Revisiting Net Neutrality in the 5G Era
Syllabus: GS2/ Government Policies & Interventions, GS3/ Digital Infrastructure
Context
- Telecom operators such as Reliance Jio and Bharti Airtel have urged the government to revisit India’s 2016 net neutrality framework to explicitly permit “network slicing” under 5G networks.
What is Net Neutrality?
- Net neutrality is the principle that all internet traffic should be treated equally, without discrimination based on content, platform, application, or user.
- It prohibits:
- Blocking of lawful content.
- Throttling (intentional slowing down of specific services).
- Paid prioritisation of certain apps or websites.
- India adopted one of the world’s strongest net neutrality frameworks in 2016–2018 following public debates on discriminatory pricing practices.
What is Network Slicing?
- Network slicing is a 5G feature that enables the creation of multiple virtual networks on a single physical infrastructure.
- Each “slice” can be optimised for specific needs:
- Ultra-low latency (autonomous vehicles, telemedicine).
- High reliability (industrial automation).
- High bandwidth (gaming, HD streaming).
- Telecom operators argue that this is a technological capability intrinsic to 5G, not content-based discrimination. Operators want to:
- Offer differentiated quality of service (QoS).
- Charge premium prices for guaranteed speeds or low latency.
Source: ET
India–Ireland Digital Partnership
Syllabus: GS2/ International Relations
Context
- India and Ireland held a high-level bilateral meeting in New Delhi to strengthen cooperation in telecommunications, digital infrastructure, and emerging technologies.
Key Highlights
- India’s Digital Transformation: India presented its achievements in ICT and digital governance. It represents;
- One of the world’s largest digital ecosystems, with over 1.23 billion telecom subscribers and nearly a billion internet users.
- 5G coverage extends to approximately 99.9% of the districts, supported by data tariffs averaging around USD 0.10 per GB, making connectivity affordable.
- Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI): India highlighted globally recognized platforms such as Unified Payments Interface (UPI), Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT), DigiLocker, Digi Yatra and Sanchar Saathi.
About Ireland
- Ireland is an island nation in Northwestern Europe, separated from Great Britain by the Irish Sea.
- Topography: A central lowland limestone plain surrounded by coastal mountains.
- Eg: MacGillycuddy’s Reeks in the southwest.
- The River Shannon is the longest river. The significant lakes include Lough Neagh and Lough Corrib.
- Capital: Dublin.
Source: PIB
Launch of SAHI and BODH Initiatives
Syllabus: GS2/Governance
Context
- The Union Health and Family Welfare Minister launched two digital health initiatives—SAHI (Secure AI for Health Initiative) and BODH (Benchmarking Open Data Platform for Health AI)—during the India AI Impact Summit 2026.
About
- SAHI is a governance framework, policy compass, and national roadmap for the responsible use of AI in healthcare, for leveraging AI in an ethical, transparent, accountable, and people-centric manner.
- The platform will also serve as a knowledge-sharing and governance hub, promoting best practices in health AI development and implementation.
- BODH, developed by the IIT Kanpur in collaboration with the National Health Authority, will enable systematic evaluation of AI models using diverse, anonymized real-world health datasets.
- It provides a structured mechanism to test and validate AI solutions before large-scale deployment.
- Together, SAHI and BODH represent India’s commitment to building a trustworthy, inclusive, and globally competitive health AI ecosystem grounded in innovation, responsibility, and public trust.
Source: TH
AI-Preneurs of India
Syllabus: GS3/ S&T
In News
- Atal Innovation Mission launches ‘AI-Preneurs of India’ at India AI Impact Summit 2026, showcasing India’s purpose driven AI Ecosystem.
About AI-Preneurs of India
- It is a flagship coffee table book chronicling the journeys of 45 pioneering AI startups shaping solutions for real-world challenges.
- AI-Preneurs of India features startups working across 30+ sector domains, including healthcare, education, sustainability, mobility, sports analytics, deep tech, and social impact.
- The book reflects the geographic and thematic diversity of India’s AI innovation landscape, extending far beyond traditional technology hubs.
