Eswatini
Syllabus: GS1/Places in news
In News
- The United States has deported five foreign nationals convicted of serious crimes to Eswatini.
About Eswatini
- It is a landlocked country bordering South Africa and Mozambique in Southern Africa.
- It is a member of the Common Monetary Area (CMA), with Lesotho, Namibia, and South Africa.
- It was formerly known as Swaziland and it changed its name in 2018 to reflect its pre-colonial identity.
- It remains one of the few countries in the world, and the only one in Africa, governed by an absolute monarch.
- King Mswati III, who has ruled since 1986, holds full control of government functions and rules by decree.
- The country faces major social and economic challenges, with over half the population living on less than $4 a day and the highest global HIV rate at about 26%.
Source :IE
Cabo Delgado Region
Syllabus: Gs1/ Places in News
In News
- A new study reveals that four planned Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) projects in the Rovuma Basin, located in the Cabo Delgado region of northern Mozambique, could have an outsized impact on the global climate if fully exploited.
About Cabo Delgado Region
- Cabo Delgado is the northernmost province of Mozambique, bordering Tanzania to the north (across the Rovuma River), the provinces of Niassa (west) and Nampula (south), and the Indian Ocean to the east.
Source: DTE
Conduct of Business in Lok Sabha
Syllabus: GS2/Polity and Governance
Context
- The Monsoon Session of Parliament will begin soon.
Parliament holds three Sessions in a year
- Budget Session—February-May;
- Monsoon Session—July-September; and
- Winter Session—November-December.
Rules for the Conduct of Business of Parliament
- Under Rule 377 of the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in Lok Sabha, Members are allowed to raise matters which are not Points of Order or which have not been raised during the same session under any other Rule.
- In the Rajya Sabha, Members are allowed to make a mention of matters of public importance under Rule 180A-E of the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in the Council of States.
- There are four main procedures under which there could be a discussion in the Lok Sabha — a debate without voting under Rule 193, a motion (with a vote) under Rule 184, and an adjournment motion or a no-confidence motion.” Except the last one, similar measures also exist in the Rajya Sabha.
Procedures
- Question Hour: Generally, the first hour of a sitting of the Lok Sabha is devoted to Questions called the Question Hour.
- Members can ask questions on every aspect of administration and governmental activity.
- MPs raise questions during Question Hour to hold the government accountable for its policies and actions.
- ‘Zero Hour’: The period of time immediately after the Question Hour is over and before the regular business as entered in the List of Business is taken up, is referred to as the ‘Zero Hour’.
- The Government is under no obligation to respond to the matters raised during the ‘Zero Hour’.
- Short Duration Discussion: Members could raise discussion for a short duration without a formal motion or vote.
- Any member may give notice in writing specifying clearly and precisely the matter desired to be raised.
- It shall state the reasons for raising the discussion and supported by the signatures of at least two other members.
- Adjournment Motion: This motion is introduced to draw attention of the house towards a recent matter of urgent public importance.
- If admitted, it leads to setting aside the normal business of the House for discussing a definite matter of urgent public importance.
- No-Confidence Motion: The Council of Ministers must enjoy the confidence of the House at all times to remain in power.
- The Opposition Parties in Lok Sabha can move a No-confidence Motion in the Council of Ministers to express the lack of confidence of the House and such a motion, if adopted, results in the fall of the Government.
Source: IE
PAC Calls for Aadhaar Review
Syllabus: GS2/Governance
In News
- The Public Accounts Committee has called for a review of the functioning of the Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI), flagging several concerns, including the high rate of failure of Aadhaar biometric verification which can lead to many beneficiaries being excluded from social welfare schemes.
About Public Accounts Committee (PAC)
- The Committee on Public Accounts was first set up in 1921 in the wake of the Montague-Chelmsford Reforms.
- It is a key parliamentary committee in India, constituted annually to examine government expenditure and financial accounts.
- It reviews the appropriation of funds granted by Parliament, annual Finance Accounts, and other relevant accounts (except those of Public Undertakings and Government Companies which come under the purview of the Committee on Public Undertakings).
- Composition: The PAC has up to 22 members—15 elected from the Lok Sabha and up to 7 from the Rajya Sabha—selected through proportional representation.
- The Chairperson, appointed by the Lok Sabha Speaker, is traditionally from the opposition.
- Ministers cannot be members of the committee.
- The term of office of the members is one year.
- Functions: The PAC’s functions include scrutinizing government spending to ensure funds are used legally and appropriately within the sanctioned limits. It examines cases of excess expenditure, financial irregularities, losses, and wasteful spending.
- The committee also reviews reports by the Comptroller and Auditor-General (CAG) on both expenditure and revenue, investigating tax administration issues like under-assessment and tax evasion, and recommends measures to prevent revenue leakage.
Source :TH
Maulana Azad National Fellowship (MANF)
Syllabus :GS2/Governance
In News
- The Union Ministry of Minority Affairs announced that the seven-month pending payments under the Maulana Azad National Fellowship (MANF) have now been released.
Maulana Azad National Fellowship (MANF) Scheme
- It is a five-year fellowship provided by the Centre in the form of financial assistance to six notified minority communities – Muslims, Buddhists, Christians, Jains, Parsis and Sikhs — to pursue M Phil and PhD.
- It was launched in 2009-10 as a Central Sector Scheme.
