Syllabus :GS3/Economy
In Context
- The Union Budget 2025-26 was framed around the theme “Sabka Vikas,” emphasizing balanced growth across all regions of India.
- The term ‘budget’ has nowhere been mentioned in the Constitution. It is mentioned as ‘Annual financial statement’ in Article 112.
About
- The Finance Minister quoted the renowned Telugu poet Shri Gurajada Appa Rao’s saying, “A country is not just its soil; a country is its people,” to highlight the importance of people-centric development.
- Principles of Viksit Bharat:
- Eradicate poverty (Zero-poverty)
- Provide high-quality, universal school education
- Ensure access to affordable, comprehensive healthcare
- Achieve full employment with a skilled workforce
- Involve 70% women in economic activities
- Strengthen agriculture to make India the “food basket of the world
| Budget Estimates 2025-26 – The total receipts other than borrowings and the total expenditure are estimated at ₹ 34.96 lakh crore and ₹ 50.65 lakh crore respectively. – The net tax receipts are estimated at ₹ 28.37 lakh crore. – The fiscal deficit is estimated to be 4.4 per cent of GDP. – The gross market borrowings are estimated at ₹ 14.82 lakh crore. – Capex Expenditure of ₹11.21 lakh crore (3.1% of GDP) earmarked in FY2025-26. |
Key Engines of Growth
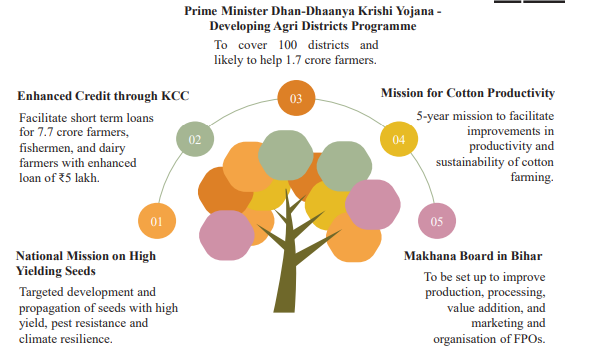
- Agriculture (1st Engine): Launch of Prime Minister Dhan-Dhaanya Krishi Yojana to cover 100 districts.
- Mission for Aatmanirbharta in Pulses for Tur, Urad, and Masoor pulses.
- Loan limit for Kisan Credit Cards raised from ₹3 lakh to ₹5 lakh.
- Comprehensive program for vegetables, fruits, high-yield seeds, and cotton productivity.
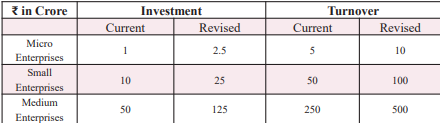
- MSMEs (2nd Engine): MSME investment & turnover limits enhanced to 2.5 and 2 times.
- Credit cards for micro enterprises and a loan scheme for 5 lakh women and marginalized entrepreneurs.
- Development of a toy manufacturing hub and National Manufacturing Mission.
- Investment (3rd Engine): 50,000 Atal Tinkering Labs to be set up in schools.
- Broadband for all secondary schools & PHCs under BharatNet project.
- Establishment of National Centres of Excellence for skilling.
- ₹1.5 lakh crore for 50-year interest-free loans to states for capital expenditure.
- Urban Challenge Fund of ₹1 lakh crore to support urban development.
- ₹20,000 crore for private sector-driven R&D and innovation.
- National Geospatial Mission for urban planning and Gyan Bharatam Mission for manuscript conservation.
- Nuclear Energy Expansion: Rs.20,000 crore for Small Modular Reactors (SMRs).


- Exports (4th Engine): Launch of Export Promotion Mission and BharatTradeNet for trade documentation.
- Support for domestic manufacturing and integration with global supply chains.
- Infrastructure support for air cargo and fisheries exports.

Reforms
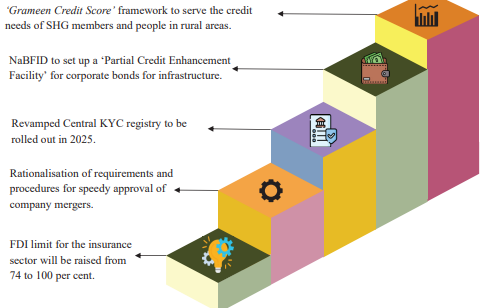
- Financial Sector : Increase in FDI limit in insurance from 74% to 100%.
- Establishment of a High-Level Committee for Regulatory Reforms.
- Introduction of the Investment Friendliness Index of States.
- Decriminalization of 100+ provisions under the Jan Vishwas Bill 2.0.
- Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC) to review regulations.
- Taxation & Fiscal Policy: Fiscal deficit target of 4.4% of GDP for FY 2025-26.
- Increased receipts and expenditure estimates for 2025-26.
- Commitment to fiscal consolidation with a clear roadmap.
Tax Proposals :
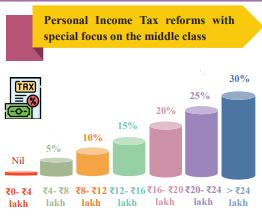
- Personal Income Tax Reform: no tax for income up to ₹12 lakh per annum.
- Standard deduction of ₹75,000 for income up to ₹12.75 lakh.
- Estimated ₹1 lakh crore revenue loss due to tax reforms.
- TDS/TCS Rationalization: TDS limit on interest for senior citizens increased from ₹50,000 to ₹1 lakh.
- TDS threshold on rent raised to ₹6 lakh from ₹2.4 lakh.
- Extension of updated returns filing to 4 years for any assessment year.
- Compliance Simplification: Increase in registration period for small charitable trusts from 5 to 10 years.
- Senior citizens benefit from tax exemption on National Savings Scheme withdrawals.
- Promotion of Employment & Investment: Presumptive taxation regime for non-residents providing services to electronics manufacturing companies.
- Extension of the Sovereign Wealth Funds and Pension Funds investment deadline to 2030.

- Customs Tariff Reforms: Removal of seven tariffs, simplification of cess, and reduction of Basic Customs Duty (BCD) on critical minerals and textiles.
- Reduction in BCD on lithium-ion battery manufacturing capital goods and shipbuilding materials.
- Duty adjustments to encourage domestic manufacturing.
- Export Promotion: Reduction of BCD on fish products and leather to boost exports.
- Fully exempted BCD on lifesaving medicines for cancer, rare diseases, and chronic illnesses.
| State wise Initiatives – Bihar: New Greenfield Airport, Western Koshi Canal Project, Makhana Board. – Uttar Pradesh: Medical College Expansion, Jal Jeevan Mission, Tourism Growth. – Maharashtra: Urban Challenge Fund, Gig Worker Social Security, Nuclear Energy Mission. – Tamil Nadu: Shipbuilding Clusters, Urban Challenge Fund. – Gujarat: Maritime Development Fund, Nuclear Energy Expansion. – Karnataka: AI for Education Centre, PM Research Fellowships at IISc. – Andhra Pradesh & Telangana: Water & Sanitation, Digital Books in Telugu. – Rajasthan: Cotton Productivity Mission, Medical College Expansion. – Punjab & Haryana: Pulses Mission, Enhanced Credit for Farmers. – North-East: New Urea Plant in Assam, Fisheries Development. Ministry-wise expenditure in 2025-26 (Rs crore) |
Source ;PIB
Previous article
Rules For Registering Live-in Relationships Under UCC
Next article
Aatmanirbharta in Pulses