
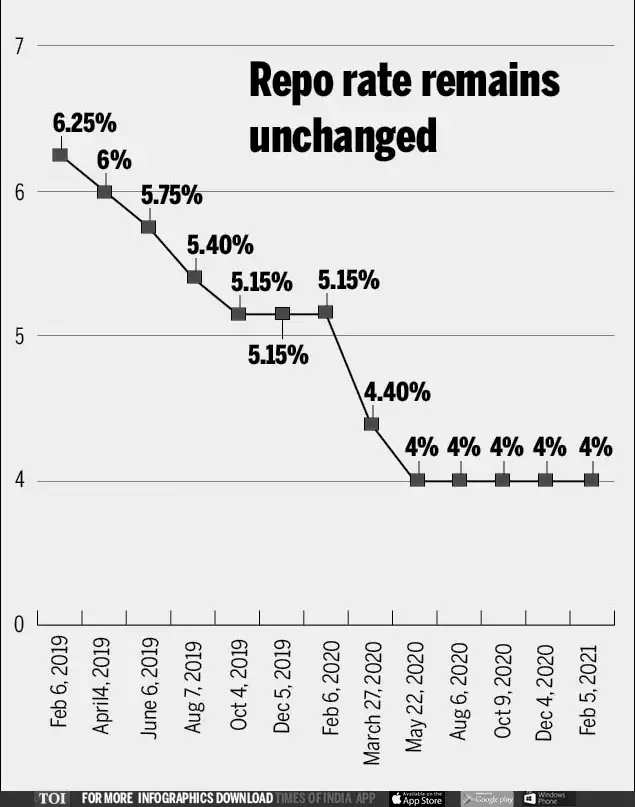
In News- The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) decided to keep the policy repo rate unchanged at 4.0% under the Liquidity adjustment facility (LAF).
- Consequently, the reverse repo rate remains unchanged at 3.35% and the marginal standing facility (MSF) rate and the Bank Rate at 4.25%.
- It was decided on the basis of an assessment of the current and evolving macroeconomic situation.
Key Highlights :
- The Monetary Policy Committee decided to continue with the accommodative stance as long as necessary to revive growth on a durable basis and mitigate the impact of COVID-19 on the economy while ensuring that inflation remains within the target.
- These decisions are in consonance with the objective of achieving the medium-term target for consumer price index (CPI) inflation of 4 % within a band of +/- 2 % while supporting growth.
- It has also projected the real GDP growth at 10.5% in 2021-22 in the range of 26.2 to 8.3% in H1 and 6.0 % in Q3.
- The sharp correction in food prices has improved the food price outlook, but some pressures persist, and core inflation remains elevated.
- Pump prices of petrol and diesel have reached historical highs.
- Growth was recovering, and the outlook had improved significantly with the rollout of the vaccine programme in the country.
What is Monetary Policy?
- It is the process of regulating the supply of money in an economy by the monetary authority of the country.
- It is meant to adjust the inflation rates or interest rates to sustain the price stability and to maintain the predictable exchange rates with foreign currencies.
- The Reserve Bank of India controls the monetary policy in resonance with the central government’s developmental goals.
- Four major objectives of the Monetary Policy are-
- To stabilise the business cycle.
- To provide reasonable price stability.
- To provide faster economic growth.
- Exchange Rate Stability.
About Monetary Policy Committee:
- It is a committee constituted by the Reserve Bank of India and is tasked with framing monetary policy using tools like the repo rate, reverse repo rate, bank rate, Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR).
- It was established on the recommendation of the Urjit Patel Committee constituted in 2013.
- The RBI Act, 1934 was amended by Finance Act (India), 2016 to constitute MPC to bring more transparency and accountability in fixing India’s Monetary Policy.
- It comprises six members – three officials of the RBI and three external members nominated by the Government of India.
- The Governor of RBI is the chairperson ex officio of the committee.
- Deputy governor of RBI in charge of the monetary policy will be a member, as also an executive director of the central bank.
- Members of the MPC will be appointed for a period of four years and shall not be eligible for reappointment.
|
Key Terms
|
Previous article
The Foundation Stone of infrastructure projects in West Bengal
Next article
Flash Floods in Uttarakhand