Syllabus: GS3/ Science and Technology
Context
- A study led by astronomers from the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) have probed the dynamic “inner weather” of the Sun – plasma currents just beneath its surface that pulse in step with its 11-year sunspot cycle.
About
- The researchers have traced giant tides of plasma beneath the Sun’s surface at a region called near-surface shear layer (NSSL).
- The plasma currents shift with the Sun’s magnetic heartbeat and could have a far-reaching influence on space weather and Earth.
- The methodology employed was helioseismology, an advanced technique that tracks sound waves as they travel through the Sun, to observe changes in the movement of solar material.
Near-surface shear layer (NSSL)
- The NSSL extending to about 35,000 km in depth is a critical region beneath the Sun’s surface.
- It is marked by distinct rotational behaviours that vary with depth and by changes, over space and time, that relate to active region magnetic fields and the solar cycle.
Patterns beneath the Sun’s surface
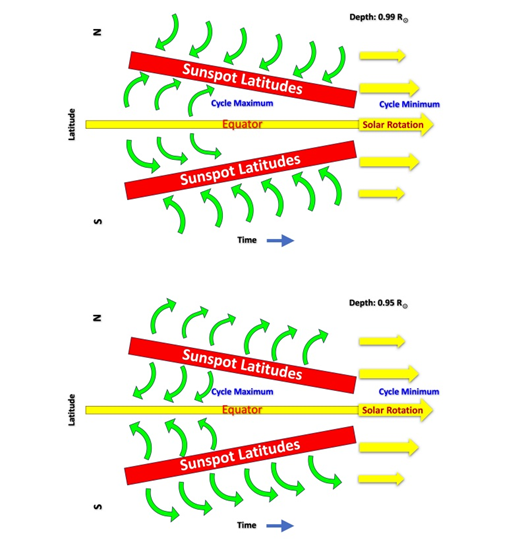
- It was found that plasma on the Sun’s surface moves toward areas where sunspots appear (sunspots latitudes).
- However the direction of the plasma flow reverses midway through the NSSL, i.e. instead of moving toward the sunspot zones, the plasma starts moving outward, away from them.
- These changes in flow direction create circular patterns called circulation cells, which are strongly influenced by the Sun’s rotation and the Coriolis force.
Way Ahead
- The spinning flows change the way the Sun rotates at different depths. This is called rotational shear (the gradient of rotation with depth).
- However these local flows, near the surface, don’t explain the Sun’s larger, deeper flows also known as torsional oscillations.
- Hence it suggests that these global flows, which ripple through the Sun’s vast interior, must be powered by something deeper and more mysterious.
Concluding remarks
- Solar activity directly affects space weather, which can disrupt satellites, power grids, and communication systems on Earth.
- This study takes a step closer to building accurate models that can predict the Sun’s behaviour more reliably.
| What is the solar cycle? – The Sun, like a bar magnet, possesses a magnetic field with north and south poles. – This magnetic field is generated by the movement of electrically charged particles within the Sun. – Approximately every 11 years, the Sun’s magnetic field completely flips, switching its north and south poles—a phenomenon known as the solar cycle. Solar Maximum and Solar Minimum – Solar maximum is the peak phase of the Sun’s 11-year cycle, characterized by heightened solar activity. 1. During this period, the Sun emits more energy, radiation, and light and experiences an increased number of sunspots. – Solar Minimum: The lowest point of the cycle, when the Sun is relatively calm and there are fewer sunspots, is called solar minimum. |
Source: TH
Previous article
UN Pushes for Reforms in Three Key Areas to meet SDGs