Syllabus: GS3/Indian Economy
Context
- The Economic Survey 2024-25 projects a GDP growth rate for the fiscal year 2025-26, offering a comprehensive and realistic assessment of India’s economic trajectory.
- This forecast is grounded in the current economic conditions and global uncertainties, providing a balanced outlook for the future.
State of the Economy (Economic Survey 2024-25)
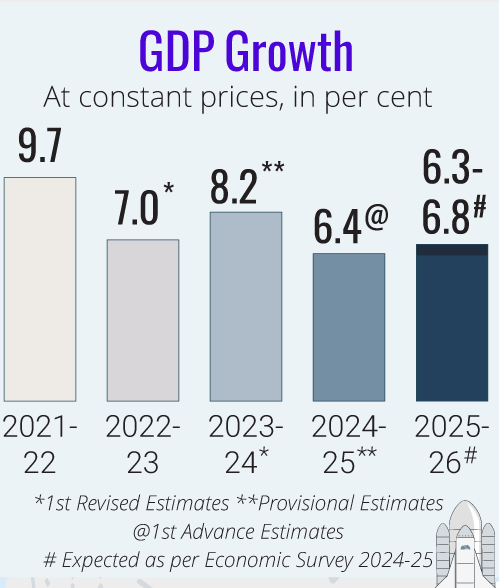
- India’s real GDP and Real Gross Value Added (GVA) growth are estimated at 6.4% in FY25 (as per first advance estimates of national income), which equates nearly to its decadal average.
- The real GDP growth in FY26 is expected to grow between 6.3 and 6.8%, keeping in mind the upsides and downsides to growth.
- The current financial year’s growth, as per the first advance estimates of the National Statistics Office (NSO), is expected to be around 6.4%, which aligns with the lower end of Economic Survey (2023-24) projection of 6.5-7%.
- The global economy on an average grew by 3.3% in 2023 against the IMF projection of 3.2% growth in the next five years.
- Despite global economic challenges, India’s economy is expected to maintain a steady growth rate and aligns with forecasts from global institutions like the International Monetary Fund and the Asian Development Bank, both anticipating a 7% growth rate.
- The survey highlights the importance of leveraging India’s demographic dividend and implementing deregulation measures to sustain long-term growth.
Assessment & Strategic Recommendations For India (Economic Survey 2024-25)
- For Viksit Bharat@2047: India needs to maintain a growth rate of 8% for the next two decades. It means India needs to accelerate the growth rate by 1.5-2 percentage points.
- To achieve the above, as the Economic Survey rightly notes, the investment rate in India will need to increase to about 35% of GDP from about 31% now.
- It requires significant investment in infrastructure and continued reforms to improve the business environment.
- Regulatory Reforms and Ease of Doing Business: The survey makes a strong case for enhancing the ease of doing business (EoDB) and positioning deregulation as a primary economic theme.
- While both the Union and state governments have taken steps to reduce regulatory bottlenecks, much work remains to be done.
- A key recommendation is that EoDB 2.0 should be a state-led initiative targeting fundamental issues in the business environment. States regulate critical sectors such as land acquisition, labor laws, logistics, and infrastructure.
- On FDI & FPI: Recent trends in Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI) suggest that relying on foreign savings to bridge the investment gap may not be viable.
- The survey warns that if capital flows remain constrained, the sustainable level of the current account deficit may be lower than the widely accepted range of 2.5-3% of GDP.
- Consequently, boosting domestic savings and reducing government dis-saving become imperative.
- Global Headwinds and Trade Policy: The medium-term global growth outlook appears weaker compared to the first two decades of the 21st century.
- Geopolitical tensions and fragmentation and China’s manufacturing prowess could dampen India’s growth trajectory, particularly in exports—a sector where India has traditionally lagged.
- The Economic Survey suggests that tariffs, if applied strategically, can foster industrial development in priority sectors.
- Inflation and Inequality: Retail inflation decreased to 5.4% in FY24 from 6.7% in FY23, attributed to effective administrative and monetary policies.
- The Survey addresses income inequality, noting that the top 1% of Indians earn 6-7% of total incomes, while the top 10% account for one-third.
- The government aims to tackle this by creating jobs, formalizing the informal sector, and increasing female labor force participation.
- Employment: The Survey underscores the necessity for India to generate approximately 7.85 million non-farm jobs annually until 2030 to accommodate the growing workforce.
- It points out that about half of Indian graduates are not immediately employable, emphasizing the need for skill development.
Conclusion and Way Forward
- Balancing Optimism with Caution: The Economic Survey 2024-25 recognizes the potential for growth while acknowledging the challenges that lie ahead.
- The survey’s recommendations focus on sustainable development, inclusive growth, and resilience to global economic shocks.
- The Economic Survey 2025 presents a realistic assessment of India’s growth path, balancing optimism with caution. It provides a roadmap for sustainable economic development by addressing both the challenges and opportunities.
- As India navigates the complexities of the global economy, the insights and recommendations from the survey will be crucial in shaping the country’s future.
| Daily Mains Practice Question [Q] How does the Economic Survey 2025’s realistic assessment of India’s growth path address the challenges and opportunities in achieving sustainable economic development? |
Previous article
Settling Sri Lanka’s Ethnic Problem
Next article
Strengthening India’s Agricultural Backbone