Gyan Bharatam Mission
Syllabus: GS1/ Art & Culture
In News
- The Gyan Bharatam Mission was announced in the Union Budget 2025-26.
About
- It is a landmark initiative focused on the survey, documentation, and conservation of India’s manuscript heritage.
- The mission aims to cover more than one crore manuscripts, ensuring their preservation and accessibility for future generations.
- With this initiative, the government is taking significant steps to reviving the National Manuscripts Mission (NMM) launched in 2003 but largely inactive, and promoting India’s rich literary and intellectual traditions at a global level.
- To accommodate this initiative, the budget for the National Manuscripts Mission (NMM) has been significantly increased from ₹3.5 crore to ₹60 crore.
Significance of the Mission
- Preserving India’s Intellectual and Cultural Heritage: Manuscripts hold knowledge on subjects such as philosophy, science, medicine, literature, mathematics, and astronomy. Their preservation helps safeguard India’s historical wisdom.
- Digital Access for Future Generations: Manuscripts often suffer from physical decay. Digitization ensures 24/7 access to these texts worldwide while preventing deterioration.
- Global Academic Impact: By making manuscripts available for study, India strengthens its position as a hub of ancient knowledge and scholarship.
Understanding Manuscripts
- A manuscript is a handwritten document on materials such as paper, birch bark, or palm leaves. To be classified as a manuscript, it must be at least 75 years old and hold scientific, historical, or aesthetic value.
- India has an estimated 10 million manuscripts in over 80 ancient scripts, including:
- Brahmi, Kushan, Gaudi, Lepcha, Maithili, Grantha, and Sharada.
- 75% of manuscripts are in Sanskrit, while 25% are in regional languages.
- India has an estimated 10 million manuscripts in over 80 ancient scripts, including:
Source: TH
Green Cardamom
Syllabus: GS3/Economy/Agriculture
Context
- Researchers have identified six species that are closely related to Elettaria cardamomum, better known as green cardamom.
About
- Of the six, four were previously placed in a separate genus, Alpinia, while the remaining two have been newly identified and described from Kerala’s Western Ghats regions.
- Following the reclassification, the genus Elettaria now has seven species, including Elettaria cardamomum. E. ensal, E. floribunda, E. involucrata and E. rufescens were earlier placed in the genus Alpinia.
- The remaining two are new species, Elettaria facifera and Elettaria tulipifera.
- Seed capsules of Elettaria cardamomum provide the commercial green cardamom.
- The genus name is based on this spice’s old Malayalam name, ‘elletari’ as used by Hendrik van Rheede in the 17th century.
About Cardamom
- Cardamom is one of the world’s most exotic spices – along with Saffron and Vanilla.
- It belongs to the same botanical family as ginger and turmeric (Zingiberaceae).
- It is also one of the world’s oldest spices – cultivated for more than 4000 years.
- Evergreen forests of Western Ghats of South India are considered as the centre origin of cardamom.
- Guatemala is the world’s largest producer of cardamom, India is the second largest producer.
- Top Producing States: Kerala (56.71%), Karnataka (35.91%) and Tamil Nadu (7.31%).
Source: TH
Samudrayaan Mission
Syllabus: GS3/Science and Technology
Context
- Samudrayaan Mission has been allocated Rs 600 crore in Union Budget 2025-26.
About
- Launched in 2021, it is India’s first manned ocean mission to explore the deep ocean.
- It is a project of the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) under the Deep Ocean Mission.
- The technology is being developed by the National Institute of Ocean Technology (NIOT).
- NIOT is an autonomous institute under MoES, has developed a 6000m depth-rated Remotely Operated Vehicle (ROV) ‘Matsya 6000’.
- The mission aims to send three people to a depth of 6,000 meters in a submersible called the MATSYA 6000.
- The submersible will have an operational endurance of 12 hours, which is extendable up to 96 hours in the event of an emergency.
- Objectives of the Mission:
- To study deep-sea marine life.
- To explore the distribution of polymetallic nodules, which are rich in minerals such as copper, nickel, and cobalt.
