200th Birth Anniversary of Dadabhai Naoroji
Syllabus: GS1/History
In News
- The 200th birth anniversary of Dadabhai Naoroji known as ‘The Grand Old Man of India ‘was recently observed .
Dadabhai Naoroji (1825–1917)
- Dadabhai Naoroji was born in Bombay on 4 September 1825 in a priestly Parsi family.
- He was a pioneering figure in India’s freedom struggle.
- He was the first Indian to be elected to the House of Commons (1892).
Contributions:
- He formulated the famous drain-of-wealth theory, which became India’s cornerstone argument against British rule. He argued that British rule impoverished India by transferring wealth to Britain.
- He used statistics on wages, prices, trade, and taxation to argue that British policies increased poverty in India—culminating in his seminal work Poverty and Un-British Rule in India (1901).
- He was the first to give expression to the demand for Swaraj from the platform of Indian National Congress (1906).
- He was an active member of the Bombay Association (1852), the first association in the western India to consider political issues
- In 1851, he founded Rast Goftar (Truth Teller), a Gujarati fortnightly with a Persian name.
- It was a progressive journal educating readers on duties of citizenship.
- In 1867, he founded the East Indian Association which was a political advocacy group for India having both British and Indians on its membership roll.
- It was the first political organization with members from different provinces of India.
- Two young law students viz. W.C. Bonnerji (1844-1906) and Pherozeshah M. Mehta (1845-1915) became his disciples
- It was the first political organization with members from different provinces of India.
- Dadabhai Naoroji was appointed as Justice of the Peace in 1883, started a newspaper called ‘Voice of India’.
- He twice served as the President of Indian National Congress (1886 and 1893) besides representing India at the International Congress of Social Democrats at Amsterdam in 1905.
Death and Legacy
- He permanently returned to India from Britain in 1908 at the ripe age of 83.
- He passed away in Bombay on June 30, 1917 leaving a weighty bequest of experience and achievements behind.
- Dadabhai Naoroji’s legacy lies in combining intellectual rigor with political activism, laying the foundation for India’s nationalist movement.
Source :PIB
Nalanda University
Syllabus:GS1/History
In News
- Bhutan’s Prime Minister Dasho Tshering Tobgay recently visited Nalanda University.
Nalanda University
- It was originally established in 427 CE by Emperor Kumaragupta and ancient Nalanda was the world’s first residential university, hosting 2,000 teachers and 10,000 students for over 800 years, and attracting scholars from across Asia.
- It is located near the Rajgir hills and symbolizes a unique blend of nature, spirituality, and learning, drawing from its ancient heritage where great thinkers like Buddha, Mahavira, Nagarjuna, and Aryabhatta once taught or meditated.
Revival
- The idea to revive Nalanda was proposed by Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam in 2006, with support from the East Asia Summit, the Singapore government, and Indian leadership. The Nalanda University Act was passed in 2010, and the first students enrolled in 2014.
- The revived Nalanda University aspires to be futuristic and global, rooted in ancient wisdom while addressing modern challenges, making it a beacon of sustainable and inclusive education welcomed worldwide.
Source :PIB
SAMHiTA Conference on South Asian Manuscripts and Mathematics
Syllabus: GS1/ History and Culture
Context
- The Minister of External Affairs of India inaugurated the SAMHiTA Conference on South Asia’s Manuscript Traditions and Mathematical Contributions in New Delhi.
About SAMHiTA (South Asian Manuscript Histories and Textual Archive)?
- SAMHiTA is an initiative to create a relational database and digital archive of Indian and broadly South Asian manuscripts housed in libraries, archives and other repositories outside India, through collaboration with institutional partners.
- Focus areas: Mathematics, astronomy, linguistics, philosophy, medicine, literature in manuscripts.
- Significance: Helps reclaim India’s intellectual traditions, prevents cultural erasure, and strengthens research in history of science.
Other Initiatives to safeguard the Manuscripts
- The Ministry of Culture established the National Mission for Manuscripts (NMM) in 2003 to document, conserve, and promote access to Indian manuscripts.
- The Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts (IGNCA) is a premier Indian institution and autonomous trust under the Ministry of Culture, functions as a vast repository for manuscripts and other cultural resources, and as a hub for academic research.
- The National Digital Library of India (NDLI), the Bharatavani Project, and the Indian Culture Portal are all digital archives initiated by the Government of India.
- UNESCO’s Memory of the World Programme (global preservation of documentary heritage).
Source: AIR
National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) 2025
Syllabus: GS2/Education
Context
- The National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) 2025 rankings were announced by the Ministry of Education.
About
- For the seventh straight year, the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), Madras, claimed the top overall position.
- IISc Bengaluru retains its position as the top-ranked university.
