Kalbelia Community
Syllabus: GS1/Population
In News
- The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) issued a notice to the Rajasthan government over protests by the Kalbelia community in Barmer, who placed a dead body on the road demanding a designated burial ground.
Kalbeliyas
- Kalbelia are a snake charming folk community from the region of Rajasthan, India.
- Their traditional occupation used to be catching snakes and trading snake venom.
- They are known for their vibrant dances and black embroidered attire.
- In 2010, their songs and dances were added to UNESCO’s Intangible Cultural Heritage list, recognizing them as a key marker of identity as the community adapts to changing social and economic conditions.
- Kalbelias follow the Nath tradition, under which their dead kin are buried and not cremated.
| Do you know? – The Kalbelia dance, also called Sapera dance, is a folk dance central to Kalbelia culture, a nomadic tribe traditionally known as snake charmers. – The dance reflects their close association with snakes through movements and costumes. – Women perform the dance, while men provide musical accompaniment using instruments like the pakhawaj, dholak, jhanjhar, harmonium, sarangi, and especially the pungi (been). – It is a fast-paced dance highlighting flexibility, with dancers wearing black lehengas and ornate jewellery. |
Source: TH
Bomb Cyclone
Syllabus: GS1/Geography
In News
- A bomb cyclone is expected to bring another round of heavy snow and severe winter weather to the eastern United States.
Bomb Cyclone
- A bomb cyclone occurs when a low-pressure system’s pressure drops at least 24 millibars in 24 hours, rapidly strengthening winds due to the increased pressure gradient—a process called bombogenesis.
- It forms when cold polar air collides with warm subtropical air, often over warm ocean currents, with rapid intensification driven by temperature contrasts and latent heat from condensation.
- Bomb cyclones most often form over the western North Atlantic, where cold North American air meets warm Atlantic air, with the Gulf Stream helping intensify storms.
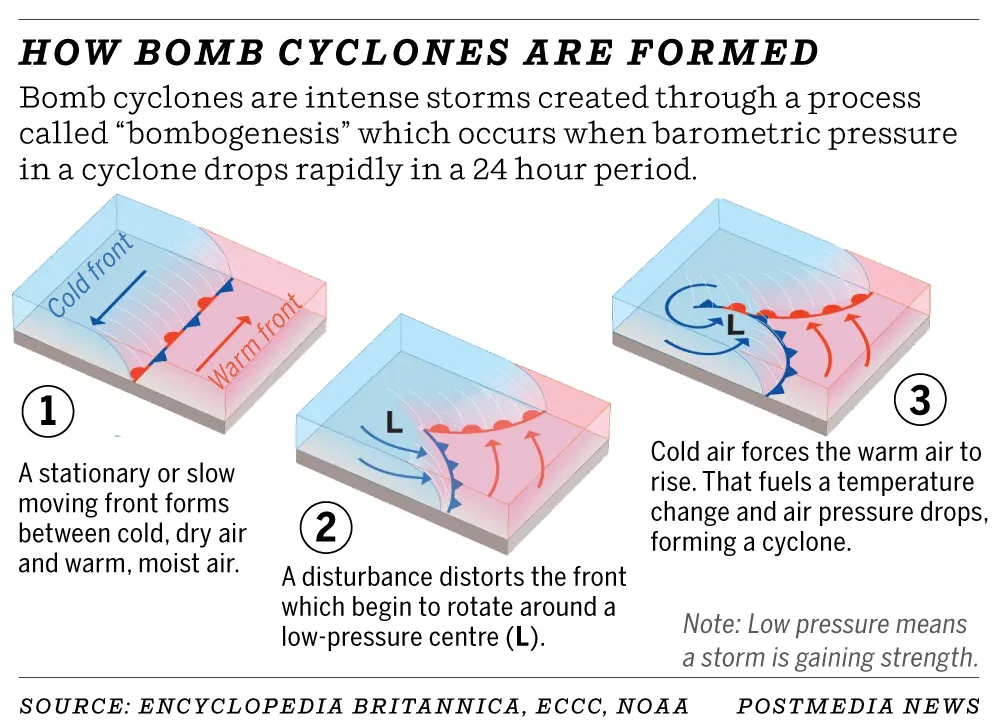
- Bomb cyclones bring heavy precipitation, including intense snowfall, with blizzard conditions and occasional lightning during rapid intensification.
Source: BBC
Kavach 4.0
Syllabus: GS2/ Governance
In News
- Indian Railways commissioned 472.3 route kilometres (RKm) of Kavach Version 4.0.
About
- Originally known as the Train Collision Avoidance System (TCAS), Kavach was adopted as the National ATP system in 2020. The 4.0 version, approved in July 2024 and significantly rolled out by January 30, 2026.
- Kavach 4.0 creates a “digital shield” by integrating several high-tech components:
- GPS & Radio Communication: Uses GPS for precise location tracking and UHF/Radio towers to maintain a constant “talk” between the locomotive and the station.
- Microprocessors: Onboard computers process real-time data to make split-second braking decisions.
- RFID Tags: Placed every kilometer on the tracks to “reset” the train’s location and direction accurately.
- Optical Fibre Network: Ensures high-speed data transfer between stations, even in remote terrains.
Source: PIB
New Consumer Price Index (CPI) Series
Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
Context
- The Union Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) has published the recommendations of an expert group revising the Consumer Price Index (CPI) base year from 2011–12 to 2023–24.
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
- CPI is an economic measure that tracks the average change in the prices paid by consumers for a basket of goods and services over time.
- The CPI in India is compiled by the National Statistical Office (NSO) and is categorized into CPI for urban and rural areas.
- These indices are then combined to calculate the CPI (Combined), which gives a comprehensive overview of inflation for the entire country.
