Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
Context
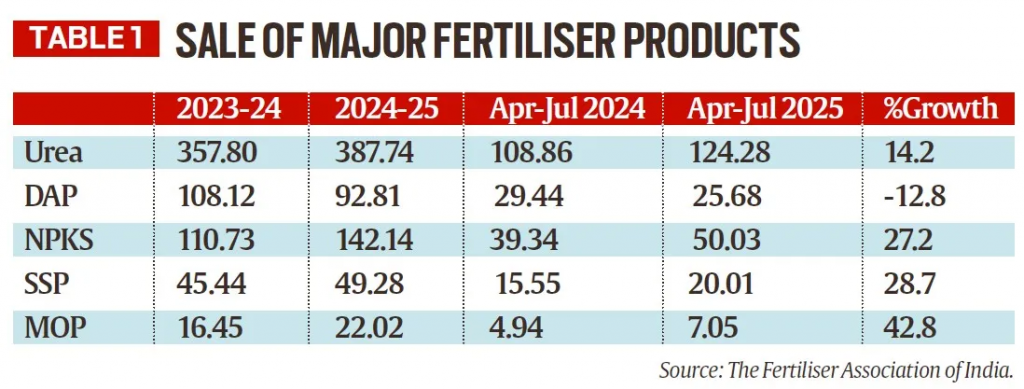
- A well-distributed southwest monsoon in 2025, has boosted kharif sowing along with triggering an unprecedented surge in fertilizer demand.
Fertiliser Sale Impact
- A good monsoon ensures soil moisture, reservoir filling, and groundwater recharge, encouraging higher sowing and proportionately higher fertilizer use.
- Fertilisers supply key nutrients like nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), and sulphur (S), that are indispensable for crop growth.
- India stands as the second-largest user and the third-largest producer of fertilizers globally
- Supply-Side Constraints:
- While demand surged, supply failed to keep pace.
- Domestic production of urea fell from 102.1 lakh tonnes in April–July 2024 to 93.6 lakh tonnes in April–July 2025, while DAP production remained stagnant at 13.7 lakh tonnes.
- Imports have also declined, largely due to supply restrictions from China, which has been a major exporter of fertilisers to India.

Subsidy Framework & Pricing Dynamics of fertilizers
- Urea Subsidy Scheme: Under the scheme, urea is provided to farmers at a statutorily notified maximum retail price (MRP).
- The MRP of 45 kg bag of urea is ₹242 per bag (exclusive of charges towards neem coating and taxes as applicable) while the actual cost is around ₹3,000 for 45 kg bag.
- Nutrient-based subsidy policy: It aims to promote the balanced use of fertilizers by linking subsidies to the nutrient content (nitrogen, phosphorus, potash, and sulfur) rather than the final product.
- Under this scheme, the government sets a fixed subsidy amount per kilogram for each nutrient in P&K fertilizers.
- In the broader budget for FY2025–26, the urea subsidy stands at ₹1.19 lakh crore, while the NPK subsidy is budgeted at approximately ₹0.49 lakh crore, reflecting the government’s massive fiscal commitment.
Government’s Initiatives in the Fertilizer Sector
- The Government introduced the Nutrient Based Subsidy (NBS) scheme in 2010 for phosphatic and potassic fertilizers.
- Under this scheme, a fixed subsidy is provided for subsidised P and K Fertilizers, including di-ammonium phosphate, based on their nutrient content.
- The One Nation One Fertilizer scheme was introduced to bring uniformity in branding and ensure transparency in the Fertilizer sector.
- PM PRANAM scheme: PM Programme for Restoration, Awareness Generation, Nourishment and Amelioration of Mother – Earth (PMPRANAM)” was launched to incentivize States/ Union Territories to promote alternate fertilizers and balanced use of chemical fertilizers.
Way Ahead
- Advance Demand Forecasting: Fertiliser allocation must be synchronised with crop acreage patterns to prevent shortages in years of good monsoon.
- Diversified Imports: Over-reliance on China for DAP and urea creates vulnerability; long-term contracts with multiple suppliers are needed.
- Capacity Expansion: Speeding up commissioning of domestic urea plants under “Atmanirbhar Bharat” will reduce import reliance.
- Sustainable Practices: Wider adoption of nano-urea, bio-fertilisers, and soil health cards can reduce chemical fertiliser intensity over time.
Source: IE
Previous article
Decarbonisation of India’s Emission-heavy Sectors
Next article
Rise in Android Package Kit (APK) Fraud