Chikungunya
Syllabus: GS2/Health
In News
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has issued a warning about a potential global chikungunya epidemic, noting alarming similarities to a major 2004–2005 outbreak and urged early action.
Chikungunya
- Chikungunya is a mosquito-borne viral disease caused by the chikungunya virus (CHIKV), an RNA virus from the alphavirus genus.
- Symptoms: It causes fever and severe joint pain, which is often debilitating. In some cases it can be deadly.
- The symptoms of chikungunya are similar to those of dengue fever and Zika virus disease, making it difficult to diagnose.
- It is transmitted to humans by the bites of infected female mosquitoes, most commonly Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes.
- The latter, which is known as the tiger mosquito, is venturing farther north as the world warms because of human-driven climate change.
- Outbreaks: CHIKV was first identified in the United Republic of Tanzania in 1952 and subsequently in other countries in Africa and Asia.
- As of 2025, major outbreaks have been reported in Reunion, Mayotte, and Mauritius, with the virus spreading to Madagascar, Somalia, Kenya, and parts of South Asia. Imported cases have also appeared in Europe, with local transmission in France and suspected cases in Italy.
- Treatment: Symptoms can be managed but there is no specific antiviral treatment.
Source :TH
Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act of 1989
Syllabus: GS2/ Polity and Governance
Context
- The Madras High Court has reaffirmed the legal obligation of the police to immediately register an FIR in cases of cognisable offences under the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, 1989, without conducting a preliminary inquiry.
About the SC/ST (PoA) Act, 1989
- Objective: To prevent atrocities and hate crimes against Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs).
- Scope: Covers offences ranging from caste-based abuse to social and economic boycotts and violence.
- Special Provisions:
- Creation of Special Courts for speedy trial.
- Relief and rehabilitation for victims.
- No anticipatory bail in certain cases.
Key Legal Provisions Cited in the Judgment
- The SC/ST (PoA) Act, 1989 was amended in 2018 to include Section 18A(1)(a), which mandates that no preliminary inquiry is required for registering an FIR under this Act.
- Rule 7(1) of Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Rules, 1995: According to it, only officers not below the rank of Deputy Superintendent of Police (DSP) are authorised to investigate cases under this Act.
Source: TH
India Reaffirms its Support for Palestine at UN
Syllabus :GS2/IR
In News
- At the UN Security Council debate on the Middle East, India called for an immediate ceasefire in Gaza and the release of all hostages, highlighting the severe humanitarian crisis with damaged hospitals, food shortages, and disrupted education.
About
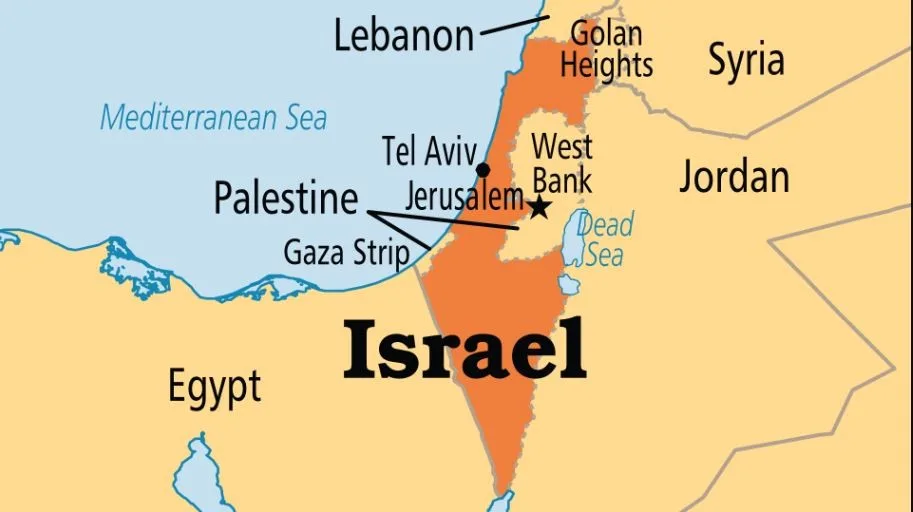
- The conflict between Israelis and Palestinians is complex and longstanding.
- The Israelis (the people who live mostly in Israel) and the Palestinians (the people who live mostly in the Gaza Strip and another area known as the West Bank).
- The Gaza Strip is a small sliver of land to the northeast of Egypt’s Sinai Peninsula— which connects Asia and Africa— in the eastern basin of the Mediterranean Sea.
- It is surrounded by Egypt to the southwest, the Mediterranean Sea to the west, and Israel to the north and east.
