Syllabus: GS3/Environment
Context
- Recently, India joined the global community in observing the World Day to Combat Desertification and Drought, reaffirming its commitment to sustainable land management and climate resilience.
About World Day to Combat Desertification and Drought
- It was established by the United Nations General Assembly in 1994, observed annually on June 17.
- It highlights the urgent need for sustainable land management and global action against desertification.
- Theme (2025): ‘Restore the Land. Unlock the Opportunities’
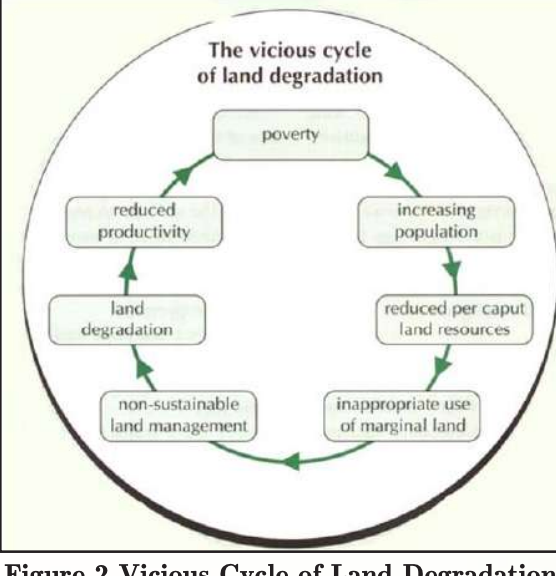
Desertification
- UNCCD (United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification) defines land desertification as “land degradation in arid, semi-arid and dry sub-humid areas resulting from various factors, including climatic variations and human activities.”
- Land degradation is accelerating, costing the global economy $878 billion annually. Africa and Asia are worst affected, with the Sahel, Middle East, and Central Asia being major hotspots.
- According to ISRO’s Desertification and Land Degradation Atlas (2021), 29.7% of India’s total geographical area (TGA) is undergoing desertification or land degradation.
- The UNCCD was created to address these issues, promoting policies that encourage sustainable land use and resilience against climate change.
Causes of Desertification
- Drought and erratic rainfall: Overgrazing, deforestation, and unsustainable agriculture
- Climate change: Urbanisation and industrialization
- Wind and water erosion: Excessive groundwater withdrawal and poor irrigation practices
- Salinization of soil: Mining and infrastructure development
Impacts of Desertification
- Environmental: Decline in soil fertility, biodiversity, and groundwater recharge.
- Intensification of climate change via reduced carbon sequestration.
- Increased frequency of dust storms and sand encroachment.
- Economic: Reduced agricultural productivity and livelihood loss for farmers and pastoralists.
- Increased rural poverty, food insecurity, and migration pressures.
- Huge costs on restoration and irrigation infrastructure.
- Social: Distress migration and resource-based conflicts.
- Erosion of traditional knowledge and indigenous land management systems.
- Geopolitical: Desertification contributes to transboundary tensions over water, land, and food security, particularly in fragile ecosystems like the Sahel or Indo-Gangetic plains.
India’s Efforts
- National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC): National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture and Green India Mission address land degradation.
- National Afforestation Programme: Through the National Mission for a Green India (GIM) and Forest Fire Protection & Management Scheme (FFPM), India supports states in afforestation and forest conservation.
- Compensatory afforestation under Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority (CAMPA) is used to increase forest cover.
- Desert Development Programme (DDP): Targets arid zones with integrated watershed management.
- Mangrove and Coastal Ecosystem Protection: India implements annual Management Action Plans for conserving mangroves and coral reefs across coastal states and UTs under the National Coastal Mission.
International Frameworks
- UN Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD): India has been a party since 1996; hosted COP-14 in 2019 in New Delhi.
- Bonn Challenge: It is a global goal to bring 150 million hectares of degraded and deforested landscapes into restoration by 2020 and 350 million hectares by 2030.
- India pledged to restore 13 million hectares of degraded land by 2020 and an additional 8 million hectares by 2030.
- 2030 Agenda (SDG 15.3): Committed to achieving Land Degradation Neutrality.
Way Forward
- Integrated Land Use Planning: Align national planning with land capability and agro-climatic zones.
- Promote multi-cropping, crop rotation, and sustainable grazing systems.
- Community-Led Watershed Management: Empower Panchayats and local communities.
- Incentivize watershed-based planning and decentralized water harvesting.
- Scientific Monitoring: Use remote sensing, GIS, and AI for real-time tracking of degradation.
- Strengthen Soil Health Monitoring Networks.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Shift towards organic farming, zero-budget natural farming, and agroforestry.
| Read this in Hindi: विश्व मरुस्थलीकरण एवं सूखा निवारण दिवस |
Previous article
India is Set to Air Conditioner Temperature Guidelines