
In Context
- Recently the Supreme Court has given a reminder to Governors that the Constitution expects that a decision to return a Bill to the State Assembly for reconsideration should be made “as soon as possible”.
The office of Governor
- About:
- Article 153 of the Constitution provides the provision that there shall be a Governor for each State.
- This Article also provides that it is not necessary for every State to have a different Governor and thus a person can be appointed as the Governor of more than one State.
- Article 154:
- The Governor’s position in the State is identical to the position of the President of India and just like the President, the Governor is the Executive Head of the State.
- This authority is conferred on him under Article 154 of the Constitution which provides that the Executive power of the State is vested in the Governor.
- Article 153 of the Constitution provides the provision that there shall be a Governor for each State.
- Governor’s powers regarding bills in the state legislature:
- The Governor’s assent is necessary for the Bills which are passed by the State legislature to become a law.
- Sending for reconsideration:
- The Governor can send the bill back to the House for reconsideration but if the bill is sent back by the House without any change, the Governor has to give his assent to that bill.
- Also, he cannot send the bill back to the State Legislature if it is a Money Bill.
- Reserving the bill for the president’s consideration:
- The Governor also has the right to reserve some bills for the consideration of the President.
- And when a governor reserves bill for the president’s consideration, he is no longer involved in the bill’s enactment.
- Even if the President refers it to the Assembly for reconsideration, the Bill will still be brought before the President and not the Governor following the reconsideration.
- Withhold assent:
- The Governor aslo has power to withhold assent to the a Bill
- Pending bill in the legislature:
- If any Bill is pending in the House(s), the governor can send a message to such House(s) for reminding them about the same.
Apex court’s recent addresses the issue of delay
- Article 200 & immediacy of returning a Bill:
- The Supreme Court has reminded Governors that the Constitution expects that a decision to return a Bill to the State Assembly for reconsideration should be made “as soon as possible”
- The Court has drawn attention to the phrase found in the first proviso to Article 200, seeking to convey a sense of immediacy in the matter of returning a Bill.
- “The expression ‘as soon as possible’ contains significant constitutional content and must be borne in mind by constitutional authorities,” the Court observed.
- What does this imply?
- This effectively means it would be constitutionally impermissible for Governors to hold on to Bills indefinitely without communicating their decision to the House.
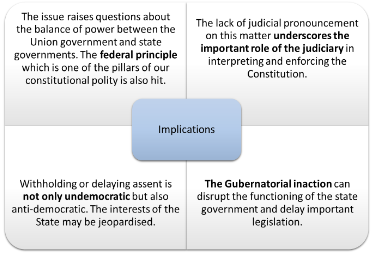
What can be done if Governors hold on to Bills indefinitely?
- Role of Apex Court:
- The framers of the Constitution would never have imagined that Governors would sit on Bills indefinitely without exercising any of the options given in Article 200.
- This is a new development that needs new solutions within the framework of the Constitution.
- So, it falls to the Supreme Court to fix a reasonable time frame for Governors to take a decision on a Bill passed by the Assembly in the larger interest of federalism in the country.
- Role of Union Government:
- Article 355 of the Constitution says that it shall be the duty of the Union to ensure that the government of every State is carried on in accordance with the provisions of the Constitution.
- If Governor does not act in accordance with the Constitution and sits on the Bills indefinitely, he is creating a situation where governance of the state cannot be carried on in accordance with constitutional provisions.
- In such a situation, the government of the State has a constitutional duty to invoke Article 355 and inform the President about it, and request her to give suitable instructions to the Governor to ensure that the government is carried on in accordance with the Constitution.
- Article 355 of the Constitution says that it shall be the duty of the Union to ensure that the government of every State is carried on in accordance with the provisions of the Constitution.
Way ahead
- These provisions give abundant scope for conflict between the government and the office of Governor.
- There is no doubt that these ought to be changed, either by amending the Constitution or through an appropriate Supreme Court verdict, so that misuse of gubernatorial discretion can be kept in check.
|
Daily Mains Question [Q] The provisions regarding ‘discretionary powers of the governor’ give abundant scope for conflict between the government and the office of Governor. Analyse. |
Previous article
The third-gen web is about public good
Next article
India’s SDG Pledge Goal & the strategy to apply