Lucknow Designated a UNESCO Creative City of Gastronomy
Syllabus: Miscellaneous
In News
- UNESCO designated Lucknow as a Creative City of Gastronomy, recognizing its rich and diverse culinary heritage, particularly its famed Awadhi cuisine.
- This makes Lucknow the second Indian city after Hyderabad (2019) to earn this honor in the gastronomy category of the UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN).
UNESCO Creative City of Gastronomy
- The UNESCO Creative City of Gastronomy designation celebrates cities with rich culinary traditions and innovative food cultures that contribute meaningfully to sustainable urban development.
- This recognition is part of the UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN), which promotes cooperation among cities that prioritize creativity in areas like music, literature, design, and gastronomy.
| Do you know? – The UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN) was established in 2004 to promote cooperation among cities that have identified creativity as a strategic factor for sustainable urban development. |
Reasons for Lucknow’s Recognition
- UNESCO acknowledged Lucknow’s contributions to creative industries and its culinary innovation, including iconic dishes like kebabs and biryani.
- With this, Lucknow joins a global network of 408 cities across 100+ countries celebrated for excellence in fields like design, music, literature, and now, architecture.
Source :TH
ICMR Pushes for Indigenous Monoclonal Antibodies Against Nipah Virus
Syllabus: GS2/ Health, GS3/ Science and Technology
Context
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has invited Expressions of Interest (EoI) from eligible organisations and manufacturers for the development and production of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) against Nipah viral disease.
Nipah Virus
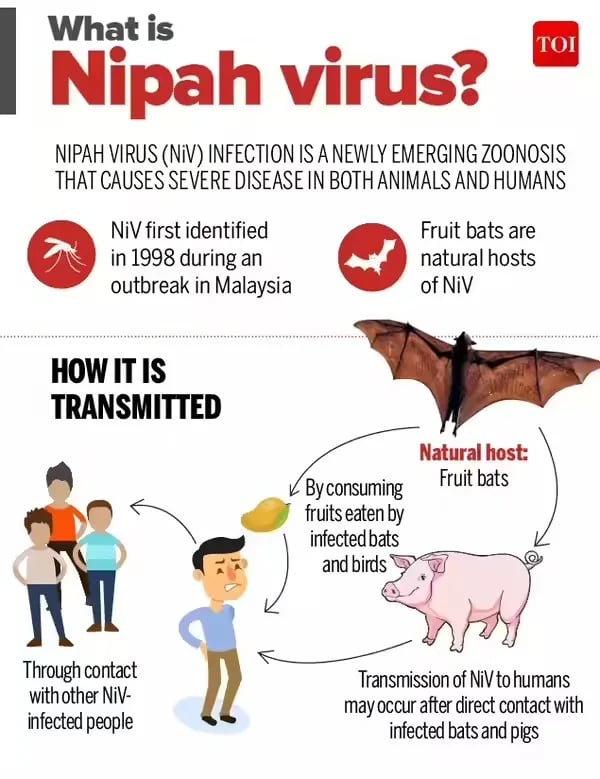
- Nipah virus is a zoonotic pathogen belonging to the Paramyxoviridae family.
- In India and Bangladesh, the Bangladesh clade (NiV-B) predominates, known for its high virulence and frequent person-to-person spread.
- The fatality rate varies between 40% and 75%, depending on clinical care and outbreak management.
- The animal host reservoir of the virus is thefruit bat, commonly known as flying fox.
- Fruit bats are known to transmit this virus to other animals like pigs, and also dogs, cats, goats, horses and sheep.
- Fever, headache, cough, sore throat, difficulty in breathing, and vomiting are the common symptoms.
What are Monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs)?
- Monoclonal antibodies are lab-engineered proteins designed to target specific antigens (foreign substances like viruses, bacteria, or cancer cells).
- They are derived from a single clone of a B-cell and hence are identical in structure and specificity.
- mAbs mimic the natural immune response but are highly specific, making them powerful tools in treating diseases.
Source: TH
Russia’s ‘doomsday missile’
Syllabus: GS3/Defence
In News
- Russia has launched its newest nuclear submarine ‘Khabarovsk’ designed to carry the underwater nuclear drone ‘doomsday missile’.
‘Doomsday Missile’
- It is also known as Poseidon and It can travel at high speeds, greater than those of existing submarines and torpedoes.