- The population is predominantly Sunni Muslim, with a Christian minority.
- The West Bank was part of the mandated former British territory of Palestine.
- It is located to the west of the Jordan River, with Jordan and the Dead Sea to the east and Israel to the north, south, and west.
- In 1948 most of Palestine became part of the country of Israel.
- Since then, the region has experienced bitter fighting between Palestinian Arabs, who are mostly Muslims, and Israelis, who are mostly Jews.
India’s Stand of Palestine
- India maintains balanced relations—it has deepened ties with Israel but continues its diplomatic and developmental engagement with Palestine.
- India reiterated its “unwavering” support for the Palestinian cause and emphasized that dialogue and diplomacy are the solutions.
- India is committed to supporting a two-state solution where the Palestinian people are able to live freely in an independent country within secure borders, with due regard to the security needs of Israel.
Source :TH
World Food India 2025
Syllabus :GS3/Economy
In News
- The Ministry of Food Processing Industries is going to organise the 4th edition of World Food India 2025 at Bharat Mandapam in New Delhi.
- The theme of the four day event is Processing for Prosperity.
World Food India
- It was launched in 2017 by the Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MoFPI) to showcase India’s rich food culture and attract global investment.
- It serves as a premier platform for stakeholders from across the world to connect, collaborate, and explore opportunities in India’s dynamic food processing landscape.
- World Food India 2025 aims to position India as a global hub for food processing and supply.
Brief overview of India’s food processing sector
- It is a priority under the Make in India initiative, with the Ministry of Food Processing Industries implementing schemes to attract investment and develop infrastructure.
- Mega Food Parks with essential utilities and common processing facilities are being established in agriculturally rich areas, offering a plug-and-play model for entrepreneurs.

Source :Air
Environmental Flow (E-Flow)
Syllabus: GS3/ Environment
In Context
- Jal Shakti Minister held a comprehensive meeting focused on the environmental flow (e-flow) of the Ganga River and its tributaries in New Delhi.
About Environmental Flow (E-Flow)
- Definition: Any managed change in a river’s flow pattern intended to maintain or improve river health. This includes both the amount and seasonal pattern of flow.
- Components: Encompasses not just the volume but also the timing and quality of flow, often aiming to mimic natural regimes.
- Purpose: Designed to sustain fish, wildlife, and plant species, maintain water quality, support estuarine productivity, and meet cultural, spiritual, and recreational needs.
Source: AIR
India Achieves 20% Ethanol Blending in Petrol
Syllabus: GS3/ Energy
Context
- India has achieved 20% ethanol blending in petrol in 2025, five years ahead of its original target set for 2030.
About
- Ethanol blending in petrol has risen from just 1.5% in 2014 to 20% in 2025- a nearly thirteenfold increase over 11 years.
- Ethanol production has surged from 38 crore litres in 2014 to 661.1 crore litres by June 2025.
- India has saved approximately ₹1.36 lakh crore in foreign exchange by reducing its dependency on imported crude oil.
Ethanol Blending
- The ‘National Policy on Biofuels’ notified by the government in 2018 envisaged an indicative target of 20% ethanol blending in petrol by 2030.
- Given the encouraging performance and various interventions made by the government since 2014, the 20% target was advanced to 2025-26.
| What is Ethanol? – Ethanol is 99.9% pure alcohol that can be blended with petrol. – Alcohol production involves fermentation of sugar using yeast. In cane juice or molasses, sugar is present in the form of sucrose that is broken down into glucose and fructose. – Also grains contain starch, a carbohydrate that has to first be extracted and converted into sucrose and simpler sugars, before their further fermentation, distillation and dehydration to ethanol. |
Source: AIR
Bambusa Tulda
Syllabus: GS3/ S&T
In News
- Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Researchers have developed an eco-friendly composite material made of ‘Bambusa tulda’, a fast-growing bamboo species in Northeast India, combined with biodegradable polymers.
About Bambusa Tulda
- Commonly known as Bengal Bamboo, Indian Timber Bamboo, or Spineless Indian Bamboo.
- It is a fast-growing, medium to large-sized, tropical clumping bamboo native to the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia (Indochina, Tibet, Yunnan).
- It is monocarpic (flowering once then dying) with an intermast interval typically of 15–60 years.
- Highly valued for its tensile strength and extensively used in paper pulp industry, construction, fencing, and various tools.
Source: TOI
Previous article
Coral Cover in Lakshadweep Saw a 50% Reduction: Study
Next article
PM State Visit to Maldives