Objectives
- The book showcases how public innovation infrastructure, sustained incubation support, and mission-led governance are enabling Indian startups to deliver scalable impact with global relevance.
- AI-Preneurs of India positions India not merely as a consumer of frontier technologies, but as a global contributor shaping responsible AI pathways.
- Reinforces AI vision for inclusive growth and ethical deployment.
Source: PIB
Bee Corridor
Syllabus: GS3/ Environment
In News
- In a first-of-its-kind initiative, the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) has unveiled an ambitious plan to create dedicated “bee corridors” along India’s national highways.
About
- The initiative aims to establish continuous linear stretches of bee-friendly vegetation featuring carefully selected flowering trees and plants.
- Unlike traditional decorative plantings, the new corridors will be designed to provide year-round nectar and pollen, ensuring sustained food sources for pollinators.
- The NHAI plans to plant around 40 lakh trees along NHs during the year 2026–27, around 60 per cent of which will be planted under the ‘bee corridor’ initiative.
Significance
- The initiative will help reduce the increasing ecological stress faced by honeybees and other pollinators, which is adversely impacting pollination services, agricultural and horticultural productivity, and overall ecological balance.
Source: IE
Gas Turbine Engine
Syllabus: GS3/Science and Technology
In News
- The Minister for Defence visited DRDO’s Gas Turbine Research Establishment (GTRE) in Bengaluru to review ongoing indigenous military gas turbine projects, including the Kaveri engine afterburner test.
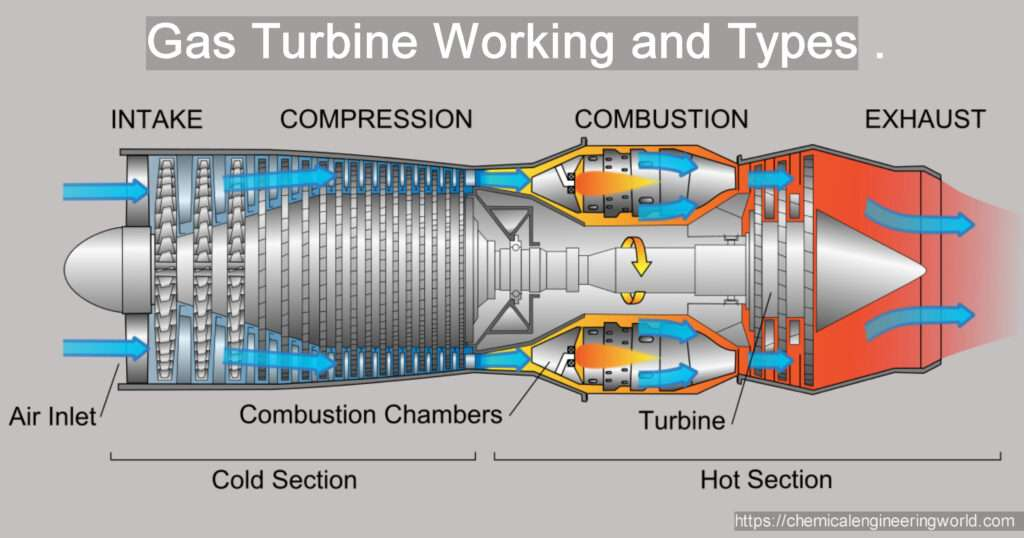
Gas Turbine Engine
- A gas-turbine engine is an internal combustion engine that uses air and fuel to generate power by turning a turbine.
- It consists of a compressor, combustion chamber, and turbine, where air is compressed, fuel is burned at constant pressure, and extra air cools the gases before reaching the turbine.
- Gas turbines are used in aviation (jet propulsion), electric power generation, and driving compressors for pipelines.
- The first successful gas turbine was built in 1903 in Paris.
Source :PIB
India AI Summit: Army’s Indigenous AI Suite
Syllabus: GS3/Defence; Science and Tech
Context
- At the India AI Summit, the Indian Army showcased a range of indigenous AI-based solutions with significant dual-use potential across defence and civilian sectors.
