Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
Context
- Warehousing, once perceived as a mere storage function, has now emerged as a crucial pillar of India’s supply chain infrastructure.
Factors Driving the Demand for Warehousing in India
- E-commerce Boom: India’s e-commerce sector is projected to reach $350 billion by 2030.
- The need for fast and efficient deliveries requires expansive warehousing networks close to consumption hubs.
- Growth of Cold Chain Logistics: Rising demand for fresh food, pharmaceuticals, and vaccines has led to increased investment in temperature-controlled warehousing.
- Initiatives like ‘Make in India’ and Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes boost the demand for warehousing to store raw materials and finished goods.
- By 2026, India is projected to be among the top 6 users of warehouse automation systems worldwide, with the market expected to reach USD 2 billion annually.
- Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Services: The rise of 3PL providers is increasing demand for Grade A warehouses with higher efficiency and better technology integration.
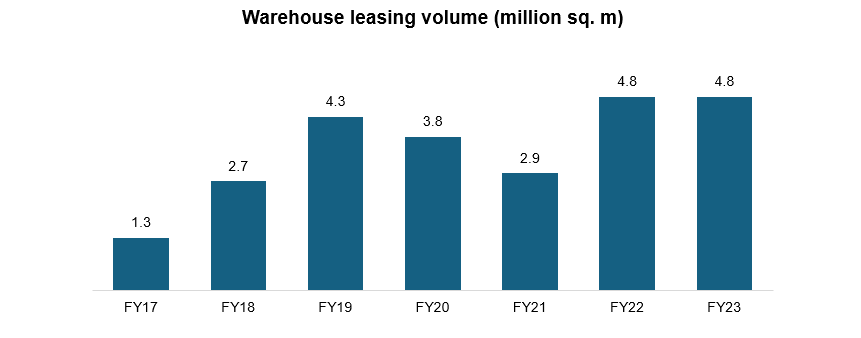
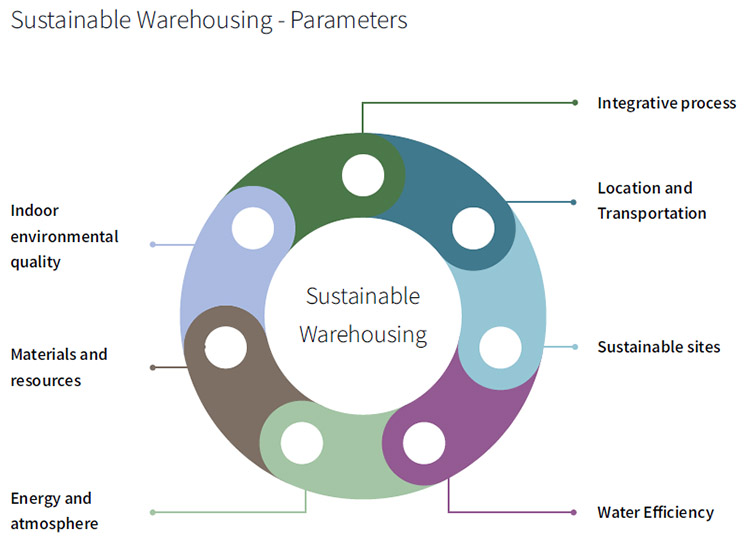
Challenges in warehousing development
- High Land Acquisition Costs: Limited availability of affordable land in key logistics corridors affects expansion.
- Policy Constraints: Complex land use regulations and inconsistent state policies hinder smooth development.
- Infrastructure Gaps: Inadequate road connectivity and power supply in certain regions slow down warehouse efficiency.
- Skill Shortages: The demand for skilled labor in warehouse management and logistics is increasing, necessitating workforce training.
Government steps
- National Logistics Policy (NLP) aims to reduce logistics costs to 10% of GDP, thereby improving cost efficiency.
- PM Gati Shakti Programme: It focuses on integrated infrastructure planning and multimodal connectivity.
- Development of Multimodal Logistics Parks (MMLPs): It improves logistics efficiency, reduces costs, and facilitates seamless movement of goods across various transportation modes (rail, road, air, and sea).
Way Forward
- Smart Warehouses: Adoption of AI, IoT, and robotics is enhancing warehouse efficiency, inventory tracking, and order processing.
- Regulatory Reforms: Streamlining state-wise policies to ensure uniformity in warehouse development.
- Sustainable Warehousing Practices: Promoting green warehousing with energy-efficient storage systems and renewable energy integration.
Source: BL
Previous article
Surge in India’s Cotton Imports
Next article
news-in-short-10-march-2025