ULLAS Program
Syllabus :GS 2/Governance
In News
- Mizoram and Goa declared themselves “fully literate” under the ULLAS adult literacy programme, with literacy rates of 98.2% and 99.72%, respectively.
ULLAS program
- ULLAS – Nav Bharat Saaksharta Karyakram, also known as the New India Literacy Programme (NILP).
- It is a centrally sponsored initiative that aligns with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
- It aims to provide functional literacy (reading, writing, numeracy) and life skills to adults aged 15+ who missed formal education, enabling their social integration and contribution to national growth.
- The programme is driven by volunteerism, promotes social responsibility (‘Kartavya Bodh’), and offers educational content in regional languages via the DIKSHA platform and ULLAS app.
- Learners and volunteers receive certificates to encourage motivation and ongoing learning.
Source :IE
Amoeba
Syllabus: GS2/ Health
Context
- Kerala’s State Public Health Laboratory (PHL) has developed molecular diagnostic kits to detect five species of free-living amoeba (FLA) that can cause amoebic meningoencephalitis.
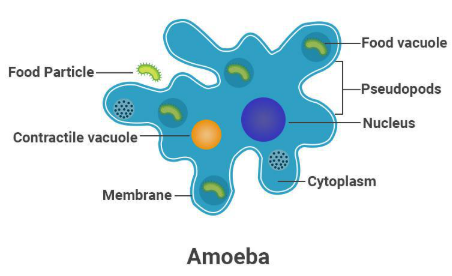
What is an Amoeba?
- Amoeba is a type of single-celled microscopic organism that belongs to the group protozoa.
- It is one of the simplest forms of life and is found in water, soil, and other moist environments.
- Key Characteristics:
- Eukaryotic: It has a well-defined nucleus.
- Shape-shifting: Amoebae have no fixed shape; they constantly change shape by extending parts of their body called pseudopodia (false feet).
- Movement and Feeding: Pseudopodia help them move and engulf food particles (a process called phagocytosis).
- Reproduction: They reproduce asexually through binary fission, where the cell splits into two.
What Is Amoebic Meningoencephalitis?
- Amoebic meningoencephalitis is a rare and often deadly brain infection caused by certain species of free-living amoeba.
- It affects the central nervous system (CNS) and usually occurs when contaminated water enters the nasal passages and reaches the brain.
- Symptoms: fever, nausea, stiff neck, seizures, and rapid progression to coma and death.
Source: TH
11th BRICS Parliamentary Forum
Syllabus: GS2/IR
Context
- The 11th BRICS Parliamentary Forum was held in Brasilia, Brazil.
About
- A broad consensus was reached on key global issues: the responsible use of Artificial Intelligence (AI), global trade and economy, inter-parliamentary cooperation, global peace and security.
- India stressed the need for joint efforts to curb financial support to terrorist organizations, enhance intelligence sharing, prevent the misuse of emerging technologies, and promote cooperation in investigation and judicial processes.
- India was entrusted with hosting the 12th BRICS Parliamentary Forum next year, and Lok Sabha Speaker Om Birla was formally handed over the chairmanship.
About BRICS
- BRICS is an acronym that refers to a group of five major emergingnational economies:Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa.
- Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, Indonesia, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates have joined BRICS as new full members.
- The term was originally coined by economist Jim O’Neill in 2001.
- Origin: As a formal grouping, BRIC started after the meeting of the Leaders of Russia, India and China in St. Petersburg on the margins of the G8 Outreach Summit in 2006.
- The grouping was formalized during the 1st meeting of BRIC Foreign Ministers on the margins of UNGA in New York in 2006.
- Initially, the grouping was termed BRIC as South Africa was inducted in 2010 and from there on it has been referred to as BRICS.
- Summits: The governments of the BRICS states have met annually at formal summits since 2009.
- BRICS countries have come together to deliberate on important issues under the three pillars of:
- political and security,
- economic and financial and
- cultural and people-to-people exchanges.
- New Development Bank: Formerly referred to as the BRICS Development Bank, is a multilateral development bank established by the BRICS states.
- The Bank shall support public or private projects through loans, guarantees, equity participation and other financial instruments.
Source: PIB
Losgna Occidentalis
Syllabus: S&T
In News
- The discovery of a new species of parasitic wasp – named ‘Losgna Occidentalis’ from Chandigarh has drawn attention to the unexplored richness of India’s biodiversity.
About
- The genus Losgna belongs to the family Ichneumonidae, commonly known as Darwin wasps. These are parasitic wasps known for laying eggs in or on other arthropods, thus playing an important role in biological pest control.
- Parasitic wasps belong to the order Hymenoptera, which also includes bees and ants.
- They do not build hives, nor do they serve a queen like social bees or ants.
- The genus was last recorded in India in 1965 by the German entomologist Heinrich. Since then, no specimens or records have been found in Indian collections.
- They serve as natural biocontrol agents by targeting pest species like crop-eating insects.
Source: TH
AI RAM Initiative
Syllabus: GS3/ Science and Technology
Context
- The UNESCO Regional Office for South Asia, in collaboration with the IndiaAI Mission and Ikigai Law, organized the 5th and final Stakeholder Consultation on AI Readiness Assessment Methodology (RAM) in India.
AI RAM Initiative
- The initiative aims to develop an India-specific AI policy report that maps strengths, identifies growth opportunities and offers actionable recommendations for the ethical and responsible adoption of AI across sectors.
- The AI RAM acts as a diagnostic tool to support governments in strengthening regulatory and institutional capacity in AI.
Significance of the initiatives
- Aligns with the INDIAai Mission, launched with over ₹10,000 crore funding.
- Prioritises the “Safe and Trusted AI” pillar focused on:
- Ethical AI development,
- Indigenous governance frameworks,
- Self-assessment guidelines,
- Capacity-building for AI innovation.
Source: PIB
Previous article
International Conference on Disaster Resilient Infrastructure 2025
Next article
Bhagwan Birsa Munda