Syllabus: GS3/Defence
Context
- The Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) launched its annual assessment of the state of armaments, disarmament and international security for 2025.
Major Findings
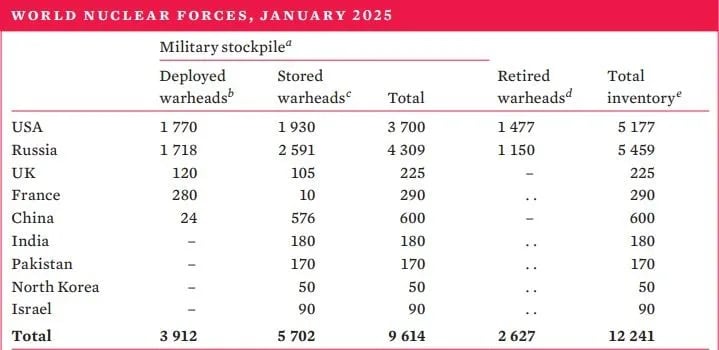
- Global Nuclear Trends (2025): Total nuclear warheads: 12,241.
- Military stockpiles (operational/potential): 9,614.
- Deployed: 3,912.
- High alert (ballistic missiles): ~2,100, mostly U.S. and Russia.
- India has 180 nuclear stored warheads as of January 2025, while Pakistan has an estimated 170.
- China has 600 nuclear warheads as of January 2025, of which 24 are deployed warheads or those placed on missiles or located on bases with operational forces.
- Expansion and Modernisation: Nearly all of the nine nuclear-armed states—the United States, Russia, the United Kingdom, France, China, India, Pakistan, North Korea and Israel—continued intensive nuclear modernization programmes in 2024.
- India slightly expanded its nuclear arsenal in 2024 and continued development of new nuclear delivery systems with enhanced capabilities.
- Pakistan continued development of new delivery systems, accumulated more fissile material, indicating intent to expand its arsenal.
- China accelerated expansion of its nuclear arsenal, It added ~100 warheads annually since 2023.
- Military Expenditure: Global spending reached $2.7 trillion in 2024, a 9.4% increase.
- Top spenders: USA ($997 billion), China ($314 billion).
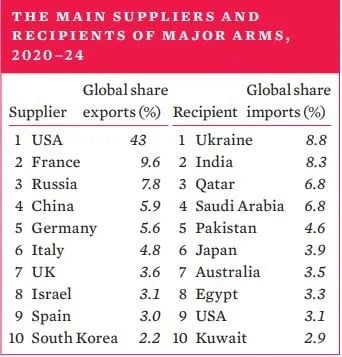
- Top importers: Ukraine, India, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Pakistan.
- Top exporters: USA (43%), France (9.6%), Russia (7.8%).
Concerns & Outlook
- Arms control weakening: No major nuclear powers fully committed to disarmament.
- The era of reductions in global arsenals may be ending.
- China is increasing its nuclear force steadily and may reach 1,000 warheads within 7–8 years.
- All nine nuclear-armed states invested heavily in modernisation in 2024, including: upgraded systems, new technologies (e.g., MIRVs, canisterisation, AI-based command and control).
- New Nuclear States: Revitalized national debates in East Asia, Europe and the Middle East about nuclear status and strategy suggest there is some potential for more states to develop their own nuclear weapons.
- Russia and the USA together possess around 90% of all nuclear weapons.
- Both states are implementing extensive modernization programmes that could increase the size and diversity of their arsenals in the future.
- If no new agreement is reached to cap their stockpiles, the number of warheads they deploy on strategic missiles seems likely to increase after the bilateral 2010 Treaty on Measures for the Further Reduction and Limitation of Strategic Offensive Arms (New START) expires in February 2026.
| About SIPRI – SIPRI is an independent international institute dedicated to research into conflict, armaments, arms control and disarmament. It is based in stockholm. – It was established in 1966, SIPRI provides data, analysis and recommendations, based on open sources, to policymakers, researchers, media and the interested public. – Funding: It was established on the basis of a decision by the Swedish Parliament and receives a substantial part of its funding in the form of an annual grant from the Swedish Government. 1. The Institute also seeks financial support from other organizations in order to carry out its research. |
Source: TH
| Read this in Hindi: SIPRI वार्षिक रिपोर्ट 2025 |
Previous article
Preservation of Traditional Seed Varieties in india
Next article
Tech Platforms for Better Disaster Management