Syllabus: GS1/ Geography, GS3/ Environment
Context
- A landslide triggered by heavy rainfall hit a military camp in Sikkim’s Lachen district causing casulities & loss to property.
What is Landslide?
- Landslides are a geological phenomenon that involves the sudden and rapid movement of a mass of rock, soil, or debris down a slope under the influence of gravity.
- Landslides, usually, occur in areas having characteristics like steep terrain such as hilly or mountainous areas, presence of joints and fissures or areas where surface runoff is directed or land is heavily saturated with water.
Causes of Landslides
- Natural Causes:
- Heavy Rainfall: Heavy rainfall is one of the most common triggers of landslides. It increases pore water pressure as well as the weight of soil by making it saturated.
- Erosion: Clay and vegetation present within the soil or rock act as cohesive elements and help bind particles together. Due to removal of these cohesive elements, erosion makes an area more prone to landslides.
- Earthquakes: Intense ground shaking due to earthquakes causes instability in rocks and soils, thus triggering landslides.
- Volcanic Eruptions: Ash and debris deposited by volcanic eruptions overload slopes while the accompanied seismic activity causes instability.
- Anthropogenic Causes
- Deforestation: By holding soils as well as obstructing the flow of falling debris, vegetation cover plays an important role in preventing landslides in any area. Deforestation takes away this preventive cover and increases vulnerability to landslides.
- Encroachment in Vulnerable Terrains: Of late, humans have been encroaching in landslide-prone areas such as hilly terrains. This has led to increased construction activities in these areas and increased chances of landslides.
- Uncontrolled Excavation: Unauthorized or poorly planned excavation activities, such as mining, quarrying, etc destabilize slopes and increase the chances of landslides.
Landslide Vulnerability in India
- India is highly prone to landslides due to its tectonic position.
- The northward movement of the Indian landmass at a rate of 5 cm/year accumulates stress to which natural disasters like landslides are attributed.
- The Landslide Atlas of India released by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) listed some of the country’s most vulnerable areas.
- India is among the top five landslide-prone countries in the world.
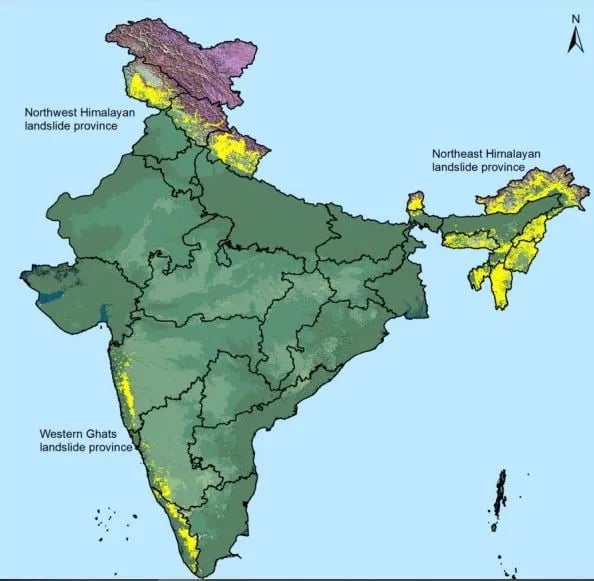
- Apart from snow-covered areas, around 12.6% of India is vulnerable.
- Among them around 66.5% are in the north-western Himalayas, 18.8% are in the north-eastern Himalayas and around 14.7% are in the Western Ghats region.
Measures taken by India
- The Disaster Management Act, of 2005 provides a comprehensive legal and institutional framework for the management of various disasters including landslides.
- The National Landslide Risk Management Strategy (2019) covers all aspects of landslide disaster risk reduction and management, such as hazard mapping, monitoring, and early warning systems.
- The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) has issued Guidelines on Landslide Hazard Management (2009) that outline the steps that should be taken to reduce the risk of landslides.
- The National Institute of Disaster Management (NIDM) has been providing capacity building and other support to various national and state-level disaster management authorities.
- Landslide Hazard Zonation Maps (LHZM): The Geological Survey of India (GSI) and the National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC) have developed hazard zonation maps to identify landslide-prone areas.
- These maps help in planning safer land use, infrastructure development, and disaster preparedness.
- Early Warning system: Efforts have been made towards better prediction of weather. E.g. Ensemble Prediction System. This will help predict disasters like landslides.
Way Ahead
- Comprehensive Hazard Zonation: Landslide Hazard Zonation Maps should be updated regularly using advanced tools like LiDAR, drones, and GIS-based techniques.
- Reforestation and Ecosystem Restoration: Afforestation drives using native species and slope stabilization using bioengineering techniques can help reduce erosion and soil instability.
- Climate-Responsive Adaptation: As climate change increases the frequency of intense rainfall events, localized adaptation strategies such as building resilient infrastructure and improving drainage systems are critical.
Source:IE
Previous article
News In Short-2-06-2025
Next article
India and Japan Agrees to Deepen Maritime Relations