Syllabus: GS2/Health
Context
- As per the World Health Organization (WHO) and ITU (International Telecommunication Union), an investment of an additional US$0.24 per patient per year in digital health interventions, can help save more than 2 million lives from noncommunicable diseases over the next decade.
Major Findings
- These investments could also prevent approximately 7 million hospitalisations over the next 10 years.
- This will significantly reduce the strain on healthcare systems and lead to a total economic gain of $199.2 billion globally.
- The economic benefits of digital health investment were found to be particularly compelling for low- and middle-income countries, where the average required spending was only $0.10 per person per year.
- The cost for upper middle-income countries is estimated to be $0.16 and for high-income countries at $0.67.
- Cumulatively, the global spending required for these interventions would total $9.8 billion over the 10-year period.
- The report mentions India’s use of digital technologies to address healthcare disparities, particularly in rural areas where more than 65% of the population lives.
- The report called on governments and stakeholders to take decisive action, ensuring that digital health tools are integrated effectively into healthcare systems to combat the rising burden of NCDs globally.
| Noncommunicable Diseases (NCDs) – NCDs, also known as chronic diseases, tend to be of long duration and are the result of a combination of genetic, physiological, environmental and behavioural factors. – The main types of NCD are cardiovascular diseases (such as heart attacks and stroke), cancers, chronic respiratory diseases (such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma) and diabetes. – The major NCDs share four behavioral risk factors- unhealthy diet, lack of physical activity, and use of tobacco and alcohol. Factors contributing to the rise of NCDs also include ageing, rapid unplanned urbanization and globalization. – NCDs including heart disease, stroke, cancer, diabetes and chronic lung disease, are collectively responsible for 74% of all deaths worldwide. |
Global Initiative on Digital Health (GIDH)
- The World Health Organization (WHO) launched the Global Initiative on Digital Health (GIDH) in 2023.
- The initiative have four main components:
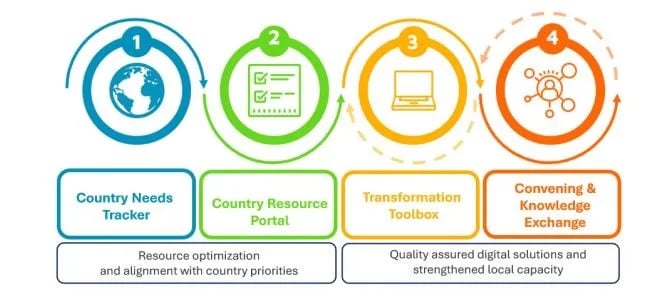
- Aim: ALIGN efforts to support the Global Strategy on Digital Health 2020–2025;
- SUPPORT quality assured technical assistance to develop and strengthen standards-based and interoperable systems aligned to global best practices, norms and standards;
- FACILITATE the deliberate use of quality assured digital transformation tools that enable governments to manage their digital health transformation journey.
Digital Health
- Digital health refers to the use of technology to improve health and healthcare delivery.
- It encompasses a broad range of tools and solutions that integrate digital technologies with health services, aiming to enhance patient outcomes, streamline processes, and increase accessibility.
- It includes tools such as Telemedicine, Mobile Health (mHealth), Electronic Health Records (EHRs), Wearable Devices, Health Applications etc.
Significance
- Improved Access: Digital tools can reach remote areas, connect patients to specialists, and enable virtual consultations, expanding healthcare access.
- Enhanced Affordability: Telemedicine, electronic prescribing, and data-driven resource allocation can potentially reduce healthcare costs.
- Personalized Care: Electronic health records (EHRs) and wearable devices facilitate personalized treatment plans and preventive care.
- Empowered Patients: Digital platforms can educate patients, enhance medication adherence, and promote self-management of chronic conditions.
- Streamlined Healthcare Delivery: Digitization empowers efficient data management, administrative processes, and resource optimization within healthcare systems.
Government Initiatives
- National Health Policy (NHP) 2017: This policy emphasizes the use of technology in health services and promotes the integration of digital health solutions.
- National Digital Health Mission (NDHM): Launched in 2020, NDHM aims to create a digital health ecosystem in India.
- It focuses on creating a Health ID for every citizen, facilitating access to health records, and ensuring the integration of healthcare services.
- Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM): It enables the establishment of health accounts, electronic health records, and health information exchanges.
- E Sanjeevani Telemedicine Platform: Facilitates virtual consultations between doctors and patients across the country.
- Health Management Information System (HMIS): This initiative aims to improve the collection and use of health data for better planning and decision-making.
- Digital India Initiative: While broader in scope, this initiative supports digital health by promoting internet connectivity, digital literacy, and technology use in various sectors, including healthcare.
Way Ahead
- Digital health is a proven accelerator to advance health outcomes and achieve Universal Health Coverage (UHC) and health-related Sustainable Development Goals. Hence, it needs to be made integral to every health policy.
- By scaling up existing initiatives, collaborating across stakeholders, and fostering innovation, India can leverage digital health to achieve its goal of universal healthcare and ensure better health outcomes for all.
Source: DTE
Previous article
India, Australia Push Forward on CECA Talks
Next article
10 Years of Make in India