- JNU holds the 2nd spot, followed by Manipal Academy of Higher Education at 3rd, making it the first private institution to enter the top three in this category.
- Hindu College (DU) continues ranking 1st among all colleges for at least the second consecutive year followed by Miranda House and Hans Raj College.
- Other Notable Leaders by Category:
- Management: IIM Ahmedabad leads this category.
- Medical: AIIMS Delhi maintains the top rank in this field.
- Law: National Law School of India University (NLSIU), Bengaluru remains the leading law institution.
National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF)
- NIRF was launched in 2015 by the Ministry of Education, to rank institutions of higher education in India.
- Five broad categories of parameters identified in the NIRF;
- Teaching, Learning & Resources
- Research and Professional Practice
- Graduation Outcome
- Outreach and Inclusivity
- Perception
- Each of these five parameters have 2 to 5 sub-parameters and a total number of 18 parameters are used for ranking of Higher Education Institutions (HEIs).
- The overall score is computed based on the weightage allotted to each parameter and sub-parameter.
Source: TH
Rare Reference Material for Enhanced Anti-Doping Testing in Sports
Syllabus: GS3/ Science and Technology
Context
- India has developed a rare and high-purity Reference Material (RM), Methandienone Long-Term Metabolite (LTM), for advanced anti-doping testing.
About
- Reference Materials (RMs) are highly purified and scientifically characterized forms of drug substances or their metabolites, essential for accurate analytical testing.
- In the context of anti-doping, they are crucial for the detection of over 450 substances that are currently prohibited by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA).
- These RMs are produced by only a few manufacturers globally, making them scarce and often expensive.
- These metabolites help in identifying athletes who have used Methandienone, even if they ceased usage months or years prior to testing.
How RMs Detect Doping?
- When a banned drug is taken, the body breaks it into metabolites, some of which (LTMs) stay for months or years.
- Labs use techniques like Mass Spectrometry to compare an athlete’s urine/blood sample with the Reference Materials (RMs).
- If there is a match, it confirms the presence of the banned drug or its metabolite.
| World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) – WADA is a Swiss private law, not-for-profit Foundation. WADA was established in 1999 as an international independent agency to lead a collaborative worldwide movement for doping-free sport. – It was created as a result of a joint initiative by the International Olympic Committee (IOC) and various governments. – Headquarters: Montreal, Canada – Seat: Lausanne, Switzerland |
Source: PIB
National Investigation Agency (NIA)
Syllabus: GS3/Security Agencies
Context
- The Supreme Court criticized the Union Government for not establishing exclusive National Investigation Agency (NIA) courts, urging budget allocations to ensure timely trials and prevent bail for serious offenders.
National Investigation Agency (NIA)
- Established under: NIA Act, 2008 after 26/11 Mumbai attacks.
- Function: Central counter-terrorism law enforcement agency.
- Mandate: Investigates offences affecting India’s sovereignty, security, international treaties, etc.
- NIA (Amendment) Act, 2019:
- Jurisdiction extended: Can investigate scheduled offences committed outside India involving Indian citizens/interests.
- Expanded mandate: Covers offences under Explosive Substances Act, 1908 Human Trafficking, Cyber Terrorism Arms Act, 1959.
- Headquarters: New Delhi
- Special Courts: Total NIA Special Courts: 51
- Exclusive NIA Courts: 2 (Ranchi & Jammu)
Source: HT
Baltic Sea
Syllabus: GS1/Places
In News
- Sweden has accused Russia of being behind a significant rise in instances of GPS signal jamming recorded over the Baltic Sea, raising concerns for aviation in the region.
- GPS jamming, also known as GPS intervention, involves a device (jammer) emitting strong radio signals on GPS frequencies in order to overpower weaker signals.
- Unlike GPS jamming, which disrupts signals entirely, GPS spoofing deceives the receiver into trusting false data.
Baltic Sea
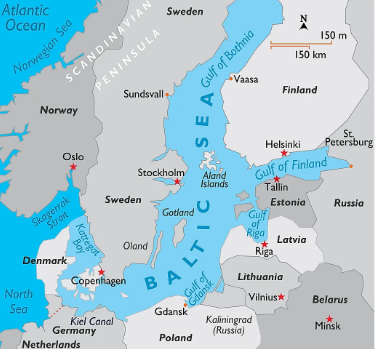
- The Baltic Sea is one of the seas of the Atlantic Ocean.
- It is located in Northern Europe, enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, and Sweden.
- It is one of the planet’s largest bodies of brackish water, where salt water from the North-East Atlantic blends with fresh water from the surrounding rivers and streams.
Source :TH
Previous article
Environment Audit Rules, 2025
Next article
Recusals By Judges