- To study the impact of climate change on the ocean.
- To develop India’s capabilities in deep-sea exploration and research as well as develop underwater vehicles and underwater robotics.
- To develop offshore-based desalination techniques, renewable energy generation techniques, and provide clean drinking water and explore the avenues of desalination of water.
- So far, countries such as the U.S., Russia, China, France and Japan have carried out successful deep-ocean crewed missions.
Source: TOI
Trial of Very Short-Range Air Defence System (VSHORADS)
Syllabus: GS3/Defence
Context
- The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) successfully conducted three successive flight-trials of the Very Short-Range Air Defence (VSHORAD) system.
About
- It targets high-speed, low-altitude drone threats.
- The test confirmed the VSHORADS precision in neutralising aerial threats.
- The VSHORAD is a portable air defence system designed and developed indigenously by Research Center Imarat in collaboration with other DRDO laboratories.
- The missile system has the capability to meet the needs of all the three branches of the armed forces — the Army, Navy and the Air Force.
- It offers close air defence protection for mobile formations, especially in the growing threat of drones and loitering munitions.
Source: TH
Democratic Republic of Congo
Syllabus: GS1/Geography
Context
- The armed group M23 is advancing in Democratic Republic of Congo, raising fears of a regional war and a public health crisis.
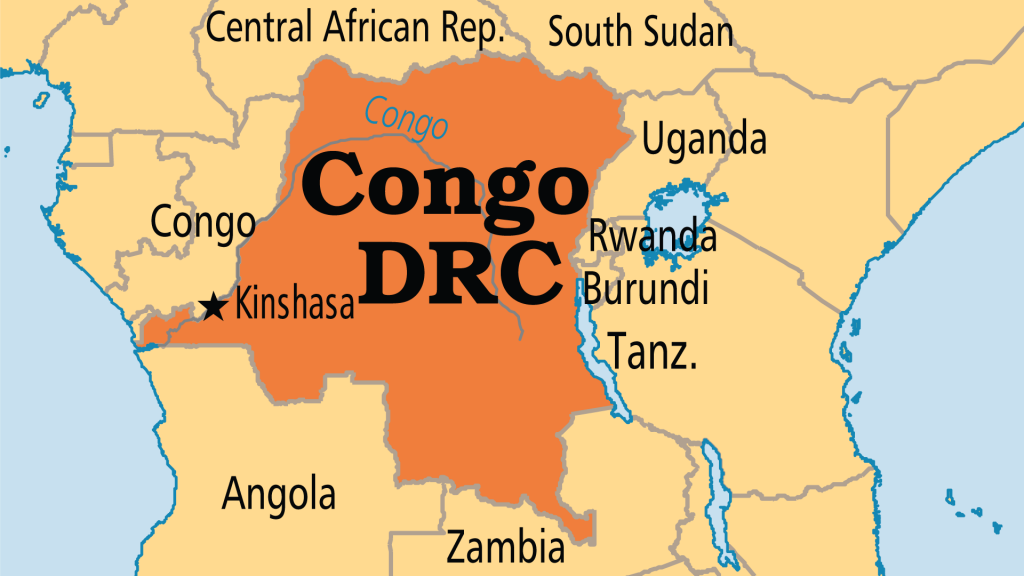
About: Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC)
- It is the second-largest country in Africa after Algeria and also Africa’s most ethnically diverse, with over 200 ethnic groups.
- It shares borders with nine countries: Angola, Burundi, Central African Republic, Republic of the Congo, Rwanda, Sudan, Tanzania, Uganda, and Zambia, extending from Eastern Africa to the Atlantic Ocean.
- Kinshasa is the capital and largest city of the DRC, situated on the banks of the Congo River.
- Though the DRC is endowed with exceptional natural resources, including minerals like cobalt, copper, and diamonds, along with hydropower potential and significant arable land, it remains one of the five poorest nations in the world.
