Rangpanchami
Syllabus: GS1/Culture
Context
- Rangpanchami is held five days after Holi, it marks the festive conclusion of the celebrations.
About
- The name “Rang Panchami” is derived from “Rang,” meaning colour, and “Panchami,” referring to the fifth day.
- Its celebration is observed primarily in Maharashtra, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and parts of Rajasthan.
- It marks the arrival of the spring season and people celebrate by throwing and applying colored powders (gulal) on each other.
Source: TOI
Competition Commission of India
Syllabus: GS2/ Statutory Bodies
In News
- The Competition Commission of India (CCI) has conducted extensive raids on the offices of major global advertising agencies over alleged IPL ad rate fixing.
About Competition Commission of India (CCI)
- Establishment: Statutory body established in 2009 under the Competition Act, 2002.
- Ministry: It is a quasi-judicial body operating under the Ministry of Corporate Affairs.
- Purpose: Aims to prevent anti-competitive practices, promote and sustain market competition, protect consumer interests, and ensure the freedom of trade in India’s markets.
- Members: It consists of a Chairperson and 6 Members appointed by the Central Government.
- Powers & Functions of CCI: Investigates anti-competitive agreements, cartelization, and abuse of dominance.
- Imposes penalties on companies violating competition laws.
- Advises the Central and State Governments on policy matters affecting competition.
- Key Cases Handled by CCI:
- Google Antitrust Case (2023): Fined Google ₹1,338 crore for anti-competitive practices in the Android ecosystem.
- Amazon-Future Group Case: Examined Amazon’s stake in Future Coupons for unfair trade practices.
Challenges Faced By CCI
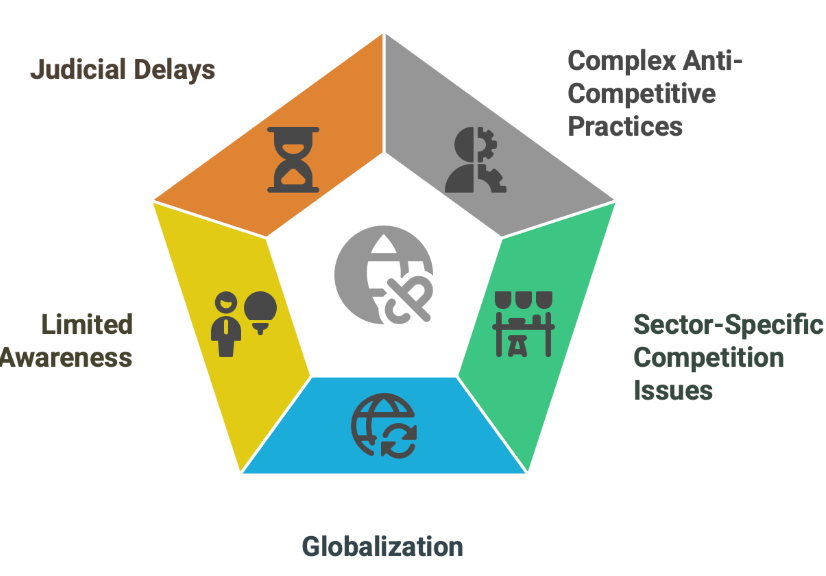
Source: BS
Online Assurances Monitoring System (OAMS)
Syllabus: GS2/ Polity
In Context
- The Union Parliamentary Affairs Minister recently highlighted the role of the Online Assurances Monitoring System (OAMS) in managing government assurances.
About
- It is a digital platform implemented by the Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs (MoPA) to enhance transparency and efficiency in managing government assurances.
- Assurances are promises, undertakings, or commitments given by Ministers during answers to parliamentary questions or debates.
- Assurances should ideally be fulfilled within three months of being made.
- The Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs (MoPA) is responsible for implementing assurances under the Government of India (Allocation of Business) Rules, 1961.
Source: PIB
Prime Minister’s Young Authors Mentorship Scheme (YUVA) Scheme
Syllabus :GS 2/Welfare Schemes
In News
- The Ministry of Education (MoE) and the National Book Trust (NBT) of India launched the third edition of the Prime Minister’s Young Authors Mentorship Scheme.
