Syllabus: GS3/Science and Technology
Context
- Scientists have found a way to detect thorium-229’s nuclear ‘tick’ in a solid, opening a path to miniaturised nuclear clocks.
About
- Conventional atomic clocks count electron transitions, which are sensitive to external disturbances (electric/magnetic fields).
- Nuclear energy levels are far more shielded, promising more stable timekeeping.
- Why Thorium-229 (²²⁹Th)?
- It has a uniquely low-energy nuclear excited state which can be directly excited using vacuum-ultraviolet (VUV) lasers—a rare and crucial property.
- Main experimental challenge: In solid materials, the excited nucleus usually relaxes via internal conversion (energy transferred to an electron) instead of emitting a detectable photon, making direct detection difficult.
- New breakthrough approach: Instead of avoiding internal conversion, researchers used it as the signal by embedding ²²⁹Th in thorium dioxide (ThO₂), exciting nuclei with VUV laser pulses and detecting the delayed electrons emitted during nuclear decay.
- Key Results:
- Clear nuclear resonance detected at 2,020,407.5 GHz.
- Internal conversion lifetime measured at 12.3 μs.
- Implies a nuclear clock accuracy of 1 second error in ~15.8 billion years.
- Significance:
- Opens new materials and designs for nuclear clocks.
- Enables miniaturisation, since time can be read via electron current rather than complex optics.
- Potential applications in fundamental physics, precision sensing, and tests of physical constants.
Nuclear Clock
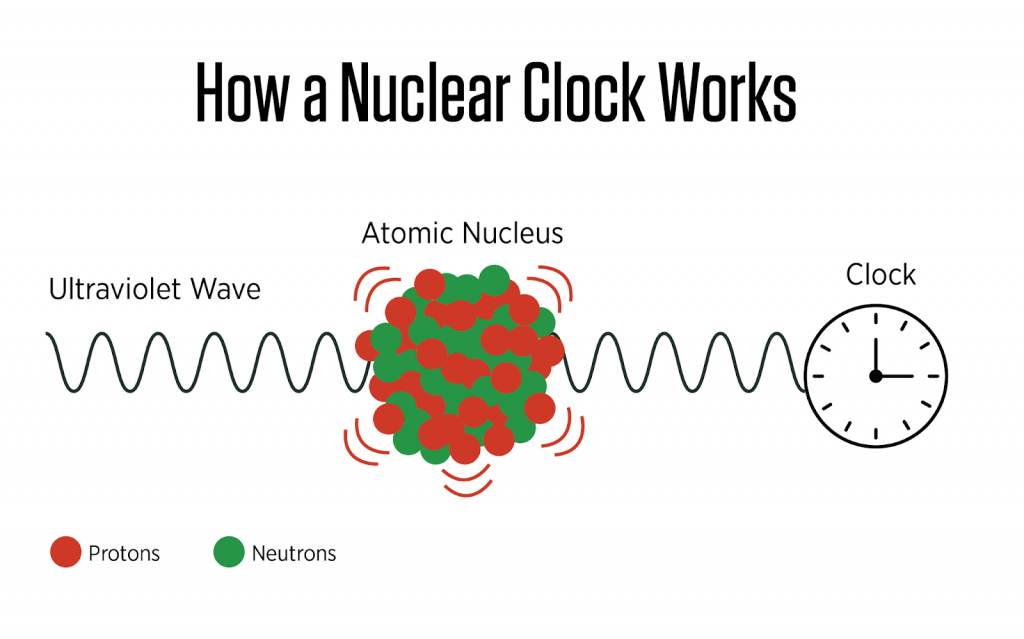
- A nuclear clock works by using ultraviolet light to excite the nucleus of a special atom, like thorium-229.
- When the light hits the nucleus at just the right frequency, it causes the nucleus to change its energy state, like flipping a tiny switch.
- By precisely measuring and counting these energy flips, scientists can create an extremely accurate timekeeping device.
Difference Between Atomic Clock and Nuclear Clock
| Aspect | Atomic Clocks | Nuclear Clocks |
| Reference System | Electron orbital transitions. | Nuclear energy transitions. |
| Oscillation Frequency | Microwave to optical (MHz-THz range). | Higher frequencies (ultraviolet). |
| Precision & stability | Very high (defines 1 second). | Potentially much higher than atomic clocks. |
| Applications | GPS, telecom, internet, satellites. | Future deep-space navigation, fundamental physics. |
| Current status | Fully operational, widely used. | Experimental / research stage. |
Key Advantages of Nuclear Clock over Atomic Clock
- Much greater accuracy and stability.
- Better for testing fundamental constants.
- Less environmental interference.
- Higher sensitivity to gravitational time dilation.
Source: TH
Previous article
Data Exclusivity in India
Next article
Human-wildlife Conflict