Somnath Swabhiman Parv
Syllabus: GS1/ History and Culture
Context
- PM Modi commemorated 1,000 years since the first attack on the Somnath Temple in 1026 AD, describing the iconic shrine as a timeless symbol of India’s civilisational resilience and unbreakable spirit.
About Somnath Temple
- Somnath is revered as the first of the twelve Jyotirlings of Lord Shiva, as mentioned in the Dwadasha Jyotirling Stotram.
- The temple is located at Prabhas Patan on the western coast of Gujarat, a region historically associated with maritime trade, cultural exchange, and prosperity.
- The shrine was first attacked in January 1026 by Mahmud of Ghazni, marking the beginning of a series of invasions aimed at destroying symbols of Indian civilization.
- Despite repeated devastation, the temple was rebuilt multiple times.
Restoration of the Temple
- Ahilyabai Holkar played a crucial role in restoring the temple in the 18th century, demonstrating the role of indigenous rulers in cultural revival.
- After Independence, Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel envisioned the reconstruction of Somnath.
- The present structure was completed and inaugurated on May 11th 1951, by Dr. Rajendra Prasad, reflecting the constitutional ethos of cultural freedom.
- K.M. Munshi was instrumental in the reconstruction of the temple.
- Swami Vivekananda viewed Somnath as a symbol of India’s national spirit that regenerates despite adversity.
Source: DD News
World Braille Day
Syllabus: GSI/ Society, GS2/ Social Justice
Context
- World Braille Day is observed annually on January 4, marking the birth anniversary of Louis Braille.
About
- The day, celebrated since 2019, is observed to raise awareness of the importance of Braille as a means of communication in the full realization of the human rights of blind and partially sighted people.
- Braille is essential in the context of freedom of expression and opinion, as well as social inclusion, as reflected in article 2 of the Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities.
- According to the 2011 Census, there are 50,32,463 persons with visual impairment in India.
Initiatives for the Empowerment of Visually Impaired Persons
- Braille Development Unit: It is an important constituent of the Department of Special Education and Research.
- It contributed to the development of Braille Codes in different Indian languages. In addition to the current publications, the institute is in the process of developing a ‘Manual on Bharti Braille’.
- Braille Production: India has developed a robust Braille printing ecosystem through; the Central Braille Press established in 1951, the Regional Braille Press established in 2008 at Chennai and 25 other Braille Presses established by the Government.
- With the combined efforts of these Braille Presses, the Braille literature is published in 14 languages.
Source: PIB
Human Rabies To Be Declared Notifiable Disease In Delhi
Syllabus: GS2/ Health
Context
- The Delhi government is set to declare human rabies a notifiable disease in the National Capital Territory of Delhi under the Epidemic Diseases Act.
What Is a Notifiable Disease?
- A notifiable disease is one that must be legally reported to public health authorities upon diagnosis or suspicion.
- Mandatory reporting enables real-time surveillance, early detection, rapid response, and evidence-based planning.
Rabies and Its Risks
- Rabies is a viral infection transmitted through the saliva of infected animals such as dogs, cats, bats, and monkeys.
- It typically spreads through bites, scratches, or saliva entering open wounds.
- Symptoms may include fever, headache, and nausea; hallucinations and fear of water (hydrophobia).
- Post-exposure vaccination, given promptly after a potential exposure, is the most reliable way to prevent infection.
- According to India’s National Rabies Control Program, 6,644 suspected human rabies cases and deaths were reported between 2012 and 2022.
- However, the WHO estimates a far higher toll, at around 18,000–20,000 deaths annually, with up to two-thirds of victims under age 15. India alone accounts for 36% of global rabies deaths.
- The issue of rabies is particularly serious because it is almost 100% fatal once symptoms appear.