- It is being implemented by the Ministry of Minority Affairs.
- It covers all Universities/Institutions recognized by the University Grants Commission (UGC).
- Scope: The Fellowship will cater to the minority community students pursuing regular and full time research studies leading to award of M.Phil/Ph.D degree within India only.
- This will enable them to be eligible for employment to the posts with M.Phil and Ph.D as pre-requisites, including the posts of Assistant Professors in various academic institutions.
Source :IE
India sends 3 lakh Measles-Rubella vaccine doses to Bolivia
Syllabus: GS2/ Health
In News
- India has sent 3 lakh doses of Measles-Rubella vaccine to Bolivia in response to a major measles outbreak.
About Measles
- Measles is a highly contagious and serious airborne viral disease.
- It is caused by a virus in the Paramyxovirus family and spreads mainly through respiratory droplets via coughing, sneezing, or direct contact.
- The virus initially infects the respiratory tract and then spreads throughout the body, often resulting in severe complications and, in some cases, death.
- No specific antiviral treatment exists for measles. However, in preventive mode, the Measles-Rubella (MR) vaccine is usually given in two doses to ensure immunity.
Source: AIR
Automotive Mission Plan (AMP) 2047
Syllabus: GS3/Economy
Context
- The government has initiated the formulation of the Automotive Mission Plan 2047 (AMP 2047).
About
- Aim: To transform India into a global automotive leader by focusing on innovation, sustainability, and exports.
- Key Objectives:
- Set concrete milestones for 2030, 2037, and 2047 for sectoral growth.
- Increase India’s share in global automotive trade through high-quality and advanced products.
- Promote an industry-led and government-supported strategy for future growth.
- Integrate sustainability, green mobility, and digital transformation in the automotive ecosystem.
- Strategic Features
- Emphasis on technology neutrality: Not tied to specific companies or technologies.
- Focus on building robust infrastructure, including charging networks for electric vehicles (EVs).
- Ensures collaborative input from all stakeholders to frame policies based on ground realities.
- Institutional Mechanism: Formation of seven sub-committees comprising experts from government ministries, industry bodies, academia, testing agencies, and think tanks.
- Role of sub-committees:
- Outline the objectives, framework, and sectoral targets.
- Guide the phased development and implementation till 2047.
- Focus on exports, innovation, digitalization, and value-chain enhancement.
Source: BS
Green Synthesis of Hydrogen Peroxide
Syllabus: GS3/Environment
Context
- Researchers from S. N. Bose Centre for Basic Sciences (SNBCBS) have developed a novel approach for synthesizing H2O2 directly from water and sunlight.
Hydrogen peroxide
- Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is a vital oxidizing agent with broad applications in chemical synthesis, sterilization, wastewater treatment, and fuel cells.
- Known for its eco-friendly nature of degrading or breaking down into only water and oxygen – H2O2 is a key component in sustainable chemical processes.
- However, its conventional production methods are energy-intensive, environmentally hazardous, and costly.
Photocatalytic hydrogen peroxide generation using M-COFs for various applications
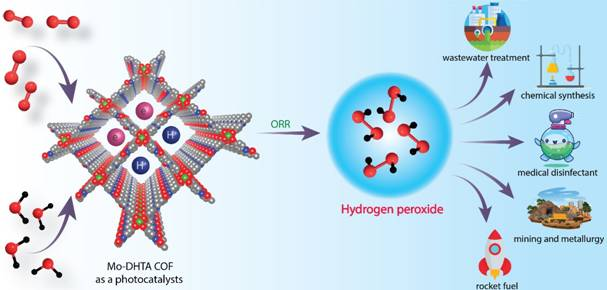
- Mo-DHTA COF, short for dimolybdenum paddlewheel-embedded covalent organic framework for synthesizing H2O2 directly from water and sunlight.
- This innovation offers a cleaner, more efficient, and recyclable route for hydrogen peroxide production, potentially transforming industries such as pharmaceuticals, green chemistry, and materials science.
Source: PIB
Prithvi-II and Agni-I
Syllabus: GS3/Defence
Context
- India successfully test-fired two key strategic ballistic missiles – Prithvi-II and Agni-I – from the Integrated Test Range (ITR) at Chandipur, Odisha.
About Prithvi-II
- Prithvi-II, developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), is a liquid-fuelled, surface-to-surface ballistic missile known for its high accuracy and precision targeting.
- It has a range of approximately 350 km and is capable of carrying a payload of up to 500 kg. The missile can be equipped with both conventional and nuclear warheads.
About Agni-I
- Designed and developed by the DRDO, Agni-I is a single-stage missile powered by solid propellants.
- It has a range of 700–900 km and is capable of carrying a nuclear warhead weighing up to 1,000 kg.
- The need for Agni-I was felt in the aftermath of the Kargil War with Pakistan.
Do you Know?
- The new-generation Agni-Prime ballistic missile, with a strike range of 1,000 to 2,000 km, is set to gradually replace the Agni-I and Agni-II missiles in India’s nuclear arsenal.
- The successful trials of Prithvi-II and Agni-I came just a day after the Indian Army conducted a high-altitude test of the indigenous Akash Prime air defence system in Ladakh, at an altitude of approximately 15,000 feet.
Source: DD News
Previous article
China’s Green Energy Transformation