opportunities across various sectors, including agriculture, manufacturing, and trade.
- Cultural Importance: Cotton has historical and cultural significance in India, being central to traditional clothing and crafts.
Union Budget
- The Union Budget for February 2025 introduced a Cotton Mission to improve cotton productivity and address the challenges faced by farmers.
Source: TH
Previous article
India’s Share in Spices Market
Next article
Booming Demand for Warehouses in India