Key Highlights Include:
- AI Examiner: An automated assessment and feedback system for education and training platforms.
- SAM-UN: A geospatial and AI-enabled situational awareness platform for mission planning, disaster response and smart command centres.
- EKAM (AI-as-a-Service): A secure, air-gapped indigenous AI cloud platform ensuring data sovereignty.
- PRAKSHEPAN: An AI-driven climatology and disaster prediction system providing advance alerts for landslides, floods and avalanches.
- XFace: An AI facial recognition system for security and identity verification.
- Nabh Drishti: A mobile telemetry-based real-time reporting and visualisation platform.
- Driver Fatigue Detection: An AI device for real-time drowsiness alerts.
- AI-in-a-Box: A portable edge AI platform for secure deployment in remote or disconnected environments.
- Vehicle Tracking System: An AI-enabled fleet monitoring and logistics optimisation.
- Deepfake Detection & AI Cyber Security Systems – A tool to counter synthetic media, malware, cyber threats and protect critical digital infrastructure.

Significance
- These initiatives reflect a decisive shift towards a secure, networked and AI-empowered ecosystem, strengthening defence preparedness while enhancing disaster resilience, cybersecurity and national development.
Source: TH
Black Box
Syllabus: GS3/Disaster Management
Context
- The Aircraft Accident Investigation Bureau recovered the black boxes from the Learjet 45 aircraft that crashed in Baramati, killing five people on board.
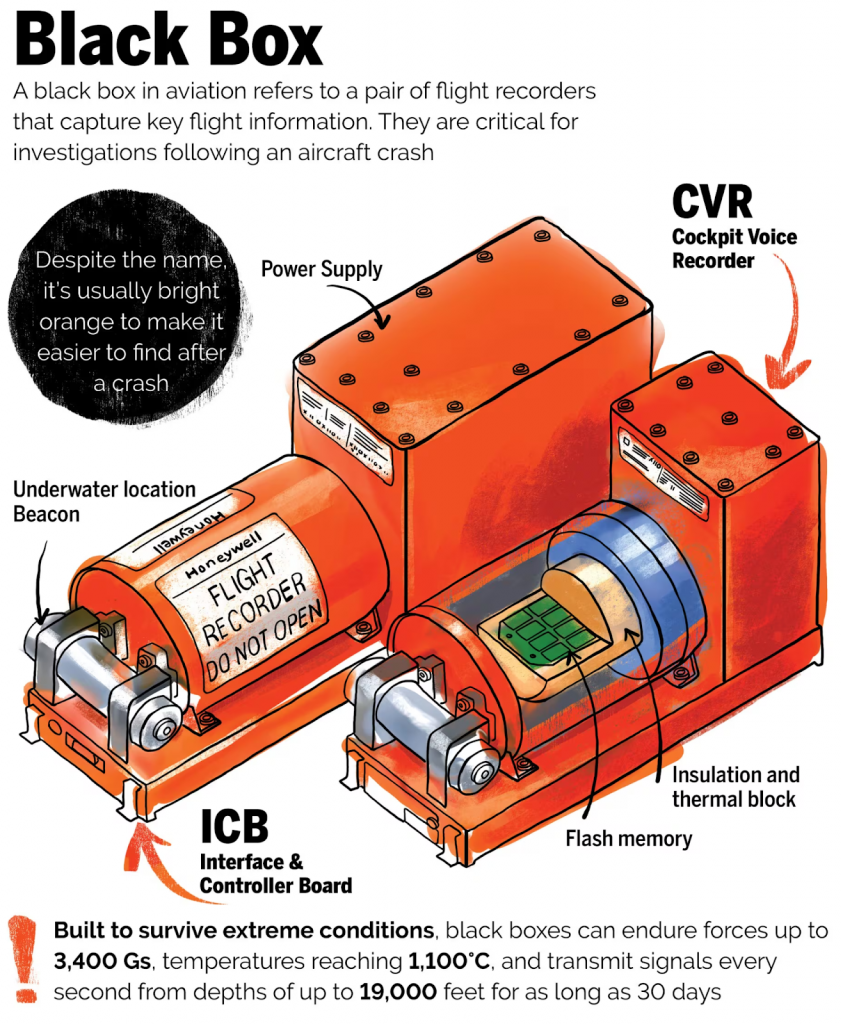
What is a Black Box?
