Syllabus: GS1/Geography
In Context
- India is closely monitoring Chinese infrastructure projects on the Brahmaputra River, particularly hydropower developments, due to their potential impact on downstream regions such as Arunachal Pradesh and Assam.
Brahmaputra River System
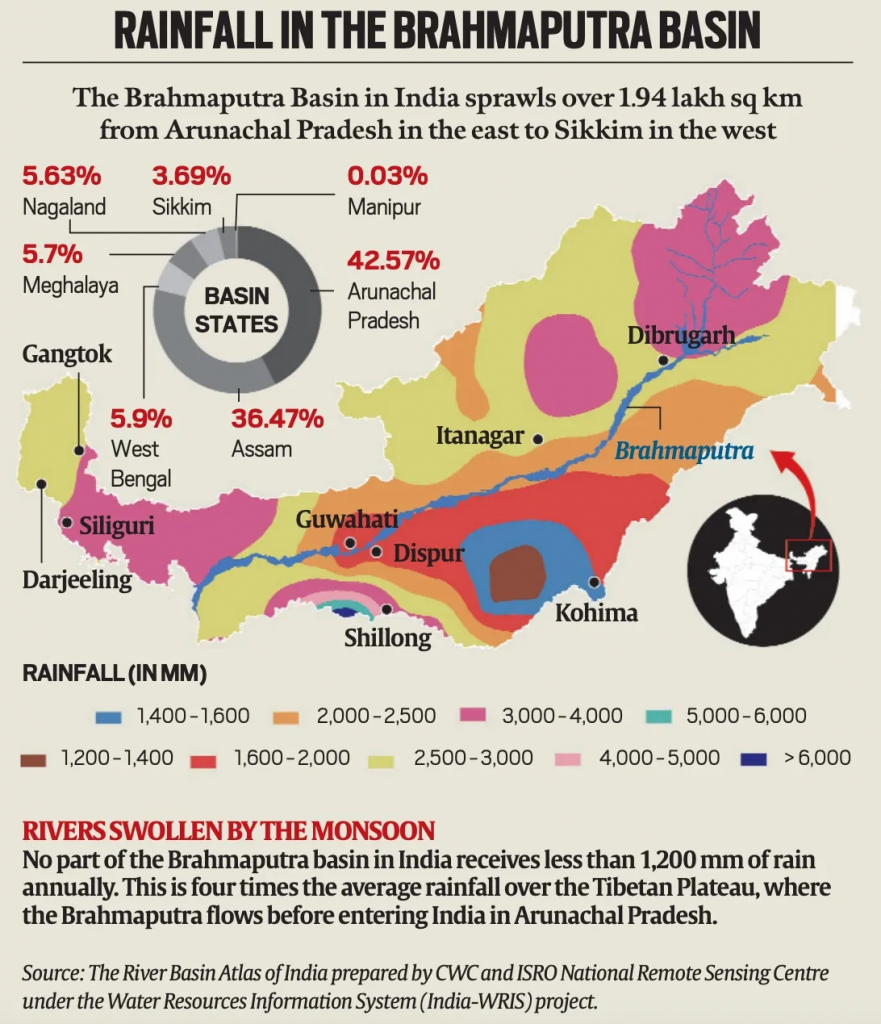
- The Brahmaputra River originates in the Kailash ranges at 5,150 m elevation, flows 2,900 km in total, including 916 km in India.
- It originates as Yarlung Tsangpo in Tibet .
- Its basin spans across Tibet (China), Bhutan, India, and Bangladesh.
- In India, it covers Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, West Bengal, Meghalaya, Nagaland, and Sikkim.
- It enters India near Gelling in Arunachal Pradesh.
- The river, which is called Siang in Arunachal, is joined by many tributaries in Assam as it flows down the plains before entering Bangladesh, where it is called Jamuna.
- Tributaries: Key right-bank tributaries include the Lohit, Dibang, Subansiri, and Teesta.
- Left-bank tributaries include the Burhidihing and Kopili.
- River-Linking Projects:
- Manas-Sankosh-Teesta-Ganga Link: Connects Brahmaputra to Ganga via Sankosh & Teesta.
- Jogighopa-Teesta-Farakka Link: Links Brahmaputra via Jogighopa Barrage to Farakka on Ganga.
- Host Riverine Island: It hosts Majuli, the world’s largest river island, and Umananda, the smallest river island in the world, both located in Assam.
Read our detailed article on Brahmaputra River System: Origin, Course & Tributaries
How Could Chinese Dams Affect the Brahmaputra in India?
- Hydrological Impact: The Chinese dams may alter natural water flow patterns, affecting seasonal water availability.
- Example: Medog Hydropower Project (proposed 60,000 MW) near the ‘Great Bend’ of the Yarlung Tsangpo in Tibet.
- A sudden release of water or temporary water retention can exacerbate floods or worsen dry spells in Arunachal Pradesh and Assam, especially during the lean season.
- Ecological Disruptions: Reduced sediment flow, altered flood regimes, and biodiversity loss.
- Example: The Kaziranga National Park, home to the one-horned rhinoceros, depends on regular flooding of the Brahmaputra for ecological regeneration.
- Strategic & Geopolitical Risk: Gives China a perceived upper hand in water diplomacy; potential tool for coercion. Like during the 2017 Doklam standoff, China withheld hydrological data on the Brahmaputra, which it is obligated to share under a bilateral agreement.
- Economic Consequences: Uncertainty in water flow can affect irrigation, agriculture, and hydropower generation downstream.
- Example: Any disruption in Subansiri and Siang tributaries, where India has planned large hydropower projects (e.g., Lower Subansiri Hydro Project), can delay infrastructure timelines or reduce output.
- Inter-State Tensions in India: Unpredictable flow from upstream may aggravate water-sharing conflicts between Indian states.
China’s Contribution Vs India’s Share
- Multiple expert studies (e.g., by PK Saxena and Teerath Mehra) indicate that China contributes only 22–30% of Brahmaputra’s annual discharge.
- 70–78% of the river’s flow is generated within India, primarily due to monsoonal rainfall and tributary inflows in Arunachal Pradesh and Assam.
- Hydrologically, China’s control over the river’s headwaters has limited influence on its overall flow in India.
- Even to address water scarcity, two river-linking projects have been proposed: the Manas-Sankosh-Teesta-Ganga Link and the Jogighopa-Teesta-Farakka Link.
Way Forward
- India should conduct detailed scientific studies and develop an adaptive strategy to assess the impact of Chinese projects on the Brahmaputra.
- It must strengthen diplomatic efforts to access hydrological data and establish data-sharing protocols with China for early warnings and disaster preparedness.
- India can use forums like BIMSTEC, SCO, and Quad to internationalize the issue and press for sustainable and equitable transboundary river management.
Source :IE
Previous article
Nine years of Pradhan Mantri Surakshit Matritva Abhiyan
Next article
Demand for Compulsory Licensing for Rare Disease