
Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
Context
- India’s economy is witnessing strong growth momentum, marked by easing inflation and record-high exports, offering relief to households and strengthening the nation’s global trade position.
Present Status
- India’s economy is the fastest growing major economy, with real GDP growth estimated at 6.5% in 2024-25 and expected to continue at the same rate in 2025-26.
- Despite global uncertainties, strong domestic demand, easing inflation, rising exports, and robust capital markets support this growth.
- Key indicators like record foreign exchange reserves, a manageable current account deficit, and increasing foreign investment highlight India’s economic resilience and global confidence in its long-term prospects.
GDP Growth
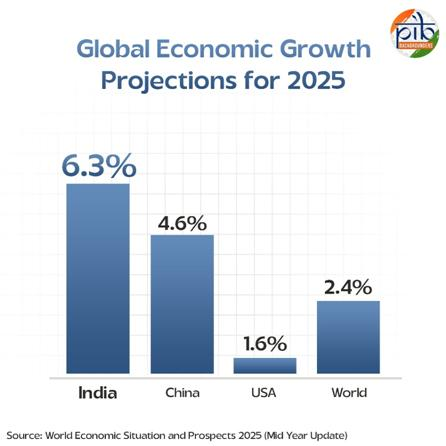
- India’s real GDP grew by 6.5% in 2024-25, with the Reserve Bank of India expecting similar growth in 2025-26.
- The United Nations forecasts 6.3% growth this year and 6.4% next year, while the Confederation of Indian Industry estimates growth between 6.4% and 6.7%, reflecting strong and consistent economic performance.
Inflation Trends in India
- The Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation dropped to 2.10% in June 2025, the lowest since January 2019, well within the Reserve Bank of India’s target range of 4% with a tolerance of ±2%.
- The Wholesale Price Index (WPI) inflation also saw a marginal decline to -0.13% in June 2025.
- The WPI Food Index inflation fell to -0.26%, signaling softer food prices over the year.
| Indicators for measuring the Inflation in India – Wholesale Price Index (WPI) which measures the average change in prices of goods before reaching the consumer. – WPI is calculated on the basis of wholesale price of Primary articles, fuel & power and manufactured products. – Consumer Price Index (CPI) measures change in price of goods that people buy for daily use such as food and beverages, clothing and footwear, housing, fuel and light and others. |

India’s Export Growth
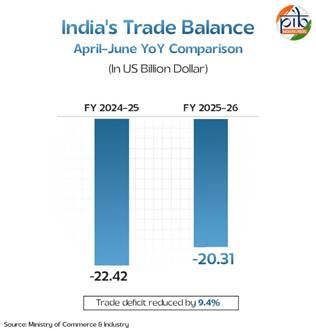
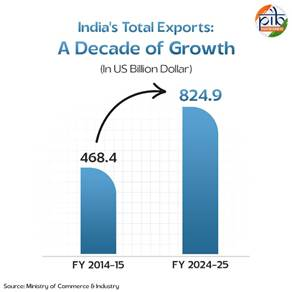
- According to the Ministry of Commerce & Industry, for the first quarter of FY 2025–26 (April–June 2025), total exports stood at US$ 210.31 billion, registering a 5.94% increase over the previous year, while imports increased by only 4.38%.
- This led to a 9.4% reduction in the trade deficit, which improved to – US$ 20.31 billion from – US$ 22.42 billion during the same period last year.
- Services exports emerged as a major growth driver, rising to US$ 98.13 billion, a 10.93% increase over the previous year.
- Non-petroleum exports grew by 5.98% and non-Gem & Jewellery exports also showed visible growth of 7.23% in April-June 2025 compared to last year.
Government Initiatives Strengthening India’s Export Landscape
- Foreign Trade & Export Promotion:
- New Foreign Trade Policy (FTP) 2023: Focuses on export incentives, ease of doing business, and emerging sectors like e-commerce and high-tech products. Introduced a one-time Amnesty Scheme to help exporters clear pending authorizations.
- RoDTEP & RoSCTL Schemes: Provide tax and duty reimbursements to exporters, benefiting sectors like pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and steel.
- Districts as Export Hubs: Identifies high-potential products in each district and provides infrastructure and market linkages.
- Trade Infrastructure for Export Scheme (TIES) & Market Access Initiative (MAI): Support infrastructure development and marketing efforts for export growth.
- Infrastructure & Logistics:
- National Logistics Policy (NLP) & PM GatiShakti: Aim to reduce logistics costs and enhance multimodal connectivity through GIS-based planning.
- Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Schemes: Government has significantly increased budget allocations for key sectors under the PLI Scheme in 2025-26, reaffirming its commitment to strengthening domestic manufacturing.
- Ease of Doing Business & Digital Initiatives:
- Compliance & Decriminalization Reforms: In March 2025, the government had over 42,000 compliances removed, and over 3700 legal provisions have been decriminalized since 2014. In the Jan Vishwas act 2023, more than 180 legal provisions were decriminalized.
- National Single Window System (NSWS): Streamlines approvals, allowing businesses to apply for 670 Central approvals and 6880 state approvals.
- Trade Connect e-Platform: Links over 17 lakh registered users with Indian missions and export councils for seamless trade facilitation.
- Support to MSME exporters: In April,2025 Ministry of MSME has set up a dedicated support system for export promotion by setting up 65 Export Facilitation Centres (EFCs).
Concluding Remarks
- Easing prices and rising exports show that India’s economy is on a steady growth path while bringing relief to households.
- With strong demand, and continued reforms, India is moving confidently towards becoming the world’s third-largest economy, ensuring stability and new opportunities for its people.
Previous article
Health Impacts of Land Degradation & Drought: UNCCD
Next article
News In Short 04-08-2025