Syllabus: GS1/ Challenges related to Urbanisation, GS2/ Governance
Context
- Recent incidents of sewage mixing with drinking water in Indian cities highlight serious gaps in Urban Wastewater Management (UWM), posing risks of large-scale public health crises.
About
- Generation vs. Treatment Gap: India generates approximately 72,368 MLD (Million Litres per Day) of urban wastewater, but the treatment capacity is only about 28-44%.
- Health Implications: Untreated sewage is the primary driver of waterborne diseases (diarrhea, cholera, typhoid), contributing to nearly 80% of diseases and a significant portion of child mortality in India.
- Infrastructure Deficit: Nearly 55% of urban households are not connected to a sewer network, relying on septic tanks which often leak or are improperly managed (septage management).
Challenges in Urban Wastewater Management
- Institutional Challenges:
- Fragmented governance with multiple departments working in silos.
- Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) lack technical, financial, and human capacity.
- Infrastructure Challenges:
- Inadequate physical separation between sewerage and drinking water networks increases cross-contamination risks.
- Ageing and corroded water supply pipelines allow seepage of sewage into drinking water lines.
- Economic Challenges:
- High Non-Revenue Water (NRW) losses.
- Unrealistic user tariffs and poor collection efficiency.
- Low cost recovery discourages private investment.
- Technological Challenges:
- Limited adoption of cost-effective and energy-efficient technologies.
- Poor mapping and monitoring of sewer connectivity.
Impacts
- Health Impacts: Contaminated drinking water leads to waterborne diseases such as diarrhoea, cholera, typhoid, dysentery, and hepatitis A and E.
- Children under five years of age face a higher risk of mortality and long-term malnutrition.
- Economic Impacts: Increased household and public healthcare expenditure reduces economic productivity.
- Loss of working days affects livelihoods, especially among informal workers.
- Environmental Impacts: Untreated sewage entering water bodies degrades urban ecosystems.
- Contamination undermines efforts towards sustainable water reuse and recycling.
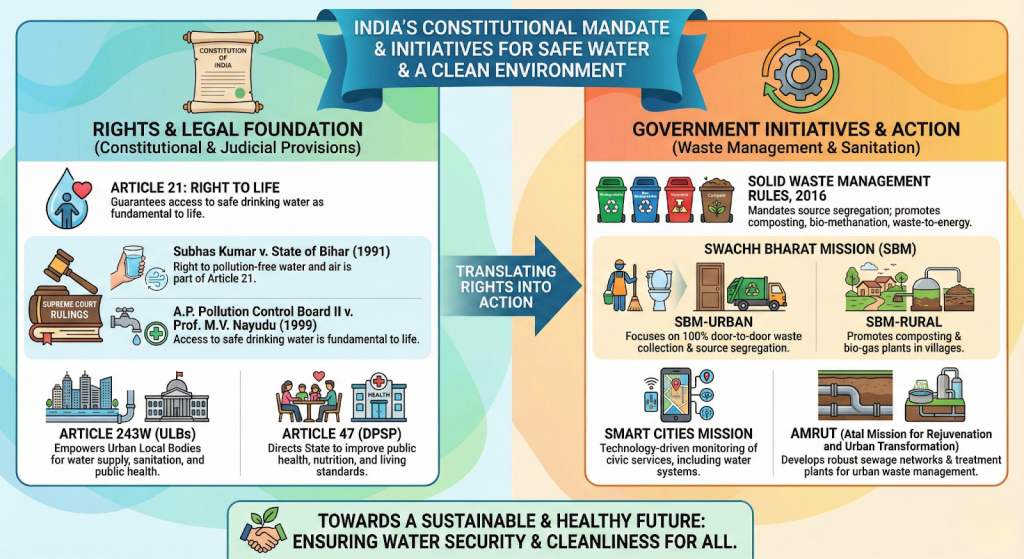
Way Ahead
- Decentralized Wastewater Treatment Systems (DEWATS): Implementing small-scale, localized treatment units (e.g., in housing societies or parks) to reduce the burden on main sewer lines.
- Dual Plumbing Systems: Mandatory for new urban developments to separate potable water from recycled water (used for flushing/gardening).
- Real-Time Monitoring: Using IoT sensors and AI (as highlighted in the 2025-26 CPCB guidelines) to detect leaks and contamination in the water-sewage network immediately.
- Polluter Pays Principle: Strengthening the financial health of ULBs through “sewerage charges” and creating a market for treated wastewater (e.g., selling it for industrial cooling or construction).
Source: IT
Previous article
News In Short 02-01-2026