- The DRC has faced decades of instability, with civil wars and conflicts involving rebel groups, particularly in the eastern regions.
| Do you know? – M23, named after a failed peace agreement signed on March 23, 2009, between a Tutsi-led rebel group and the Congolese government, claims to be fighting for the rights of Congo’s Tutsi ethnic minority. – The group accuses the Congolese government of failing to uphold the agreement, particularly regarding the integration of Congolese Tutsis into the army and administration. – Congo and UN experts allege that neighboring Rwanda, governed by a Tutsi-led administration, is backing M23. |
Source: IE
Point Nemo
Syllabus: GS1/Geography, Places In News
Context
- INSV Tarini, sailed by two Indian Navy women officers, successfully crossed Point Nemo during the third leg of Navika Sagar Parikrama II.
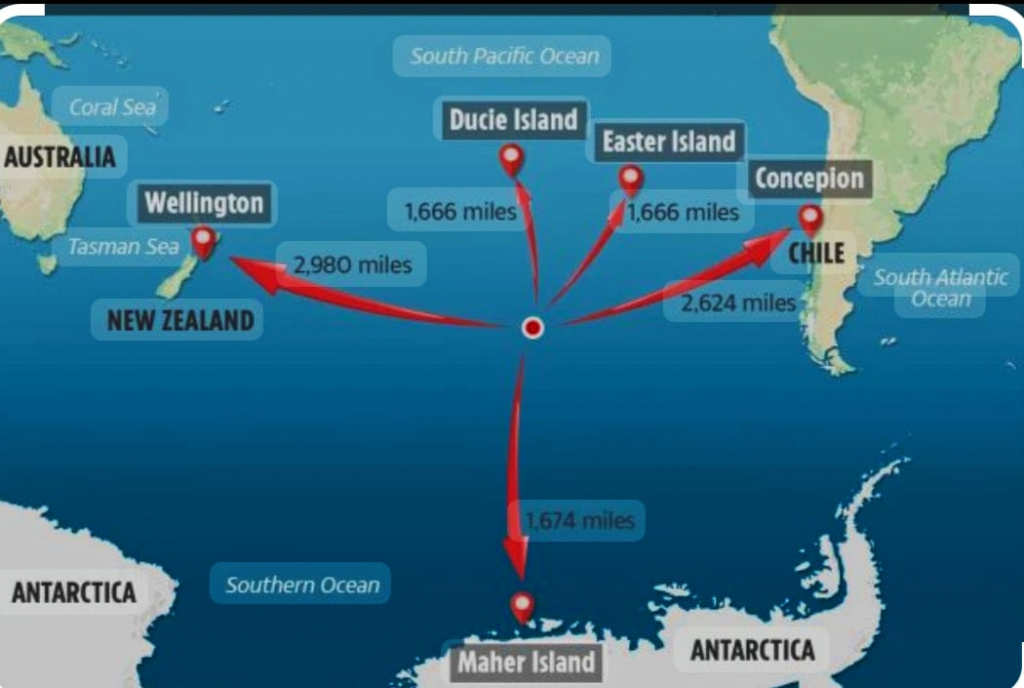
About the Point Nemo
- Point Nemo, located in the South Pacific and also known as the Oceanic Pole of Inaccessibility, is one of the most remote places on Earth, situated approximately 2,688 kilometers from the nearest landmass.
- Due to its extreme isolation, the closest human presence is often aboard the International Space Station (ISS) orbiting above.
- Additionally, Point Nemo serves as a spacecraft cemetery, where space agencies deliberately direct decommissioned satellites and space stations to safely re-enter Earth’s atmosphere and fall into the ocean, minimizing risks to populated areas.
| Navika Sagar Parikrama II – Covering more than 21,600 nautical miles (approx 40,000 km), it will unfold in five legs with stopovers at four ports for replenishment and maintenance. – The five legs are: 1. Goa to Fremantle, Australia 2. Fremantle to Lyttleton, New Zealand 3. Lyttleton to Port Stanley, Falkland 4. Port Stanley to Cape Town, S Africa 5. Cape Town to Goa. |
Source: PIB
Previous article
Aatmanirbharta in Pulses
Next article
Health Insurance Cover for 1 crore Gig Workers