Muhammad Iqbal
Syllabus :GS 1/History
In News
- The Beating Retreat Ceremony at Vijay Chowk concluded with Muhammad Iqbal’s ‘Saare Jahan Se Achha’.
Muhammad Iqbal
- He is also known as Allama Iqbal (a title given to Islamic scholars).
- Born in Sialkot, he was an influential philosopher, poet, and politician.
- He studied in Europe and later became a prominent figure in Indian and Muslim philosophy.
- He is regarded as the ideological father of Pakistan, his work gained prominence in both India and Pakistan.
- Sarojini Naidu had called Iqbal the ‘poet laureate of Asia’.
- Literary works : His work, particularly ‘Saare Jahan Se Achha’, was adopted as a symbol of unity during India’s independence struggle.
- He is awarded a knighthood for works like Bang-e-Dara and Rumuz-e-Bekhudi.
- Javidnama is a spiritual journey under the guidance of Rumi.
- ‘Lab Pe Aati Hai Dua’ continues to be popular in schools.
- Controversy Around Legacy: Iqbal’s 1930 speech on the two-nation theory and his support for Muhammad Ali Jinnah has led to mixed perceptions, especially in India.
- Some controversies have arisen, such as recent protests over students reciting Iqbal’s poems, with some groups calling them “anti-national.”
- Despite this, Iqbal remains an influential figure in both Indian and Pakistani thought.
- Some controversies have arisen, such as recent protests over students reciting Iqbal’s poems, with some groups calling them “anti-national.”
| Do you know ? – Saare Jahan Se Achha’ is a patriotic poem originally written by Iqbal in 1904 as Tarana-e-Hindi (Urdu poem). – It eulogizes Hindustan (India, Pakistan, Bangladesh), with the famous lines “Saare jahan se achha, Hindustan hamara” meaning “Better than the entire world is our Hindustan.” – The poem became a symbol of resistance during British rule and was later set to a faster tune by Pandit Ravi Shankar. |
Source :IE
Kurdistan Region
Syllabus: GS1/ Places In News
In News
- India has sent a shipment of medical supplies, including bronchodilators, inhalers, and ventilators, to support the residents of the Kurdistan region in Iraq.
Strategic Importance of India’s Aid
- Enhances India’s humanitarian outreach in West Asia.
- Strengthens healthcare diplomacy and goodwill in a geopolitically sensitive region.
- Reinforces India’s commitment to global disaster relief and medical support.
- Example of India being as a ‘Vishwabandhu Bharat’, or a global friend
About Kurdistan Region
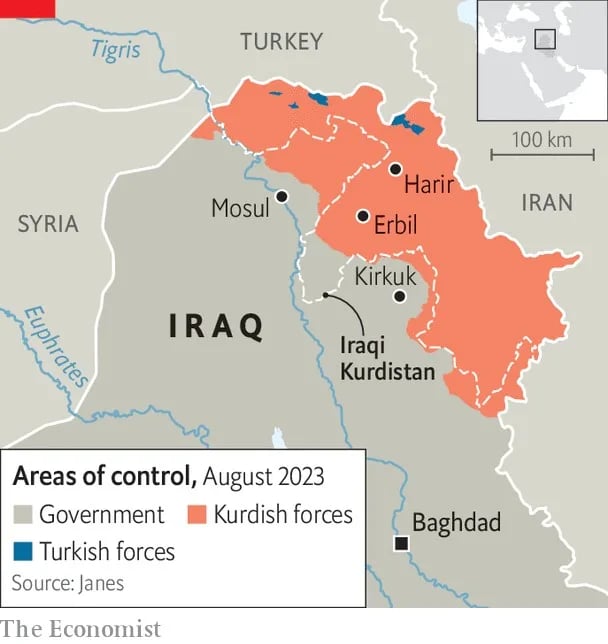
- Country: Iraq (semi-autonomous region).
- Capital: Erbil.
- Governorates: Erbil, Sulaymaniyah, Dohuk, Halabja.
- Neighbouring Nations: Shares borders with Turkey, Iran, Syria, and Iraq-controlled territories.
- Political Structure: The Kurdistan Regional Government (KRG) operates autonomously.
- Tensions exist with Iraq’s central government over resource control and autonomy.
- Mountains: Zagros Mountains dominate the landscape, forming natural borders with Iran and Turkey.
- Rivers: The Tigris and Greater Zab Rivers support agriculture and settlements.
Source: DD News
Human African Trypanosomiasis
Syllabus: GS2/Health
Context
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has announced that Guinea has successfully eliminated the Gambiense form of Human African Trypanosomiasis (HAT).
