Syllabus: GS2/ Health
Context
- The Union Cabinet has approved the addition of 10,023 medical seats with an investment of Rs. 15,034 crore, as part of the goal to create 75,000 medical seats within the next five years.
About
- The Cabinet approved 5,000 post-graduate and 5,023 undergraduate (MBBS) seats in government colleges and hospitals by 2028-29.
- The Union government will fund 68.5% of the project (Rs. 10,303.20 crore), with the remaining Rs. 4,731.30 crore contributed by states.
India’s Flourishing Medical Infrastructure
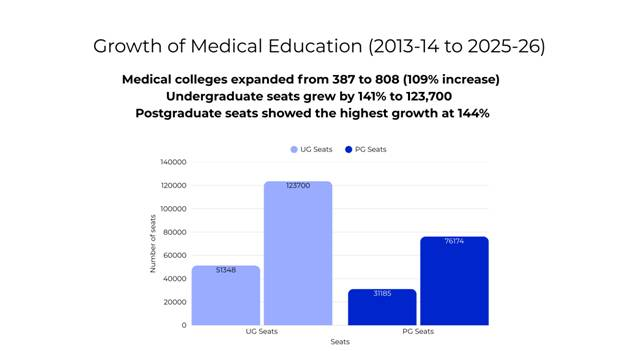
- Medical colleges in India doubled to 808 in 2025-26 from 387 in 2013-14, with undergraduate seats up 141% and postgraduate seats up 144%.
- There are 1,23,700 MBBS (Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery) seats today.
- 22 new All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) were approved under the Pradhan Mantri Swasthya Suraksha Yojana, which aims to make affordable and reliable tertiary healthcare accessible to all people.
- To facilitate the addition of new faculty, the National Medical Commission notified the Medical Institution (Qualifications of Faculty) Regulations, 2025 recently.
Impacts of Expanding Medical Education in India
- Aspiring medical students will get more opportunities to pursue a medical education in India.
- The quality of medical education will be enhanced and will meet global standards.
- With more doctors and specialists, India can become a prime destination for providing affordable healthcare and boost foreign exchange.
- Underserved rural and remote areas will get accessible healthcare.
- New direct and indirect jobs will get added (doctors, faculty, paramedical staff, researchers, administrators and support services).
What are the Challenges?
- Rural Doctor Shortages: Despite efforts, rural India continues to face severe shortages of doctors and healthcare professionals, leading to disparities in healthcare access.
- Limited Medical Research Funding: Medical research in India is constrained by inadequate funding and resource limitations, leading to a gap in research and innovation in medical education.
- Brain Drain: Many highly skilled doctors and specialists prefer working abroad due to better pay, research opportunities, and work environment.
- Expansion of seats may not automatically retain talent if incentives and career growth opportunities are not improved.
Way Ahead
- Expand the pool of qualified teachers by leveraging experienced specialists, retired faculty, and visiting professors.
- Introduce continuous professional development programs and incentives for rural postings.
- Leveraging Technology: Integrate digital learning, telemedicine, and AI-based training tools into medical education.
- Resource Upgradation: Modernize teaching hospitals with advanced labs, simulation facilities, and research centers.
- Research and Innovation Opportunities: Establish state-of-the-art research centers and collaborations with global institutions to encourage doctors to pursue advanced studies domestically.
Concluding remarks
- Expanding medical seats marks a significant leap forward in India’s journey toward universal healthcare.
- It will strengthen the medical workforce, raise education standards, and expand quality healthcare nationwide, making India a global leader in affordable care.
Source: PIB
Previous article
News In Short – 27 September, 2025
Next article
Food Loss and Waste