- A black box is a small machine that records information about an aircraft during its flight.
- It is a bright orange or yellow rectangular box crafted to withstand explosions, fire, water pressure, and high-speed crashes.
- Discovered by Australian scientist David Warren, it is used to discover the cause of a plane crash.
What Does A Black Box Do?
- The black box comprises two components:
- Cockpit Voice Recorder (CVR): Captures cockpit audio, including pilot conversations, alarms, and engine sounds.
- Flight Data Recorder (FDR): Logs key flight parameters such as, Altitude, Airspeed, Flight heading, Vertical acceleration, Pitch and roll angles etc.
- Location: Both recorders are usually placed in the tail section of the aircraft—an area statistically least impacted in crashes.
- Crash Survival Capabilities:
- Materials: Titanium or stainless steel casing
- Impact Resistance: Can survive 3,400 g of force
- Fire Resistance: Endures 1,100°C for at least 60 minutes
- Pressure Resistance: Tolerates deep-sea pressure up to 6,000 meters.
Aircraft Accident Investigation Bureau (AAIB)
- Established: In 2012 under the Ministry of Civil Aviation.
- Mandate: Investigates civil aircraft accidents and serious incidents to determine causes and recommend safety measures (as per Annex 13 of ICAO).
- Legal Backing: Aircraft (Investigation of Accidents and Incidents) Rules, 2017.
Source: IE
Malabar Pied Hornbill
Syllabus: GS3/Species
In News
- The Chhattisgarh Forest Department is setting up six “hornbill restaurants” in the Udanti Sitanadi Tiger Reserve to provide a permanent habitat for the rare Malabar Pied Hornbill and promote forest regeneration.
Malabar Pied Hornbill (Anthracoceros coronatus)
- It stands 2 to 2.5 feet tall, has a large beak and vibrant plumage.
- It inhabits moist evergreen and tall deciduous forests, plantations, and low-altitude riparian areas
- It feeds mainly on figs and makes seasonal movements following fruiting events, sometimes visiting isolated trees in cultivated areas.
- Occurs in the western Ghats, and in eastern/central India from south-west West Bengal and Bihar, to Andhra Pradesh, India, as well as Sri Lanka
- They are recognised as keystone seed dispersers in tropical forests.
- The hornbill’s natural predators include leopards, snakes, and the Indian Shaheen Falcon, which has recently seen an increase in population at the Udanti Sitanadi Tiger Reserve.
- In the most recent assessment by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), the Malabar Pied Hornbill was listed in the ‘Red List of Threatened Species’ in 2024, under the ‘Near Threatened’ criteria.
Source :IE
Architects of Artificial Intelligence
Syllabus: GS3/ Science and Technology
Context
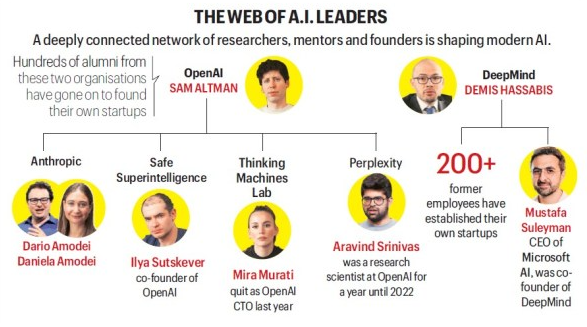
- Time magazine named the “Architects of AI” as its 2025 Person of the Year, highlighting key tech leaders like Sam Altman, Elon Musk, Demis Hassabis etc.
What is an AI Architect?
- An AI Architect is a senior technology professional who designs, plans, and oversees the development and deployment of Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems within an organisation.
- The role combines technical expertise, system design capability, and strategic vision.
Source: IE
Previous article
A Separate Classification for Denotified Tribes
Next article
India Unveiled Sovereign AI Models