About
- It is also known as sleeping sickness, and has become the first neglected tropical disease to be eliminated in the country.
- Neglected tropical diseases are a group of mostly infectious diseases that thrive among resource-poor populations, especially in tropical climates.
- The announcement was made on the global observance of Neglected Tropical Diseases Day which is marked on January 30.
- So far, seven countries have been validated by WHO for eliminating the gambiense form of HAT: Togo (2020), Benin (2021), Côte d’Ivoire (2021), Uganda (2022), Equatorial Guinea (2022), Ghana (2023), and Chad (2024).
- The rhodesiense form of the disease has been eliminated in one country only, Rwanda, in 2022.
Human African Trypanosomiasis
- HAT is caused by trypanosome parasites that are transmitted by tsetse flies.
- HAT is found only in sub-Saharan Africa.
- Two subspecies of Trypanosoma brucei cause disease: T. b. gambiense in West and Central Africa, and T. b. rhodesiense in East Africa.
- Symptoms: Fever, headaches, and joint pain, confusion, disrupted sleep, and behavioural changes.
- If left untreated it can be fatal.
- Transmission can be interrupted by depleting the parasite reservoirs through detection and treatment of infected people and/or domestic animals.
- There is no vaccine for African trypanosomiasis.
Source: DTE
Leprosy Elimination
Syllabus: GS2/Health
Context
- The Union Health Ministry is looking at a more targeted approach to containing leprosy in India.
About
- The five states in India with the highest prevalence of leprosy are Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Maharashtra, and Odisha.
- The Union Health Ministry launched the National Strategic Plan (NSP) and Roadmap for Leprosy (2023-27) in 2023, to achieve zero transmission of leprosy by 2027.
- The Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 3.3 aims to end leprosy by 2030.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) declared Jordan as the first country in the world to eliminate leprosy in 2024.
Leprosy
- Leprosy is also known as Hansen’s disease, it is a chronic infectious disease caused by a type of bacteria, Mycobacterium leprae.
- It is known to occur at all ages ranging from early childhood to old age.
- Symptoms: The disease predominantly affects the skin and peripheral nerves.
- Loss of sensation in affected areas.
- Left untreated, the disease may cause progressive and permanent disabilities.
- Transmission: Through droplets from the nose and mouth.
- The disease is not spread through casual contact with an infected person.
- Treatment: Leprosy is a curable disease through the multi-drug therapy (MDT).
Source: TH
Teesta Bridge
Syllabus: GS3/Economy
In News
- The West Bengal government has approved the Teesta bridge project after over 10 years.
About Teesta Bridge
- After the state government gave its nod, the Centre has approved Rs 1,100 crore for the project and will link Sikkim and West Bengal.
- The Coronation Bridge, the existing bridge over the Teesta, was built in the memory of King George VI and Queen Elizabeth from 1937 to 1941. At that time, its construction cost over Rs 1 lakh. Its foundation stone was laid by then Bengal Governor John Anderson.
- but it was damaged in the 2011 earthquake.
- Now the new bridge will boost tourism and serve strategic purposes, particularly for military connectivity to the China and Bhutan borders.
- The Doklam standoff in 2017 highlighted the need for a new bridge to secure the route for military operations.
| Do you know ? – The Teesta river originates from Tso Lhamo Lake in north Sikkim at an elevation of about 5,280 meters. – The river travels through Sikkim, West Bengal, then enters Bangladesh at Mekhligunj. – It flows another 140 km in Bangladesh before joining the Bay of Bengal. 1. 83% of the Teesta’s catchment area lies in India, and the remaining 17% is in Bangladesh. – It is a tributary of the Brahmaputra river. |
Source :TH
Tannery Pollution in Palar River
Syllabus: GS3/ Environment
In News
- The Supreme Court has strongly condemned the unregulated discharge of untreated effluents from tanneries in Vellore, Tamil Nadu, into the Palar river, likening the environmental damage to an “ecocide.”
Supreme Court’s Directives
- Compensation to affected families: The Tamil Nadu government must distribute compensation fixed in 2001 by the Loss of Ecology Authority to over 29,000 affected families in Vellore.
- ‘Polluter Pays’ Principle: The government and tannery owners are held responsible for the damage caused.
- Formation of an Expert Committee: For conducting audit and maintaining a healthy environment.
Tannery Pollution & Its Impact
- Tamil Nadu houses 45% of India’s tanneries. 50% of chemicals in leather processing turn into wastewater or sludge.
- India produces 13% of global leather and Tannery wastewater contains harmful pollutants like Suspended solids, nitrogen, sulphate, sulphide, chloride.
