Syllabus :GS 3/Economy
In News
- NITI Aayog released a report on improving Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) competitiveness in India.
| About the Report – It was prepared by NITI Aayog in collaboration with the Institute for Competitiveness (IFC). – The aim is to unlock the potential of India’s MSMEs through systemic reforms in financing, skilling, innovation, and market access. – It highlights challenges in financing, skilling, innovation, and market access across key sectors like textiles, chemicals, automotive, and food processing. |
India’s MSME sector
- It is a key driver of India’s industrial economy, with 5.93 crore registered enterprises employing over 25 crore people.
- In 2023-24, MSME-related products contributed 45.73% to India’s total exports.
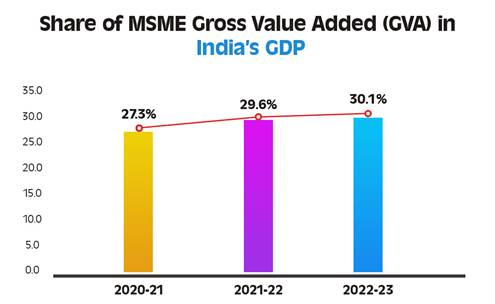
- In recent years, the MSME sector has displayed remarkable resilience, with its share in the country’s Gross Value Added (GVA) increasing from 27.3% in 2020-21 to 29.6% in 2021-22 and 30.1% in 2022-23, highlighting its growing role in national economic output.
- The Union Budget 2025-26 includes measures to strengthen the MSME sector, such as enhanced credit access, support for first-time entrepreneurs, and promotion of labour-intensive industries.
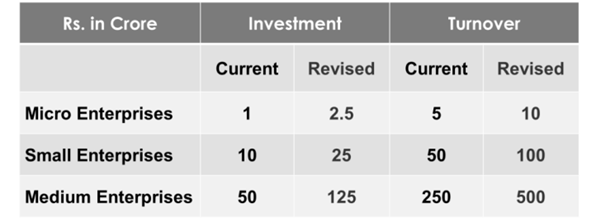
- The classification criteria for MSMEs have been revised, increasing investment and turnover limits by 2.5 times and 2 times, respectively. This is expected to boost efficiency, technological adoption, and employment generation.
Challenges Highlighted in recent report
- Although, between 2020 and 2024, MSME access to formal credit improved (micro and small enterprises from 14% to 20%, medium enterprises from 4% to 9%), however, 81% of MSME credit demand remains unmet, with an estimated ₹80 lakh crore gap.
- Credit Guarantee Fund (CGTMSE) has expanded but still faces limitations.
- Many MSME workers lack formal vocational or technical training, hindering productivity and scalability.
- A significant portion of MSMEs also underinvests in research and development, quality improvement, and innovation.
- MSMEs face challenges in adopting modern technologies due to unreliable electricity, weak internet connectivity, and high implementation costs.
- State government schemes supporting technological advancements are often inaccessible due to low awareness.
- Despite several MSME support policies, their effectiveness is limited by low awareness and poor implementation.
Suggestions and Way Forward
- India’s MSMEs can become a key driver of sustainable economic growth by focusing on targeted interventions, building stronger institutional collaborations and enhancing global competitiveness.
- The report calls for enhanced support for MSMEs through digital marketing training, partnerships with logistics providers and creating platforms for direct market linkages, especially in regions with high growth potential, such as India’s northeastern and eastern belts.
- It calls for a robust, adaptive and cluster-based policy framework at the state level that fosters innovation, enhances competitiveness and enables MSMEs to drive inclusive economic transformation.
Source :PIB
Previous article
Port Economy to Drive India’s Growth
Next article
Terror Financing