Syllabus: GS3/ Disaster Management
In News
- India has released an updated seismic zonation map under the new Earthquake Design Code (2025).
- This revision aims to align India’s seismic safety standards with modern scientific understanding, replacing the outdated 2016 map and historical-epicentre-based models.
Need For Upgradation
- Earlier Maps Underestimated Himalayan Risk: Previous zonation divided the Himalaya into Zones IV and V, despite the belt sharing one of the world’s most active tectonic systems.
- Outdated Methodology: Older models relied heavily on known past earthquake locations, magnitudes, broad geology, soil types & historical damage patterns.
- Underestimation of Rupture Propagation: Earlier maps did not adequately account for southward propagation of Himalayan Frontal Thrust ruptures
- Populated foothill regions like Dehradun (near Mohand) faced underestimated risk despite proximity to major thrust faults.
- Growing Exposure and Vulnerability: Nearly three-fourths of India’s population now resides in seismically active areas.
- Gap with International Best Practices: Need to adopt internationally accepted Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Assessment (PSHA) methods.
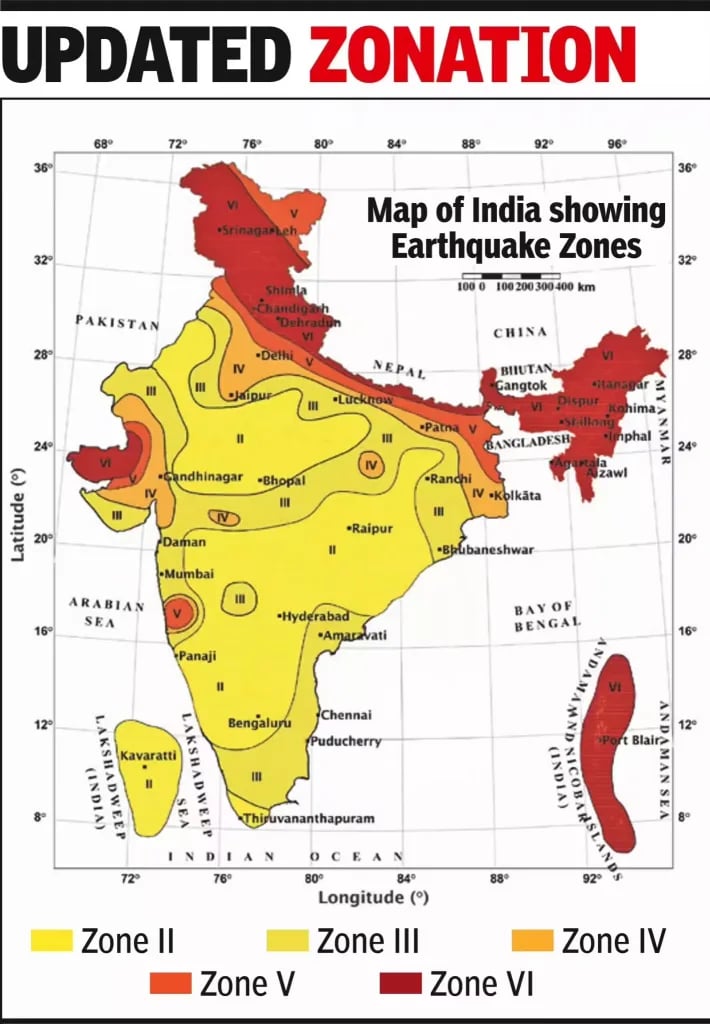
What is a Seismic Zonation Map?
- A seismic zonation map is a scientific representation that divides a geographical area into zones based on the intensity and frequency of earthquakes expected in different regions.
- It is published by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) & integrated into the Earthquake Design Code (IS 1893).
- It serves as a foundational tool for urban planning, risk assessment & disaster preparedness.
Key Features of the New Seismic Map (2025)
- Introduction of Zone VI:
- The entire Himalayan arc (Jammu & Kashmir-Ladakh to Arunachal Pradesh) is now classified under the newly created highest-risk Zone VI.
