
Syllabus: GS3/Economy
Context
- There is a growing consensus that India must transition from being primarily a service-driven economy to a product nation amid US punitive tariff action.
What is Product Nation?
- A “product nation” is a term often used to describe a country that moves beyond being primarily a service provider or outsourcing hub and instead becomes a creator of globally competitive products.
- Key Features of a Product Nation:
- Focus on Innovation: Strong emphasis on research, development, and intellectual property creation rather than just providing labour or services.
- Globally Scalable Products: Building products that can be sold worldwide, not just customized for a single client.
- Ecosystem Development: Supportive policies, venture capital, incubators, and strong collaboration between government, industry, and academia.
- Talent Utilisation: Leveraging a skilled workforce for product design, engineering, and entrepreneurship rather than primarily for back-end or outsourced work.
- Export Orientation: Products become a significant contributor to exports, enhancing national competitiveness.
Need for India to Become a Product Nation
- Strategic Leverage in Global Geopolitics: Current US tariff action shows India’s vulnerability — unlike China, India does not control any strategic products or supply chains that can be leveraged in negotiations.
- To avoid being a soft target in great power rivalries, India must create irreplaceable, high-value products.
- Reducing Import Dependence: Excess reliance on imports of critical technologies (chips, rare earths, batteries) weakens economic security.
- Solely focusing on manufacturing/assembly risks trapping India in low-value segments; profits lie in IP, design, and innovation.
- Economic Competitiveness & Value Creation: Services-led growth has limitations; India needs IP-driven, globally competitive products to boost exports and climb global value chains.
- Like Taiwan (chips) and the Netherlands (EUV machines), owning niche products ensures sustained economic resilience.
- Employment & Talent Utilization: India produces a large pool of engineers but most work for foreign specifications.
- Harnessing talent for home-grown design and innovation can create high-skilled jobs and prevent brain drain.
- Diplomatic & Strategic Autonomy: Earlier, India’s diplomatic heft came from ideals and moral leadership. Today, economic and product strength is essential for global respect.
- Owning strategic products enhances bargaining power, ensuring India is taken seriously in trade and security negotiations.
- National Security: Critical technologies (AI, semiconductors, defence, biotech, batteries) are increasingly weaponised in global trade wars.
- Without strong product capabilities, India risks economic coercion and strategic vulnerability.
Challenges for India in Becoming a Product Nation
- Innovation & R&D Deficit: India spends less than 1% of GDP on R&D (vs 2–3% in advanced economies).
- Skewed IT Ecosystem: Dominance of IT services outsourcing leads to service mindset persists.
- Funding & Risk Capital Constraints: Venture capital still favors proven service/startup models over risky deep-tech products.
- Talent Gaps: Abundance of engineers, but shortage of product managers, designers, chip developers, AI researchers.
- “Brain drain” of top talent to Silicon Valley and other innovation hubs.
- Infrastructure Bottlenecks: Inadequate hardware manufacturing ecosystem (semiconductors, electronics).
- Logistics and supply-chain inefficiencies increase cost of product scaling.
- Global Competitiveness Challenges: Indian products often face branding, quality perception, and global market access issues.
- Intense competition from China, USA, South Korea in electronics, AI, biotech, EVs.
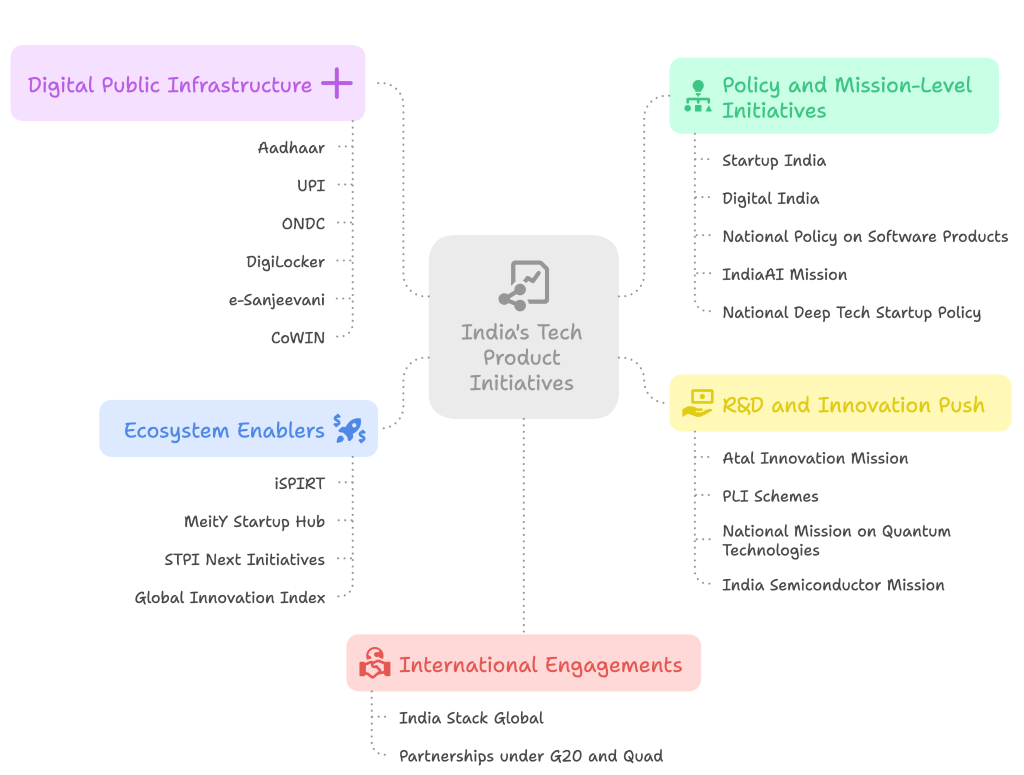
Way Ahead
- India must enhance R&D investment, strengthen IP protection, and nurture deep-tech talent to build globally competitive products.
- Greater access to risk capital, world-class infrastructure, and innovation clusters is essential.
- A “Made in India, Designed for the World” approach, supported by simplified policies and global branding, will accelerate India’s transition into a true Product Nation.
Source: IE
Previous article
Understanding India’s Internal Diasporas
Next article
Global Shift Towards Younger Forests