Syllabus: GS3/ Science and Technology
Context
- PM Modi launched the ₹1 Lakh Crore Research, Development and Innovation (RDI) Scheme Fund while inaugurating the Emerging Science, Technology and Innovation Conclave (ESTIC) 2025 in New Delhi.
About the scheme
- The scheme has an outlay of Rs 1 lakh crore over 6 years, with Rs 20,000 crore allocated for FY 2025–26, funded from the Consolidated Fund of India.
- The Department of Science and Technology (DST) will serve as the nodal department for implementation of the RDI Scheme.
- Key objectives of the Scheme are as follows;
- Encourage the private sector to scale up research, development, and innovation (RDI) in sunrise domains and in other sectors relevant for economic security, strategic purpose, and self-reliance,
- Finance transformative projects at higher levels of Technology Readiness Levels (TRL),
- Support acquisition of technologies which are critical or of high strategic importance,
- Facilitate setting up of a Deep-Tech Fund of Funds.
- The Governing Board of Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF), chaired by the Prime Minister, will provide overarching strategic direction to the RDI Scheme.
India’s R&D Landscape
- India’s R&D expenditure has doubled in the last decade, but still remains around 0.7% of GDP, lower than global leaders such as the USA (2.8%) and China (2.4%).
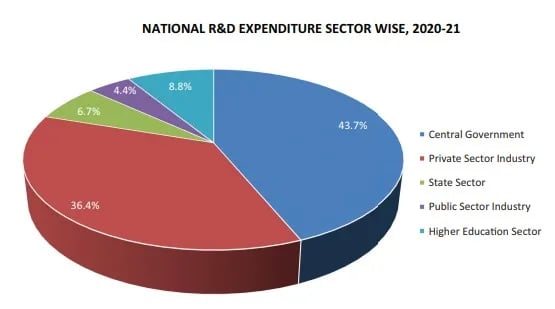
- The private sector contributes less than 40% of total R&D spending, compared to over 70% in advanced economies.
Government Initiatives to Boost R&D
- National Research Foundation (NRF): Aims to enhance research funding and collaboration between academia and industry.
- Atal Innovation Mission (AIM): Encourages startups, entrepreneurship, and innovation among students and professionals.
- Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme: Supports high-tech manufacturing through incentives for R&D-driven industries.
- Launch of National Missions such as;
- National Quantum Mission to make India one of the leading nations in the development of Quantum Technologies & Applications (budget outlay: ₹6,003.65 crore),
- Electric Vehicle-Mission program under ANRF’s MAHA (Mission for Advancement in High-impact Areas) programme;
- India Semiconductor Mission (₹76,000 crore) for building up semiconductor ecosystem in India;
- Deep Ocean Mission to explore and sustainably utilize the deep ocean’s resources (budget outlay: ₹4077 crore);
- India AI Mission to strengthen AI capabilities (budget outlay: ₹10,372 crore).
- Introduction of enabling policy frameworks such as the Geospatial Policy 2022, Space Policy 2023, and BioE3 (Biotechnology for Economy, Environment and Employment) Policy 2024.
Challenges in India’s R&D Ecosystem
- Limited University-Industry Collaboration: Weak links between academia and industry hinder commercialization of research.
- Fragmented Institutional Ecosystem: Overlapping responsibilities reduce efficiency in fund utilisation.
- Skilled Workforce Deficit: Shortage of trained R&D professionals in deep-tech and interdisciplinary fields.
Way Ahead
- Global Collaborations: Leveraging partnerships under frameworks like the Indo-US iCET, G20 S&T Cooperation, and BRICS Innovation Network.
- Performance-Based Funding: Regular monitoring and performance-linked disbursements can enhance accountability.
- Regional Innovation Clusters: Encouraging R&D hubs in Tier-II and Tier-III cities can democratise innovation.
Source: PIB
Previous article
National Beekeeping & Honey Mission
Next article
ISRO’s LVM3 Rocket Launches GSAT-7R