Source: BS
Nanobots in Cancer Therapy
Syllabus:GS3/Science and Tech
In News
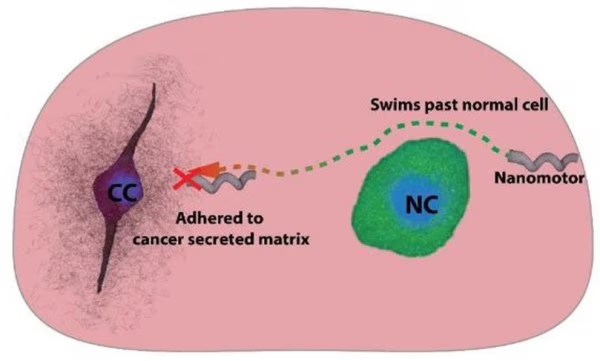
- Professor at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) Bangalore Dr. Ambarish Ghosh has developed magnetic nanorobots that can deliver drugs deep into tumors, enabling targeted, minimally invasive cancer therapy with fewer side effects and faster recovery.
Nanobots
- They are tiny robots designed for specific tasks, such as targeted drug delivery.
- They allow drugs to reach precise disease-affected areas, making treatment more effective and reducing side effects compared to conventional methods.
Applications in Drug delivery
- Magnetic nanorobots mimic bacterial movement with a helix-shaped tail and magnet, allowing them to swim through tissues and deliver drugs precisely to cancer cells without harming healthy tissue.
- They can generate localized heat to destroy tumors, act as drugs themselves, and serve as MRI beacons.
- Effective against ovarian and breast cancer and certain bacteria, they also show potential in dental treatments like root canals and tooth remineralization.
Source : IE
India Becomes World’s Largest Rice Producer
Syllabus: GS3/Economy
In News
- India has become the world’s largest producer of rice, surpassing China.
- India’s rice production has reached 150.18 million tonnes, compared to China’s 145.28 million tonnes.
Rice
- It is the most important food crop of India.
- It is predominantly a Kharif or summer crop.
- Geographical conditions
- Temperature: Rice requires hot and humid conditions. The temperature should be fairly high i.e. 24°C mean monthly temperature with average temperature of 22°C to 32°C.
- Rainfall ranging between 150-300 cm is suitable for its growth in areas of Punjab, Haryana and Western Uttar Pradesh where rainfall is less than 100 cm, rice is cultivated with the help of irrigation.
- Soil: Rice is grown in varied soil conditions but deep clayey and loamy soil provides the ideal conditions.
Importance
- It is the staple food crop of a majority of the people in India.
- It plays a significant role in the national food and livelihood security system
- It helps earn significant foreign exchange as it is exported to other countries
Current Status
- ICAR has developed India’s first genome-edited rice varieties – DRR Rice 100 (Kamla) and Pusa DST Rice 1. These varieties have the potential to bring about revolutionary changes in terms of higher production, climate adaptability, and water conservation.
Source :Air
Battery Pack Aadhaar Number (BPAN)
Syllabus: GS3/ Environment
In News
- The Union Government has proposed a Battery Pack Aadhaar Number (BPAN) system to create a unified digital identity for battery packs, especially electric vehicle (EV) batteries, to ensure their traceability across the entire lifecycle.
What is BPAN?
- Battery Pack Aadhaar Number (BPAN) is a 21-character unique identification number proposed for every battery pack introduced in the Indian market.
- It works like a digital Aadhaar for batteries, allowing authorities to track batteries from manufacturing to recycling or disposal.
- The focus is primarily on EV batteries, which form the bulk of India’s lithium-ion battery demand.
- This will promote efficient recycling, second-life use, and safe disposal of batteries.
Key Features of BPAN
- Mandatory Unique ID: Every battery producer or importer must assign a BPAN to batteries sold or used internally.
- Lifecycle Data Capture: Covers sourcing of raw materials, manufacturing, usage, performance, repurposing, recycling, and final disposal.
- Dynamic Updating: Any major structural or ownership change in the battery requires issuance of a new BPAN.
- Visible & Durable Marking: BPAN must be marked on the battery pack at a location that cannot be easily destroyed or degraded.
Source: TH
Previous article
India’s Seafood Export Gets Boost
Next article
Reclaiming India’s Buddhist Civilisational Legacy