
Syllabus: GS3/Economy
Context
- Women-led development has been recognised as a structural game-changer for advancing India’s economic ambitions, yet its full potential remains under-leveraged.
Current Scenario
- Agriculture: It is a backbone of India’s economy & largest employer of women.
- Workforce shift: Rural men are moving to non-farm jobs leading to women replacing them in agriculture.
- Rise in women’s participation:
- Employment in agriculture surged by 135% in a decade.
- Women now account for 42% of the agricultural workforce.
- 2 in 3 working women are engaged in agriculture.
- Economic Impact: Women’s greater participation has not translated into higher income for the economy, as agriculture’s share of the national GVA fell from 15.3% in 2017-18 to 14.4% in 2024-25.
Challenges Faced by Women in Agriculture
- Unpaid Labour: Nearly half of the women in agriculture are unpaid family workers, with their numbers jumping 2.5 times from 23.6 million to 59.1 million in just eight years.
- In States such as Bihar and Uttar Pradesh, more than 80% of women workers are in agriculture, and over half of them receive no wages.
- Systemic Inequities: Women as farmers, own only 13-14% of land holdings, and earn 20-30% less than men for equivalent work.
- Asset ownership, decision-making power, and access to credit and government support remain male-dominated, trapping women in low-value activities.
- Digital Divide: Barriers in digital literacy, language, affordability of devices limits the participation in modern agri-markets.
Emerging Opportunities
- Global Trade: The India-U.K. Free Trade Agreement (FTA) is projected to boost Indian agricultural exports by 20% within three years, granting duty-free access to over 95% of agricultural and processed food products.
- Many of these export-oriented value chains employ a significant share of women.
- If FTA-embedded provisions for women, such as training, credit access, and market linkages, are catalysed, it could enable women’s transition from farm labourers to income-generating entrepreneurs.
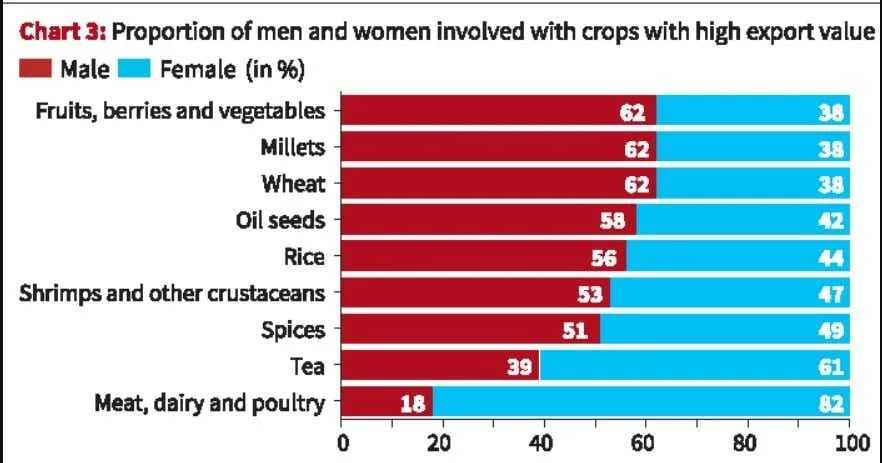
- High-Value Segments: With global demand rising for organic products and superfoods, India’s value chains for tea, spices, millets and certified organic produce are poised for expansion — sectors where women are already strongly represented.
- Geographical Indications, branding initiatives, and support for meeting export standards can help women producers shift from subsistence farming toward premium, value-added product markets.
Government Initiatives for Women in Agriculture
- Mahila Kisan Sashaktikaran Pariyojana (MKSP): Under National Rural Livelihood Mission (NRLM), supports women farmers in sustainable agriculture, livestock, and NTFP (non-timber forest produce).
- Joint Land Titles: States encouraged to issue land pattas in joint names of husband and wife.
- Priority Sector Lending (PSL): Mandates credit flow to women farmers.
- Rural women SHGs & FPOs: Supported through NABARD and DAY-NRLM.
- Agri-Clinics & Agri-Business Centres (ACABC): Special provisions for women agri-entrepreneurs.
- Maternity Benefits & Health Schemes: Support women farmers’ welfare indirectly.
- Support for Women FPOs: Encouraged under the 10,000 FPOs Scheme (2020) with special provision for women-led groups.
- GI Tags, Branding, and Export Facilitation: Helps women producers in spices, tea, millets, organic produce.
Way Ahead
- Without targeted measures, women risk being excluded from the export-led opportunities emerging in Indian agriculture.
- To transform women’s role in agriculture, land and labour reforms are equally vital.
- Policies must recognise women as independent farmers by promoting joint or individual land ownership, which in turn strengthens their eligibility for credit, insurance, and institutional support.
Source: TH
Previous article
Wassenaar Arrangement: Need to Reform Export Control Regimes