Syllabus: GS3/Economy
Context
- The Union Cabinet chaired by the PM approved the Electronics Component Manufacturing Scheme with a funding of Rs.22,919 crore to make India Atmanirbhar in the electronics supply chain.
About
- Objectives:
- Develop a robust component ecosystem by attracting both global and domestic investments.
- Increase Domestic Value Addition (DVA) through capacity and capability development.
- Integrate Indian companies into Global Value Chains (GVCs).
- Expected Outcomes:
- Attract an investment of Rs.59,350 crore.
- Result in production of Rs.4,56,500 crore.
- Generate 91,600 direct jobs and numerous indirect jobs.
- Duration: Tenure of six years with a one-year gestation period.
Electronics Sector
- The electronics sector encompasses the design, manufacturing, and marketing of electronic components and systems.
- Electronics is one of the highest-traded and fastest-growing industries globally and is expected to play a pivotal role in shaping the global economy.
- Since electronics permeates all sectors of economy it has economic and strategic importance.

India’s Electronic Sector
- Domestic Production: It has increased from Rs.1.90 lakh crore in FY 2014-15 to Rs.9.52 lakh crore in FY 2023-24 at a CAGR of more than 17%.
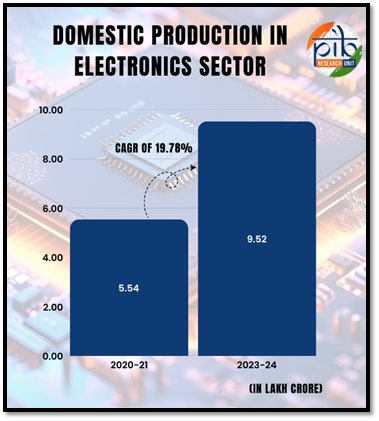
- Exports: The exports of electronic goods have also increased from Rs.0.38 lakh crore in FY 2014-15 to Rs.2.41 lakh crore in FY 2023-24 at a CAGR of more than 20%.
- India is the second largest mobile phone producer in the world.
- India’s semiconductor ecosystem has gained significant momentum, with five landmark projects receiving approval with a total combined investment nearing Rs 1.52 lakh crores.
- Future Projections: It indicates that India’s electronics production will reach USD 300 billion by 2026.
Challenges
- Dependence on Imports: High reliance on imported components, especially semiconductors, increases costs and supply chain vulnerabilities.
- Infrastructure Gaps: Inadequate infrastructure for large-scale manufacturing and logistics hampers efficiency.
- Skilled Labor Shortage: Limited availability of skilled workers for advanced manufacturing processes and R&D.
- High Capital Investment: Significant investment required for setting up world-class manufacturing facilities, making entry challenging for new players.
- Technology Gaps: Lack of cutting-edge technology and innovation in certain segments of the electronic value chain.
- Competition from Global Players: Intense competition from established global electronics manufacturers and countries with lower production costs.
Government schemes for the Electronics boom in India:
- Make in India: launched in 2014, aimed at boosting India’s manufacturing sector and economic growth.
- Transform India into a global hub for design and manufacturing.
- Phased Manufacturing Programme (PMP): Launched in 2017, aimed to promote domestic value addition in mobile phones and their parts.
- Increased investment and set up significant manufacturing capacities in India.
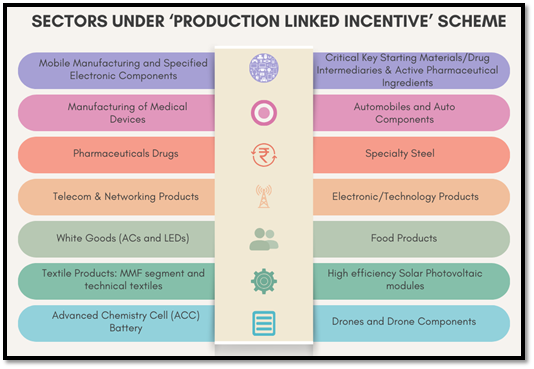
- Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme: Introduced in 2020, aimed to boost domestic manufacturing in mobile phones, electronic components, and semiconductor packaging.
- Incentives: 3% to 6% on incremental sales (over base year) for eligible companies.
- Duration: 5 years.
- Semicon India Program: Launched in 2021 with a financial outlay of ₹76,000 crore, it is structured to promote the domestic semiconductor industry through incentives and strategic partnerships.
- At Global Investors Summit 2025, it was announced that India’s first indigenous semiconductor chip will be ready for production by 2025.
- The Scheme for Promotion of Manufacturing of Electronic Components and Semiconductors (SPECS): The scheme will provide financial incentive of 25% on capital expenditure for the identified list of electronic goods that comprise downstream value chain of electronic products.
- Increased Budget: Allocation for electronics manufacturing rose from ₹5,747 crore (2024-25) to ₹8,885 crore (2025-26), highlighting the government’s commitment to industrial growth.
Conclusion
- India’s rapid transformation into a global electronics manufacturing hub is a testament to the success of the Make in India initiative.
- With numerous schemes to support the manufacturing processes in India, the country has significantly boosted local manufacturing, exports, and investment.
- India aims for USD 300 billion in electronics production by 2026 that will position it as a major hub in the electronics and semiconductor industries.
Source: PIB
Previous article
Dark Side of Digital Gambling in India