Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
Context
- The IP filings in India in the last five years have increased by 44%, rising from 4,77,533 in 2020–21 to 6,89,991 in 2024–25.
Key Findings
- The highest growth was observed in Geographical Indications (GI) with a 380% increase, followed by Designs (266%), Patents (180%), Copyright (83%), Trademarks (28%), and Semiconductor Integrated Circuits Layout-Designs (SICLD) with a 20% rise.
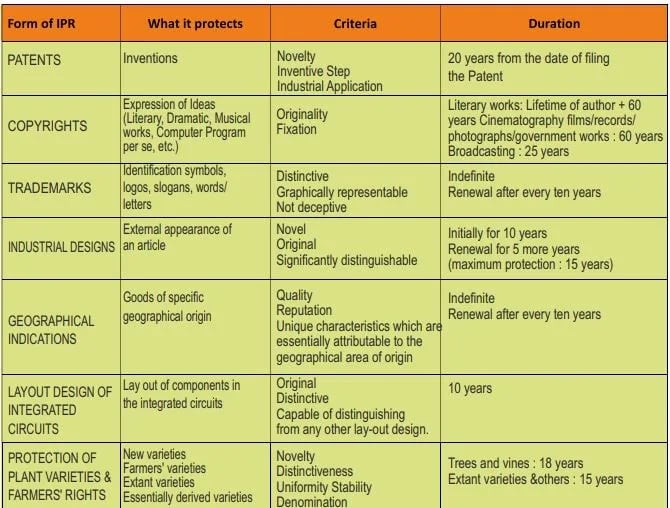
Intellectual Property (IP) Rights
- Intellectual Property (IP) is generally defined as the ‘Product of Mind’.
- It is a property that results from the creations of intellect in industrial, scientific, literary or artistic fields.
- Intellectual Property Right (IPR) is the legally enforceable exclusive right granted to the owner of the intellectual property for a limited period.
- IPR rewards creativity & human endeavor which fuel the progress of humankind.
- Forms of IPR: Patents, Copyrights, Trademarks, Industrial Designs, Geographical Indications, Layout Design of Integrated Circuits, Protection of Plant Varieties & Farmers’ Rights, Protection of undisclosed information/ Trade Secrets.
Is an Indian Patent valid in other Countries?
- No. Patent rights are territorial rights, which will be valid within the territory of the Country which has issued Patent.
- Hence, an Indian Patent, which is granted by the Indian Government, will be valid only in India.
India’s Initiative
- National IPR Policy 2016 encompassing all IPRs into a single vision document setting in place an institutional mechanism for implementation, monitoring and review of IP laws.
- The policy encourages innovation and creativity by providing stronger protection and incentives for inventors, artists, and creators.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) based Trademark Search Technology has been introduced for a more efficient and accurate examination and faster disposal of Trade Mark applications.
- The Start-Ups Intellectual Property Protection (SIPP) scheme was launched in 2016 to provide pro bono facilitation to startups for the filing and processing of patent, trademark, and design applications.
- Cell for IPR Promotion and Management (CIPAM): It has been set up to coordinate the implementation of the National IPR Policy.
- National Intellectual Property Awareness Mission (NIPAM), a flagship program to impart IP awareness and basic training in educational institutes.
- Atal Innovation Mission (AIM): It was set up by NITI Aayog in 2016 to promote a culture of innovation and entrepreneurship in India. AIM has created four programs to support these functions:
- Atal Tinkering Labs
- Atal Incubation Centers
- Atal New India Challenges and Atal Grand Challenges
- Mentor India.
Concluding Remarks
- India’s impressive IP growth, marked by significant advancements in patents, industrial designs, and trademarks, underlines its commitment to fostering innovation and reinforcing its global economic presence.
- This momentum supports India’s broader goals of economic expansion and innovation-driven development.
Source: PIB
Previous article
Manual Scavenging and Sewer Deaths in India
Next article
RBI’s Financial Inclusion Index