- It can operate at great depths and across intercontinental distances, which could make it difficult to intercept.
- It is capable of intercontinental travel and immense destruction.
- It can travel deep underwater across long distances with a nuclear power source. It can reach coastal targets and serve as a strategic deterrent.
Source :TH
Auditory Fusion
Syllabus: GS3/Science and Technology
Context
- Sometimes two sounds reach your ears so quickly one after the other that the brain joins them together and hears them as a single sound. This is called auditory fusion.
Fusion Threshold:
- It’s the smallest time gap needed between two sounds for you to tell them apart.
- For very short sounds like clicks, people usually need a gap of 2–3 milliseconds.
- For more complex sounds like tones, words, or drum beats, the gap must be longer — about 5–10 milliseconds or more.
- The threshold can change depending on how loud the sounds are, or how different they are in pitch or tone.
Why it matters:
- In echoey places, like big halls or churches, the original sound and its echo can reach your ears within a few milliseconds.
- If they come too close together, your brain fuses them, and you hear one clear sound instead of many.
- This helps you understand where the sound is coming from — a process known as the precedence effect (the brain uses the first sound to guess direction).
- Fusion vs Masking:
- Fusion: The brain joins two close sounds into one.
- Masking: One loud or similar sound hides the other so you can’t hear it clearly.
Applications:
- Audio engineers use this idea in music, speech processing, and sound compression.
- Architects use it when designing concert halls and theaters to make sounds clear and pleasant.
Source: TH
Employee Enrollment Scheme 2025
Syllabus: GS3/Economy
Context
- The Centre launched the Employee Enrollment Scheme 2025, aimed at voluntarily enrolling employees under the Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO).
About
- It was launched by the Union Minister of Labour during the 73rd foundation day of the EPFO.
- It has been made effective from November 1, and aims at encouraging employers to voluntarily declare and enroll eligible employees.
- Employers can enrol workers who joined their organisations between July 1, 2017 and October 31, 2025, but were not registered under the Employees’ Provident Fund (EPF) for any reason.
- Employers will not have to pay the employee’s share of the PF contribution if it was not deducted earlier.
- They will only need to pay their own share along with a nominal penalty of Rs 100.
Significance
- The Scheme provides a chance for employers to regularise their workforce without fear of heavy penalties or legal action.
- By paying only their own share of the contribution and a small fee, they can ensure compliance with labour laws.
- For employees, this scheme gives them access to social security, retirement savings, and other EPF benefits.
| Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO) – EPFO is a statutory body under the Ministry of Labour and Employment. – It administers the Employees’ Provident Fund and Miscellaneous Provisions Act, 1952. – Objectives: To ensure financial security and social welfare of employees post-retirement. 1. To promote voluntary savings among employees. 2. To regulate and supervise provident fund, pension, and insurance schemes. |
Source: TM
Rowmari-Donduwa Wetland Complex
Syllabus: GS3/Environment
Context
- Experts from academic institutions and conservation groups are collaborating to propose the Rowmari and Donduwa wetlands in Assam for Ramsar site designation.
About the Rowmari-Donduwa Wetland Complex
- The Rowmari-Donduwa wetland complex is within the Laokhowa Wildlife Sanctuary, which is a part of the Kaziranga Tiger Reserve.
- Laokhowa and the adjoining Burhachapori Wildlife Sanctuaries function as connectivity corridors for wild animals migrating between the Kaziranga Tiger Reserve and Orang National Park (Kaziranga-Orang landscape).
- It hosts around 120 species of resident and migratory birds annually, including globally threatened species such as, the knob-billed duck, black-necked stork, and the ferruginous pochard.
- This complex has recorded more birds than the only two Ramsar sites in the northeast, Assam’s Deepor Beel and Manipur’s Loktak Lake.
| What is the Ramsar Convention? – A Ramsar site is a wetland designated as one of international importance under the Ramsar Convention. – The Ramsar Convention is one of the oldest inter-governmental accords signed by member countries to preserve the ecological character of their wetlands of international importance. – It was signed on February 2, 1971 in Ramsar, Iran and came into force in 1975. 1. India became a signatory to the Ramsar Convention in 1982. |
Source: TH
Previous article
ISRO’s LVM3 Rocket Launches GSAT-7R
Next article
Challenges Linked to High Seas Treaty