Earlier editions
- YUVA 1.0 (launched in May 2021) marked the beginning of the initiative during the Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav celebrations, commemorating 75 years of India’s independence.
- Its theme was the National Movement of India, focusing on unsung heroes, little-known facts, and various aspects of the freedom struggle.
- YUVA 2.0 (launched in October 2022) built upon the foundation of YUVA 1.0 with a focus on Democracy as the core theme.
- It aimed to develop young writers who could explore India’s democratic values, traditions, and governance structures.
PM-YUVA 3.0 Launch
- It aims to nurture young writers under 30 years of age, providing them with mentorship and exposure to hone their creative writing skills.
- It builds upon the success of its predecessors, YUVA 1.0 and YUVA 2.0, continuing the government’s commitment to fostering literary talent and promoting reading, writing, and book culture in India.
- It focuses on three themes: the Contribution of the Indian Diaspora in Nation Building, Indian Knowledge System, and the Makers of Modern India (1950-2025).

Importance
- The scheme aims to nurture young writers who can explore various aspects of India’s past, present, and future.
- It also provides aspiring youth with an opportunity to express themselves and present a comprehensive view of India’s contributions across different fields, both ancient and modern.
- The scheme aligns with the vision of Ek Bharat, Shreshtha Bharat, encouraging the documentation and dissemination of India’s rich cultural heritage and knowledge.
Source :PIB
India Takes 24th Spot in Free Speech Survey
Syllabus :GS 2/Governance
In News
- A global survey by The Future of Free Speech ranked India 24th out of 33 countries on support for free speech.
About the survey
- The survey, conducted in October 2024, revealed that more countries have seen declines in free speech support since 2021, with democratic nations like the United States, Israel, and Japan experiencing the most significant drops.
- It found that abstract support for free speech is strong, but commitment to protecting controversial speech is eroding globally.
Key Findings
- Norway and Denmark ranked at the top of the Future of the Free Speech Index with scores of 87.9 and 87.0, respectively.
- Indonesia (56.8), Malaysia (55.4), and Pakistan (57.0) showed the biggest improvements but remained at the lower end of the rankings.
- Some authoritarian-leaning countries, such as Hungary (85.5) and Venezuela (81.8), scored high, suggesting a disconnect between government restrictions and public attitudes.
India’s Specific Findings
- India scored 62.6, ranked 24th, between South Africa (66.9) and Lebanon (61.8).
- The majority of Indians consider it important to speak freely without government censorship.
- 37% of Indians supported the idea that governments should be able to prevent criticism of government policies—the highest among all surveyed countries.
- In comparison, only 5% in the U.K. and 3% in Denmark endorsed this sentiment.
- India, along with Hungary and Venezuela, was an exception to the general trend where support for free speech aligns with actual protection.
| Freedom of Speech in India – Article 19(1)(a) : Guarantees every Indian Citizen the Right to Freedom of Speech and Expression. – As per the rulings of the Supreme Court, the ‘Freedom of Speech and Expression’ as contained in Article 19(1)(a) includes the following: 1. Right to propagate one’s own as well as others’ views. 2. Freedom of silence. 3. Freedom of the press. 4. Right against the imposition of pre-censorship on a newspaper. 5. Freedom of commercial advertisements. 6. Right against tapping of telephonic conversation. – Restrictions Article 19(2) : The ‘Freedom of Speech and Expression’ is subject to reasonable restrictions by the State on the following grounds: |
Source: TH
Sustainable Development vs. Environmental Protection
Syllabus: GS3/ Environment
In Context
- The Supreme Court recently set aside the National Green Tribunal (NGT) order restraining the Auroville Foundation from proceeding with its township project in Puducherry without environmental clearance.
Key Aspects of the Judgement
- The Supreme Court recognized both the precautionary principle and the polluter pays principle as part of India’s environmental law.
- However, it ruled that while the right to clean environment is a guaranteed fundamental right under Articles 14 (equality) and 21 (right to life) of the Constitution of India, the right to development through industrialisation equally claims priority under fundamental rights, particularly under Articles 14, 19 (right to engage in any profession, occupation, trade or business) and 21 of the Constitution of India.
- The Court stressed a “golden balance” between development and environmental protection.
