Syllabus: GS3/Disaster Management
Context
- The Economic Outlook for Southeast Asia, China and India: Enhancing Disaster Risk Financing report 2025 was released recently.
About
- It is a regular publication on Asia’s regional economic growth and development processes.
- Releasing Body: Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
- It focuses on the economic conditions of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) member countries.
- This edition of the Outlook comprises a thematic chapter focusing on enhancing disaster risk financing in Emerging Asia.
Major Findings
- Growing Disasters: Emerging Asian economies that comprise India, China, and the ASEAN11, face an escalating threat from natural disasters that are growing in both frequency and intensity.
- Over the past decade, the region has had an average of 100 disasters annually, impacting approximately 80 million people.
- The nature of these threats varies by geography: while floods and storms are the primary drivers of risk in India, tropical cyclones frequently batter the Philippines and Vietnam.
- Meanwhile, China and Indonesia have significantly higher seismic risks.
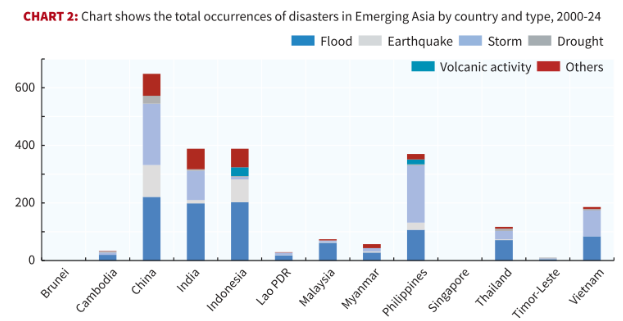
- Loss of GDP: From 1990 to 2024, India sustained average annual disaster related losses equivalent to 0.4% of GDP.
- India’s vulnerability is primarily hydro logical (non storm related floods and land slides).
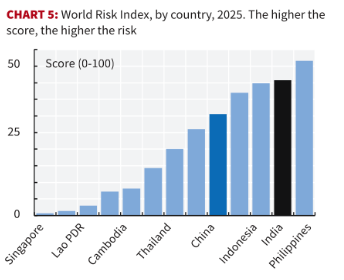
- World Risk Index: Among the Asian economies, India ranks second only to the Philippines in the World Risk Index.
- The index calculates risk as the geometric mean of exposure (population burden) and vulnerability (a combination of structural susceptibility, coping capacity, and longterm adaptation).
- To support the enhancement of disaster risk finance, key policy priorities to be considered by countries in the region include:
- improving regulatory frameworks and institutional capacity,
- facilitating and broadening DRF policy options,
- enhancing disaster risk finance education, and
- strengthening regional co-operation.
Disaster Resilient Infrastructure
- Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (DRI) refers to the design and construction of infrastructure systems that can withstand, adapt to, and rapidly recover from disasters.
- This resilience ensures uninterrupted essential services even during calamities.
- As urbanization and national growth accelerate, infrastructure, such as power, water, and transportation become ever more crucial.
| International Conference on Disaster Resilient Infrastructure – CDRI is a global partnership of National Governments, UN agencies and programmes, multilateral development banks and financing mechanisms, the private sector, academic and knowledge institutions. – CDRI was launched by India during the United Nations Climate Action Summit in 2019, at New York. – Members: More than 50 members. – Secretariat: New Delhi. |
Conclusion
- Building a disaster-resilient infrastructure is a complex task, requiring a blend of strategic planning, innovation, finance, and most importantly, a collective approach.
- Nations need to champion these components, ensuring they are not only prepared for future calamities but also poised for sustainable growth.
Source: TH
Previous article
India’s Emerging Concert Economy
Next article
India’s Silk Value Chain Projected To Double By 2030