- Pollutants further increase the Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) in Palar River.
- BOD measures the amount of oxygen required by microorganisms to decompose organic matter in water.
Source: TH
Axiom Mission 4
Syllabus: GS3/Science and Technology
Context
- ISRO astronaut Shubhanshu Shukla will serve as a pilot on the Axiom Mission 4 to the International Space Station (ISS).
About
- He will be the first Indian astronaut to reach the International Space Station (ISS) on a private mission.
- He became only the second Indian to go to space after Wing Commander Rakesh Sharma in 1984.
- He is elected as an astronaut-designate for India’s Gaganyaan mission (tentatively scheduled for 2026).
Axiom Mission 4
- Axiom Mission 4 (or Ax-4) is a private spaceflight to the International Space Station to be launched in April 2025.
- Duration: Up to 14 days.
- Countries: USA, India, Poland, and Hungary.
- It is the first government-sponsored spaceflight in over 40 years for Poland & Hungary.
- Objectives: The astronauts will execute a mission that includes outreach, scientific, and commercial operations during their 14-day stay in orbit.
- Significance:
- Each participating country can build on this experience for future missions.
- It will create new pathways for low-Earth orbit missions.
- Strengthens global partnerships in space research and exploration.
- It is a valuable experience for Gaganyaan.
- Strengthens ISRO’s collaboration with NASA and private space entities.
| Note: For Detailed Analysis about this you can refer our Daily News Decoded Video on NEXTIAS Youtube Channel |
Source: BS
Atmospheric River
Syllabus: GS3/ Environment
In News
- The Atmospheric River named “Pineapple Express” heads for North America. Pineapple Express is a type of atmospheric river that transports warm, humid air from Hawaii to the U.S. West Coast.
What are Atmospheric Rivers (ARs) (also called Flying Rivers)?
- Definition (NOAA): Long, narrow corridors in the atmosphere that transport large amounts of water vapor outside the tropics—like rivers in the sky.
- Formation: ARs are part of the larger extratropical cyclone system, moving heat and moisture from the tropics toward the poles.
- Typically found within low-level jets (strong winds in the lower atmosphere).
- Freshwater Transport: ARs are the largest transport mechanisms of freshwater on Earth.
- They account for 90% of moisture transfer from the tropics to higher latitudes.
Impact of Atmospheric Rivers
- Weak ARs: Bring much-needed rain and snow, replenishing water sources.
- Strong ARs: Can cause extreme rainfall, floods, mudslides, and destruction.
- Example of Destructive ARs: California’s “Pineapple Express” brings torrential rain and flooding.
- 2013 Uttarakhand floods and 2018 Kerala floods in India were linked to AR activity.
Source: BBC
Polar Bear Fur & Forever Chemicals
Syllabus :GS3/Environment
In News
- A recent study revealed that polar bear fur contains an oily substance (sebum) that helps them stay dry despite sliding on ice and diving into water.
About sebum
- Sebum is similar to the fluorinated coatings used on skis, which help them glide on ice but contain harmful “forever chemicals” (Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAs).
- Sebum could potentially be used to develop environmentally friendly alternatives to PFAs in coatings.
About Polar Bears
- They are the largest bears in the world and top predators of the Arctic.
- Their Latin name, Ursus maritimus, meaning “sea bear,” reflects their life spent predominantly on sea ice in the Arctic.
- Characteristics : Polar bears are skilled swimmers, capable of reaching speeds of six miles per hour, and have thick fat layers and water-repellent fur to insulate them from the cold.
- They spend over 50% of their time hunting, primarily for seals, as they require large amounts of fat for survival.
- Habitat: Polar Bears occur at low densities throughout the circumpolar Arctic and are more abundant in shallower, ice-covered waters associated with the continental shelf
- Distribution : The species is found in Canada, Greenland/Denmark, Norway, Russian ,United States (Alaska).
- Importance : Polar bears are at the top of the food chain and have an important role in the overall health of the marine environment.
- The loss of sea ice habitat is the biggest threat to the survival of polar bears.
- IUCN Status : Vulnerable
Note: India has four species of bears : Asiatic Black, Sloth, Sun and Himalayan Brown Bear.
| Do you know ? – Forever chemicals, scientifically known as per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), are a group of synthetic chemicals that have been widely used in various industrial and consumer products due to their resistance to water, oil, and heat. – These chemicals are found in items such as non-stick cookware, water-repellent clothing, stain-resistant fabrics, and firefighting foams. |
Source :IE
Previous article
India To Develop Its Own AI LLM Model