Syllabus: GS2/ Health
Context
- India hosted the 2nd WHO Global Summit on Traditional Medicine in New Delhi.
- The theme of the summit is “Restoring Balance for People and Planet: The Science and Practice of Well-Being.”
Key Outcomes of the summit
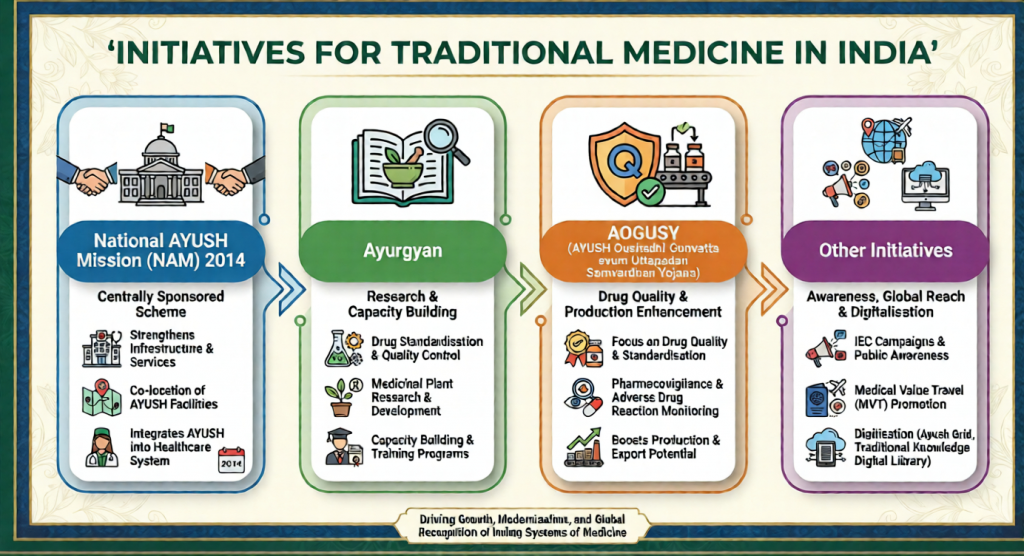
- Initiatives Launched:
- My Ayush Integrated Services Portal (MAISP): A master digital portal for services, research and governance in the Ayush sector.
- Ayush Mark: Envisioned as a global quality benchmark for Ayush products and services.
- Traditional Medicine Global Library (TMGL), the world’s largest digital repository on traditional, complementary and integrative medicine.
- The initiative is grounded in the Gujarat Declaration (2023) and aligned with WHO’s Global Traditional Medicine Strategy 2025–2034.
- Announcement of international collaborations, including a Centre of Excellence for BIMSTEC countries and an India–Japan partnership in traditional medicine.
- The summit stressed the use of digital health tools and AI for research, data generation and wider access to traditional medicine.
What are Traditional Medicines?
- Traditional medicine refers to codified or non-codified systems for health care and well-being, comprising practices, skills, knowledge and philosophies originating in different historical and cultural contexts, which are distinct from and pre-date biomedicine, evolving with science for current use from an experience-based origin.
- Traditional medicine emphasizes nature-based remedies and holistic, personalized approaches to restore balance of mind, body and environment.
- The WHO Global Traditional Medicine Centre (GTMC) in Jamnagar, Gujarat.
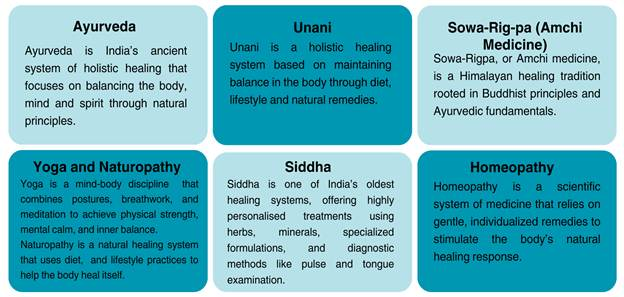
- Traditional Medicine system in India:
| 1st WHO Global Summit on Traditional Medicine – India hosted the 1st WHO Global Summit on Traditional Medicine in 2023 in Gandhinagar, Gujarat. 1. It adopted the Gujarat Declaration, which; 1. Reaffirmed global commitment to evidence-based traditional, complementary and integrative medicine (TCIM), 2. Called for improved data and regulatory frameworks, and 3. Acknowledged India’s leadership in shaping a holistic, culturally rooted and scientifically aligned global health agenda. |
Source: TH