Syllabus: GS2/IR
Context
- The first India–Egypt Strategic Dialogue was held in New Delhi co-chaired by EAM Dr. S. Jaishankar and Egyptian FM.
- Both leaders discussed the progress of India-Middle East EU Economic Corridor (IMEC).
About
- Egypt’s Position: Egypt supports regional connectivity projects like India-Middle East EU Economic Corridor (IMEC) but believes progress is impossible without addressing the Palestinian question.
- It proposed that India join the Egyptian Suez Canal Economic Zone (SCZONE) — where Russia, China, and others already have industrial complexes — to strengthen connectivity and trade cooperation.
- India’s Support to Palestine: EAM reiterated India’s consistent support for the two-state solution, i.e. peaceful coexistence of Israel and Palestine as independent states.
- Egypt’s Geostrategic Role: Egypt aims to act as a bridge between Asia, Africa, and Europe, leveraging its Suez Canal Economic Zone for industrial and trade cooperation.
- Egypt’s mediation in Gaza and participation in the Gaza Peace Agreement (2025) reinforce its centrality in Middle East peace efforts and connectivity diplomacy.
Brief on India-Egypt Relations
- Diplomatic relations at Ambassadorial level were established in 1947.
- Both countries were founding members of the Non‑Aligned Movement (NAM) in 1961.
- Bilateral Relations: The India-Egypt Bilateral Trade Agreement (based on MFN clause) has been in place since 1978.
- Trade reached a high of US$ 7.26 billion in FY 2021-22.
- In FY 2024-25, bilateral trade was about US$ 5.2 billion (India exports to Egypt ~ US$3.84 billion; imports ~ US$1.3 billion).
- Defence & security cooperation: MoU on Defence Cooperation signed during an Indian Defence Minister’s visit in 2022.
- First ever IAF-EAF joint tactical air exercise “Desert Warrior” in 2021.
- The 3rd edition of Exercise “Cyclone”, involving special forces of both countries, held in 2025.
- Indian community: Over 6,000 Indians live in Egypt, ~2,000 Indian students study in Egypt.
- Mechanisms: Joint Foreign Office Consultations (FOC), Joint Trade Commission (JTC), Joint Defence Committee (JDC), Joint Working Groups (JWGs) on varied issues such as new & renewable energy, animal husbandry, health & medicine.
India-Middle East EU Economic Corridor (IMEC)
- Background: The IMEC, a proposed 4,800 km long route was announced in 2023 on the sidelines of the G20 Summit.
- This followed a meeting between the leaders of India, the US, the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, Italy, France, Germany, and the European Commission.
- Members: India, European Union, France, Germany, Italy, Saudi Arabia, UAE and US announced the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC).
- Aim: Integration of Asia, Europe and the Middle East.
- The IMEC will comprise of two separate corridors:
- The east corridor connecting India to the West Asia/Middle East and
- The northern corridor connecting West Asia/Middle East to Europe.
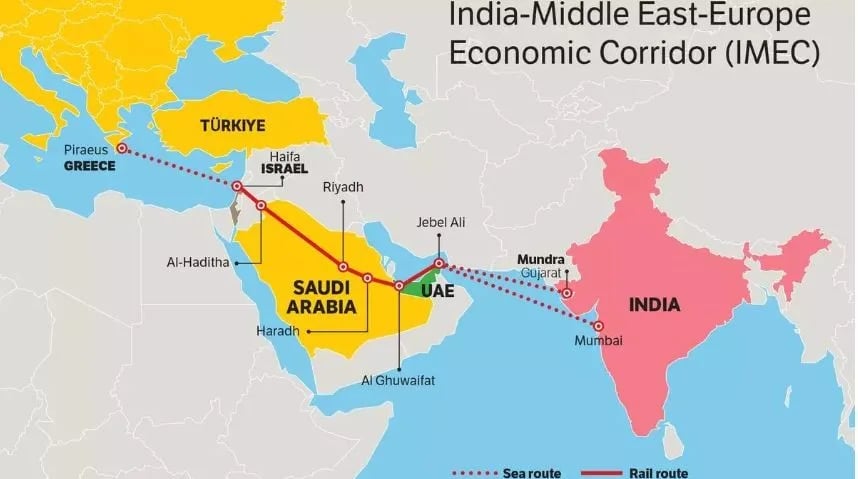
Ports Which are Part of IMEC
- India: Ports in Mundra (Gujarat), Kandla (Gujarat), and Jawaharlal Nehru Port Trust (Navi Mumbai).
- Europe: Piraeus in Greece, Messina in Southern Italy, and Marseille in France.
- Middle East: Ports include Fujairah, Jebel Ali, and Abu Dhabi in the UAE, as well as Dammam and Ras Al Khair ports in Saudi Arabia.
- Israel: Haifa port.
- Railway Line: The railway line will link Fujairah port in the UAE to Haifa port in Israel, passing through Saudi Arabia (Ghuwaifat and Haradh) and Jordan.
Significance of IMEC
- Economic Development: By linking Asia, West Asia, the Middle East and Europe through enhanced connectivity and economic integration, the corridor aims to give a boost to economic development in the regions.
- Enhances India’s Connectivity and Trade Access: IMEC provides India with a direct, faster, and safer trade route connecting Indian ports to Europe via the Arabian Peninsula and the Mediterranean.
- Reduces dependence on the Suez Canal route, cutting shipping time by up to 40% and costs by 20–30%.
- Strengthens India’s Strategic Partnerships: Deepens India’s ties with the U.S., EU, Saudi Arabia, UAE, and Israel, all core IMEC participants.
- Aligns with India’s broader “Act West Policy” and encourages cooperation among traditional partners and new regional players.
- Boost to Energy Security: The corridor can integrate energy pipelines and green hydrogen networks linking India with Gulf producers and European consumers.
- Facilitates diversification of India’s energy imports and enhances collaboration in renewable and clean energy sectors.
- Eco-friendly Infrastructure: It places emphasis on developing environmentally friendly infrastructure.
Concerns
- The security challenges in the region have made other partners reluctant to invest in the project.
- The instability in the Middle East has given a fatal blow to the project, the delay in the project could negatively impact the aspirations of India in the region.
- Lack of Political Consensus: Although signed during the G20 Summit 2023, the IMEC memorandum is not legally binding, relying on voluntary participation.
- Divergent priorities among members slow coordination and execution.
- Economic and Financial Viability: Estimated project costs are high, involving ports, railways, pipelines, and digital infrastructure across multiple jurisdictions.
- There is a lack of clarity on financing mechanisms—whether it will be multilateral, public-private, or state-funded.
- Infrastructure Gaps and Technical Challenges: Significant infrastructure deficits in West Asian countries—especially in cross-border railway connectivity.
- Integration of different railway gauges, standards, and customs procedures remains unresolved.
Way Forward
- The geopolitical concerns need to be managed by striking a delicate balance in accommodating the geopolitical interests of the participating nations and addressing potential political sensitivities.
- There is also a need to maintain the required security apparatus as the project passes through certain unstable regions of the world.
Source: TH
Previous article
SC Forms Panel on Transgender Persons
Next article
Sri Lankan PM’s State Visit to India