Source: TH
National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG)
Syllabus: GS 3/Conservation
In News
- The National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) is facing significant tax issues, with demands amounting to ₹243.74 crore from the Income Tax (I-T) department.
More About the News
- The issue arose because, despite being upgraded to an ‘authority’ under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986 in 2016, NMCG’s PAN remained classified as an Association of Persons (AOP), triggering scrutiny by the I-T department’s software, which flagged it as a high-income entity.
The National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG)
- It was registered on 12th August 2011 as a society under the Societies Registration Act 1860 and initially served as the implementation arm of the National Ganga River Basin Authority (NGRBA).
- However, the NGRBA was dissolved on 7th October 2016, and the National Ganga Council was established under the Environment (Protection) Act (EPA), 1986, to oversee the rejuvenation and protection of the Ganga.
Structure
- The mission operates under a five-tier structure at the national, state, and district levels.
- This structure includes:
- National Ganga Council under chairmanship of Hon’ble Prime Minister of India.
- Empowered Task Force (ETF) on river Ganga under chairmanship of Hon’ble Union Minister of Jal Shakti (Department of Water Resources, River Development and Ganga Rejuvenation).
- National Mission for Clean Ganga(NMCG).
- State Ganga Committees and
- District Ganga Committees in every specified district abutting river Ganga and its tributaries in the states.
Functions
- The National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) is responsible for abatement of pollution in river Ganga and its tributaries
- It aims to address pollution, ensure adequate water flow, and rejuvenate the Ganga.
Source :IE
World’s Largest White Hydrogen Deposit
Syllabus: GS3/Environment
Context
- France has discovered a massive 46-million-ton white hydrogen reserve in the Moselle region, valued at $92 trillion.
About
- White hydrogen, a naturally occurring gas in the Earth’s crust, is a relatively new discovery in the energy sector.
- Unlike other forms — gray, brown, blue, and green hydrogen — white hydrogen requires no industrial production and emits no carbon, making it an environmentally superior energy source.
- Its potential is enormous, with deposits found worldwide, including in the US, Russia, Australia, and Europe.
Extraction of Hydrogen
- Hydrogen exists in combination with other elements, so it must be extracted from naturally occurring compounds like water (H2O).
- Green hydrogen is produced using renewable energy sources (wind, solar, hydropower) through electrolysis—splitting water into hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2).
- When the electricity for electrolysis comes from renewable sources, the hydrogen produced is green.
- Grey hydrogen is produced from natural gas using steam methane reforming (SMR), releasing CO2 and contributing to greenhouse gas emissions.
- Blue hydrogen involves capturing and storing CO2 emissions from hydrogen production using natural gas.
Source: TN
Vikram and Kalpana: ISRO Develops High-speed Microprocessors
Syllabus: GS3/Science and Technology
Context
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and the Semiconductor Laboratory (SCL) in Chandigarh have jointly developed two cutting-edge 32-bit microprocessors, Vikram 3201 and Kalpana 3201.
About
- They are optimised for efficiency and performance, specifically designed for space applications.
- Vikram 3201 is India’s first fully indigenous 32-bit microprocessor qualified for use in the harsh conditions of launch vehicles and it can process 32 bits of data at a time.
- It supports floating-point computations and offers high-level language compatibility.
- Kalpana 3201 is also a 32-bit SPARC V8 RISC microprocessor based on the IEEE 1754 Instruction Set Architecture.
- It is designed to be compatible with open-source software toolsets and has been tested with flight software, making it versatile for various applications.
Source: ISRO
Exercise VARUNA 2025
Syllabus: GS3/Defence
Context
- The 23rd edition of the annual naval ‘Exercise VARUNA’ between India and France has commenced in the Arabian Sea.
About Exercise VARUNA
- It was started in 2001 to enhance interoperability and operational synergy between India & France.
- VARUNA 2025 features a series of drills and manoeuvres involving underwater, surface, and air operations.
Other Exercises
- EXERCISE SHAKTI: Indian and French Armies
- EXERCISE GARUDA: Indian Air Force (IAF) and French Air and Space Force (FASF).
Source: PIB
Previous article
NBRI Develops GM Cotton Resistant to Pink Bollworm
Next article
Ramnath Goenka Awards for Excellence in Journalism