- Significance:
- CPI is the primary measure of retail inflation in India.
- It is used by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) for inflation targeting and monetary policy formulation.
- CPI serves as the basis for indexing Dearness Allowance (DA) for government employees and pensioners. It is also used as a deflator in national accounts.
Source: DTE
New Country Partnership Framework
Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
In News
- India and the World Bank group announced a new Country Partnership Framework (CPF) to help accelerate India’s next phase of growth and support its vision of Viksit Bharat.
About
- CPF is the strategic roadmap that guides the World Bank Group’s financial, technical, and knowledge support to a country.
- The new CPF for India will provide $8–10 billion annually over the next five years.
- The Country Partnership Framework (CPF) is designed to achieve four specific results:
- Rural Prosperity: Diversifying income beyond farming and strengthening agri-value chains.
- Urban Transformation: Making cities “livable” and sustainable as the urban population heads toward 800 million by 2050.
- Investing in People: Scaling up health, nutrition, and market-aligned skills.
- Energy & Resilience: Strengthening energy security (e.g., Green Hydrogen, E-mobility) and climate resilience.
Key Projects Under Implementation
- PM-SETU (Skilling): Upgrading 1,000 ITIs via a “Hub-and-Spoke” model to make 1 million youth job-ready.
- Maharashtra PoCRA-II: Using precision farming and digital tech to boost smallholder resilience and profitability.
- Kerala Health Systems: Strengthening digital health and cybersecurity in state-wide medical services.
Source: BL
FPI Outflows Hit Five-Month High
Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
Context
- Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs) recorded net outflows of ₹35,962 crore from Indian equities in January 2026.
Foreign portfolio investment (FPI)
- FPI consists of securities and other financial assets held by investors in another country.
- It does not provide the investor with direct ownership of a company’s assets and is relatively liquid depending on the volatility of the market.
- FPI holdings can include stocks, American Depositary Receipts (ADRs), Global Depositary Receipts (GDRs), bonds, mutual funds, and Exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
- It is different from Foreign direct investment (FDI), which is an ownership stake in a foreign company or project made by an investor, company, or government from another country.
Key Drivers of FPI Selling
- Weak corporate earnings momentum remains a major concern for foreign investors.
- Continued depreciation of the Indian rupee has added to currency risk perceptions.
Source: TH
Coking Coal as Critical & Strategic Mineral under MMDR Act, 1957
Syllabus: GS/Economy
Context
- The government has notified Coking Coal as a Critical and Strategic Mineral under the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957 (MMDR Act).
About
- The decision has been taken on the basis of the recommendations of the High-Level Committee on Implementation of Viksit Bharat Goals (HLC-VB) and policy inputs from NITI Aayog.
- India has an estimated 37.37 billion tonnes of coking coal resources, largely located in Jharkhand, with additional reserves in Madhya Pradesh, West Bengal and Chhattisgarh.
- Despite this domestic availability, imports of coking coal have increased from 51.20 million tonnes in 2020–21 to 57.58 million tonnes in 2024–25.
- Currently, around 95 % of the coking coal requirement of the steel sector is met through imports, leading to significant foreign exchange outgo.
| Coking Coal – Coking coal, also known as metallurgical coal or “met coal,” is a type of coal that is used in the steelmaking process. – It’s essential in the production of coke, a key component in the steelmaking process. – Coking coal needs to have specific properties such as high carbon content, low sulfur and phosphorus content, and strong coking properties to be suitable for steelmaking. |
Significance
- The inclusion of coking coal in this category is expected to facilitate faster approvals, improve ease of doing business, and accelerate exploration and mining activities, including of deep-seated deposits.
- The reform is anticipated to reduce import dependence, strengthen supply-chain resilience for the steel sector, and support the objectives of the National Steel Policy.
Source: PIB
World Nuclear Outlook Report
Syllabus: GS2/IR/GS3/Science and Tech
In News
- According to the new World Nuclear Outlook Report , Five countries — China, France, India, Russia and the United States — could together account for nearly 980 GWe of global capacity in 2050.
World Nuclear Outlook Report
- It reviews national targets for nuclear capacity and assesses these against the global goal to triple nuclear capacity by 2050.
- It also reviews the current and future contribution of nuclear technology to energy provision and summarises the range of different nuclear reactor technologies available.
Key Findings
- Global nuclear capacity could reach 1,446 GWe by 2050, exceeding the tripling target of 1,200 GWe, with growth driven by reactors under construction, planned projects, and proposed or government-driven programs.
- China, France, India, Russia, and the USA would account for most capacity, while newcomer nations aim for 157 GWe.
- South Asia, led by India, is emerging as a key growth region due to rising electricity demand, urbanization, and industrialization.
Recommendations
- Governments, financial institutions, and industry should work together to expand nuclear energy by integrating it into climate plans, extending reactor lifetimes, reforming markets, supporting neutral financing, and scaling up supply chains and deployment, including new reactor technologies.
| India’s progress – India is steadily expanding its nuclear energy capacity under strict safety, cost, and regulatory oversight, with projects like a new facility near Kanyakumari progressing cautiously. – Current nuclear capacity stands at about 8.8 GW, with a long-term target of 100 GW by 2047, supported by policy reforms that allow private and foreign participation while the state retains majority control. – Nuclear is positioned as part of India’s low-carbon energy transition, complementing renewables, hydro, and pumped storage, while ensuring affordability, grid stability, and safety. – India is recognized as a key driver of global nuclear growth through 2050, reflecting its dual focus on operating existing plants and developing new projects to meet rising electricity demand and climate goals. |
Source :DTE
Next article
Union Budget 2026: Key Highlights