Syllabus: GS2/Government Policy & Interventions
Context
- The Ministry of Development of North-Eastern Region (DoNER) is organizing the ‘Rising Northeast: The Investor Summit’ in New Delhi to showcase the investment and trade potential of the Northeast Region of India.
| Key Highlights of Rising Northeast Investors Summit 2025 – Inaugurated by: Prime Minister of India 1. He outlined the EAST Vision: Empower, Act, Strengthen, and Transform, as the guiding principle for development. – Summit Agenda: Includes ministerial sessions, Business-to-Government (B2G) and Business-to-Business (B2B) meetings, and an exhibition zone. – Focus Sectors: Agri, Food Processing & Allied Sectors; Textiles, Handloom & Handicrafts; Entertainment and Sports; Education & Skill Development; Healthcare; IT & ITES; Tourism & Hospitality; Infrastructure and Logistics; and Energy. – It serves as a platform for policy discussions, business collaborations, and investment partnerships to accelerate the Northeast’s growth trajectory. |
About Northeast Region of India
- It consists of eight states: Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, and Tripura.
- Geographical Area: Covers 7.97% of India’s total landmass.
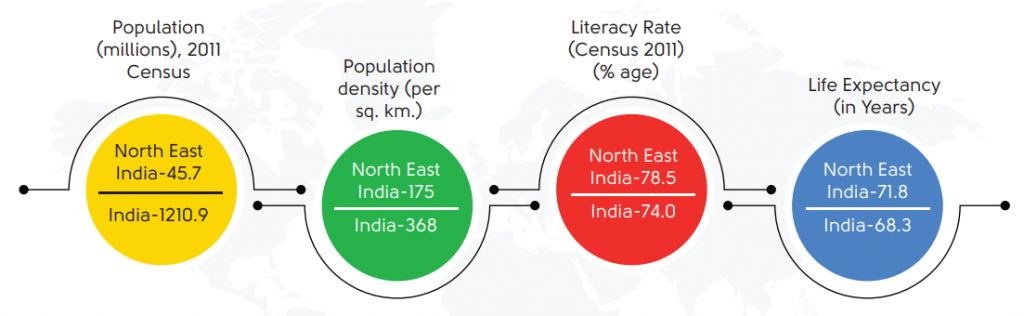
- Population: Around 3.78% of India’s total population.
- Hilly areas population: Over 54%
- International Borders: Shares 5,484 km of borders with Bangladesh (1,880 km), Myanmar (1,643 km), China (1,346 km), Bhutan (516 km) and Nepal (99 km).
- It is positioned as a gateway to ASEAN and East Asia, reinforcing India’s Act East Policy.
Concerns and Challenges Hindering Development of Northeast Region
- Geographical & Connectivity Issues: The region’s rugged terrain and heavy monsoons make infrastructure development difficult.
- Limited rail and road networks restrict trade and mobility.
- Political & Ethnic Conflicts: Insurgency and ethnic tensions have historically disrupted stability. Demands for autonomy and special status create governance challenges.
- Naga and Mizo separatist movements gained momentum until the 1980s.
- ULFA and NDFB emerged in Assam demanding autonomy and sovereignty.
- Infiltration from Bangladesh led to large-scale protests, culminating in the Assam Accord of 1985.
- Economic Underdevelopment: The region contributes only about 2.8% to India’s GDP, with Assam being the largest contributor.
- Limited industrialization and dependence on agriculture slow economic growth.
- Environmental Challenges: Deforestation, floods, and landslides impact agriculture and infrastructure.
- Climate change threatens biodiversity and traditional livelihoods.
- Policy & Governance Gaps: Delayed implementation of key policies like the Inner Line Permit (ILP) in Meghalaya.
- Need for better coordination between central and state governments.
Policy Transformation in Northeast India
- From Insurgency to Integration: Post-Independence, the Northeast remained marred by insurgencies.
- The government viewed the Northeast mainly through a security lens, with little focus on development. Many in the region felt alienated, both physically and emotionally.
Strategic Shift: Look East to Act East
- The Look East policy was initiated by the Narasimha Rao government to boost ties with Southeast Asia.
- Atal Bihari Vajpayee formalized this direction by establishing the DoNER Ministry in 2001.
- In 2014, the Modi government adopted the Act East policy, marking a decisive turn in India’s regional strategy.
Era of Infrastructure and Integration
- Ground-Level Transformation: The Northeast became central to India’s economic and geopolitical vision.
- Union ministers maintained a continuous presence in the region, closing the emotional gap between people and government.
- Infrastructure Push: Government initiatives like NESIDS and PM-DevINE aim to improve roads, water supply, and power infrastructure.
- North East Special Infrastructure Development Scheme (NESIDS) launched in 2018 with a $1 billion budget for roads, power, and water supply.
- 4,950 km of National Highways constructed.
- More than $5Bn invested via the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways, allocating 10% of its budget to the region.
- Key Infrastructure Projects:
- India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway
- Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project
- Revival of Stilwell Road
- These initiatives aim to boost land-based trade with ASEAN. Additionally, maritime connectivity will be strengthened through the upcoming Sittwe Port (Myanmar), and the Chittagong Port (Bangladesh).
Conclusion
- The ‘Rising Northeast’ summit symbolizes the transformation of a once-neglected region into a dynamic investment and strategic hub.
- With enhanced connectivity, committed infrastructure development, and sustained political engagement, the Northeast is now poised to serve as India’s gateway to Southeast Asia.
| Daily Mains Practice Question [Q] How does the vision for the Northeast align with India’s broader economic and strategic goals, and what challenges might hinder its full realization? |
Next article
Time For a New India-Africa Digital Compact