Syllabus: GS3/Science and Technology
Context
- The discovery of altermagnetism has emerged as a new class of magnetic order.
Magnetism and Types
- Magnetism is a force of attraction or repulsion that acts between certain materials — mainly those containing iron, nickel, cobalt, or their alloys — due to the motion of electric charges (like electrons).
- For more than a century, scientists recognized only two main types of magnetism:
- Ferromagnetism: All atomic magnetic moments (spins) align in the same direction, producing a strong external magnetic field — like a fridge magnet.
- Antiferromagnetism: Neighboring atomic spins point in opposite directions (“up” and “down”), cancelling each other’s fields and resulting in no external magnetism.
- Recently, researchers have discovered a third form, called altermagnetism, first theorized around 2019 and confirmed through experiments in 2024.
Altermagnetism
- It is rotating or mirror-flipping the crystal pattern matches sites in cancelling pairs, leaving no net magnetisation — thus bridging the gap between other two types.
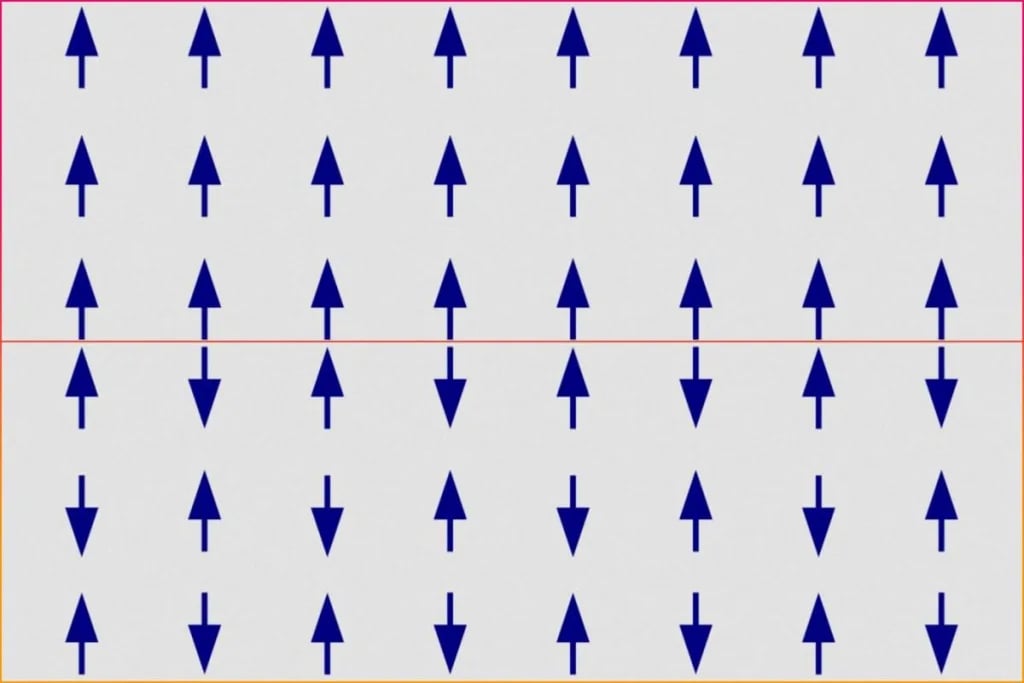
- In altermagnets, the magnetic moments of neighbouring atoms point in opposite directions — one up, the next down — just like in antiferromagnets.
- These opposite spins cancel each other, so the material shows no overall (net) magnetic field.
- However, their internal electronic structure resembles that of ferromagnets, where electrons have different energy levels depending on their spin.
- This unusual combination of no net magnetisation but internal spin imbalance gives altermagnets unique properties.
Applications
- Quantum Computing: Altermagnets are also being explored for quantum computing applications.
- Their lack of stray magnetic fields helps reduce magnetic noise, which is crucial for maintaining quantum coherence (stability of quantum bits).
- Spintronics: These properties make them very attractive for spintronics — a technology that uses electron spin (not just charge) to store and process information, enabling faster, smaller, and more efficient electronics.
- Wide Range of Materials: One of the most exciting findings is that altermagnetism can exist in many types of materials including insulators, semiconductors, metals, and possibly even organic crystals.
- This opens vast opportunities for materials design and new device architectures.
Key Challenges
- Material Quality: Producing high-quality, single-domain altermagnetic materials is a major hurdle.
- Fabrication and Scalability: Developing scalable and cost-effective fabrication methods is essential to use these materials in commercial electronic or spintronic devices.
- This includes perfecting the crystal synthesis process for large-scale production.
- Limited Tested Materials: So far, only a few materials—like manganese telluride (MnTe) and chromium antimonide (CrSb) have clearly shown altermagnetic effects.
- Expanding the material library is a current focus of global research.
Way Ahead
- Despite these difficulties, the rapid progress of discoveries, strong global scientific interest, and ongoing experimental breakthroughs are all encouraging signs that these challenges can be overcome with time.
- With continued progress in material design and fabrication, it holds promise to revolutionize next-generation information and quantum technologies.
Source: TH
Previous article
Recurring Rail Tragedies in India
Next article
News in Short – 11 November, 2025