- Recognizes consistent, extreme tectonic stress along the Indian-Eurasian plate boundary.
- Scientific Methodology – PSHA:
- Built using internationally accepted Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Assessment (PSHA) methods.
- Considers ground shaking attenuation with distance, tectonic regime, and underlying lithology.
- Enhanced Geographic Coverage:
- 61% of India’s landmass now classified under moderate to high hazard zones (increased from 59%).
- The southern peninsula shows minor refinements with a broadly stable hazard profile due to relatively stable tectonic behavior.
- Boundary Rule Enhancement:
- Towns situated along boundaries separating two zones will automatically be placed in the higher-risk zone.
- Comprehensive Non-Structural Elements Safety:
- First-time focused attention on non-structural components like parapets, ceilings, overhead tanks, façade panels, electrical lines, lifts, and suspended fixtures.
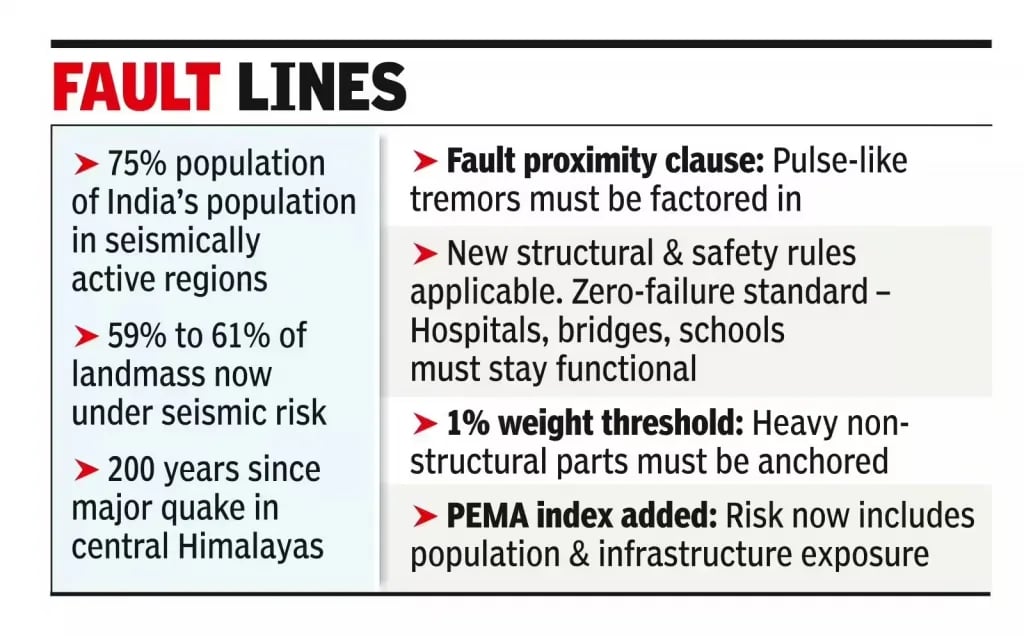
- Near-Fault Provisions:
- Structural design must consider severe pulse-like ground motions for buildings close to active faults
- Updated limits on displacement, ductility, and energy dissipation.
- Site-Specific Requirements:
- New provisions addressing liquefaction risks, soil flexibility, and site-specific response spectra.
- Critical Infrastructure Standards:
- Hospitals, schools, bridges, pipelines, and major public buildings must remain functional after major earthquakes.
Challenges in Implementation
- Retrofitting Legacy Infrastructure: High costs of retrofitting, technical complexity & coordination challenges across multiple jurisdictions.
- Economic Burden: Higher construction costs due to stricter standards.
- Geotechnical Investigation Requirements: Site-specific assessments require specialized expertise and equipment.
Source: TOI
Previous article
News in Short – 28 November, 2025
Next article
India–US Defence Deal & Strategic Relations