Syllabus :GS 3/Economy
In News
- In August 2025, U.S. President Donald Trump imposed a 50% tariff on imports from India, including a 25% penalty related to India’s oil purchases from Russia.
India’s vulnerabilities in the global system.
- U.S. tariffs averaged 2–3% for two decades until April 2024 but the new hike marks a sharp departure.
- In return for tariff relaxation, the U.S. is demanding greater market access, especially for agricultural and dairy products, which could hurt Indian farmers.
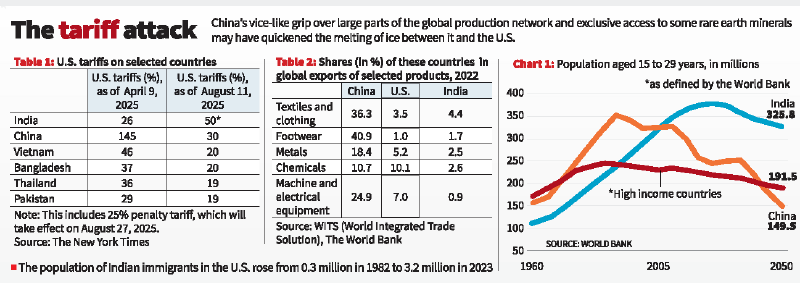
- Despite being a U.S. ally, India faces steeper tariffs than China (now reduced to 30%).
- The tariff war highlights India’s vulnerabilities in the global system.
China’s influence
- China’s dominance stems from its massive production capacity and technological prowess.
- China holds 36.3% of global textile exports and 24.9% in machinery/electricals; India lags at 4.4% and 0.9% respectively.
- Initial 145% tariffs on China were reduced after diplomatic engagement.
Consequences for India
- Comparative Disadvantage: Indian exports (e.g., textiles) now face higher tariffs than competitors like Vietnam and Bangladesh, making them uncompetitive.
- Trade Deficit Risk: U.S. export earnings are vital for India’s external balance; tariffs threaten this inflow.
- Sectoral Vulnerability: Textiles, pharmaceuticals, and IT services may suffer job and income losses.
- Investment Implications: Continued tariff instability may deter global firms from shifting supply chains to India.
India’s Policy Options
- Engage with the U.S. to recalibrate tariffs and protect strategic sectors.
- Leverage WTO and regional blocs to contest discriminatory trade practices.
- Shift from export-led to demand-driven growth via rising wages and consumption.
- Boost public spending to build human capital and resilience.
- Invest in high-value sectors (tech, pharma, clean energy) to reduce dependence on low-wage competitiveness.
- Role of youth : Indian immigrants in the U.S. have Excelled in education, technology, and entrepreneurship and Contributed to U.S. technological and economic dominance.
- Restricting Indian talent from U.S. jobs or visas could hurt U.S. interests long-term.
- Ensure equitable access to opportunities to prevent social fragmentation.
Conclusion and Way Forward
- A robust domestic market, empowered youth, and innovation-led growth are India’s best defence against global economic turbulence.
- This requires rapid increases in wages, incomes, and investment in high-value, tech-driven industries.
- India’s 120 million youth (15–29 years) can power a knowledge economy and therefore there is a need to expand vocational training, STEM education, and digital literacy.
- Harness diaspora networks for technology transfer and global influence.
Source :TH
Previous article
Adi Karmayogi Abhiyan
Next article
Draft Framework of India’s Climate Finance Taxonomy