Syllabus: GS1/ Social Issues
In News
- Despite a strong legal framework and multiple schemes tackling Child marriage in India, India is still off-track to fully eliminate child marriage by the 2030 SDG deadline.
Concept, Trend and Legal Framework
- Definition: Child marriage refers to any marriage in which at least one party is below 18 years of age; globally, the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child defines a child as any human below 18 years.
- NFHS data: The proportion of women aged 20–24 years married before 18 declined from about 47.4% (2005–06, NFHS-3) to 26.8% (2015–16, NFHS-4) and further to 23.3% (2019–21, NFHS-5).
- State variation: Eight states are above the national average; West Bengal, Bihar and Tripura have over 40% of women 20–24 years married before 18, making them among the worst performers.
- Indian law: The Prohibition of Child Marriage Act (PCMA), 2006 defines a “child” as a male below 21 years and a female below 18 years, and a “child marriage” as a marriage where either party is a child.
- Child Marriage Prohibition Officer: Under Section 16, states appoint these officers to prevent child marriages, collect evidence for prosecution, create awareness and maintain statistics.
Major Factors
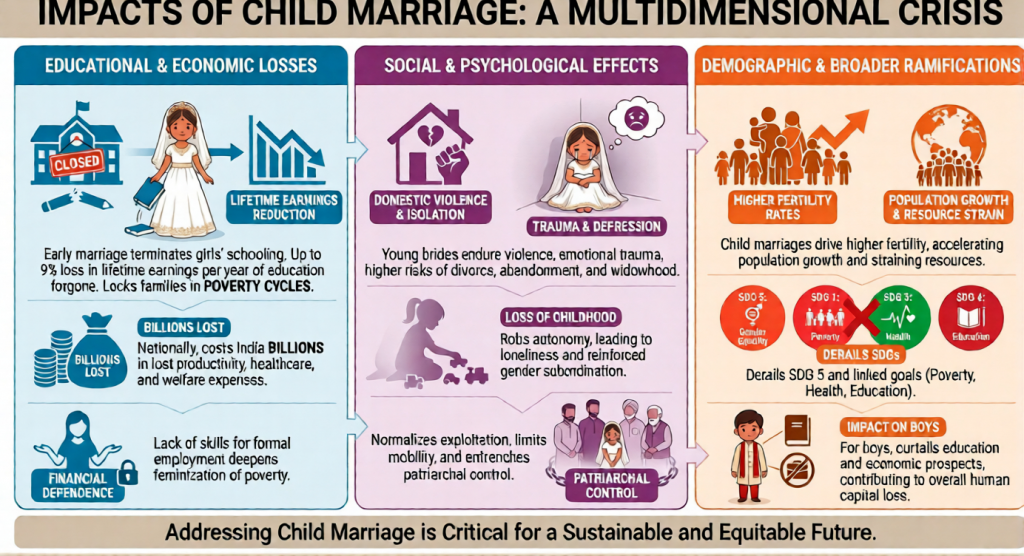
- Poverty and economic insecurity: Poor households often see early marriage as a way to reduce economic burden and “secure” a girl’s future
- Patriarchy and gender norms: Girls’ education and autonomy are devalued; they are pushed into unpaid domestic labour and early marriage to uphold family “honour”.
- Socio‑cultural and religious practices: In some communities, marrying girls before or soon after puberty is considered auspicious.
Initiatives
- The Prevention of Child Marriage Act was passed in 2006, and national child marriage rates have halved since then.
- The Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act, 2012 has also helped prevent child marriage.
- Beti Bachao Beti Padhao (BBBP) aims to improve the child sex ratio and promote girls’ education.
- District‑level models (e.g., Panchayats declaring themselves “child marriage‑free”) use community monitoring, school‑based vigilance and local campaigns to deter such marriages.
- States cash transfers and scholarship schemes to encourage girls schooling.
- India is party to the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child and has endorsed the 2030 Agenda, including SDG Target 5.3 to eliminate child, early and forced marriage.
Source: TH
Previous article
News In Short 20-12-2025