Syllabus: GS2/ International Relations
In News/Context
- At the 18th India–Japan Strategic Dialogue, India and Japan reaffirmed the upward trajectory of their Special Strategic and Global Partnership, with a strong focus on economic security, resilient supply chains, critical technologies, and defence cooperation.
Key Highlights
- Announced the launch of Japan–India Private-Sector Dialogue on Economic Security (B2B) in early 2026.
- It will help in identification of five priority areas: semiconductors, critical minerals, ICT, clean energy, and pharmaceuticals.
- Establishment of the Japan–India AI Strategic Dialogue under the Japan–India AI Cooperation Initiative (JAI).
- Japan will invite 500 highly skilled Indian AI professionals by 2030 for joint research.
- Early convening of Joint Working Group on Mineral Resources to strengthen resilient supply chains.
- Both emphasised on de-risking the global economy and ensuring stability of critical supply chains.
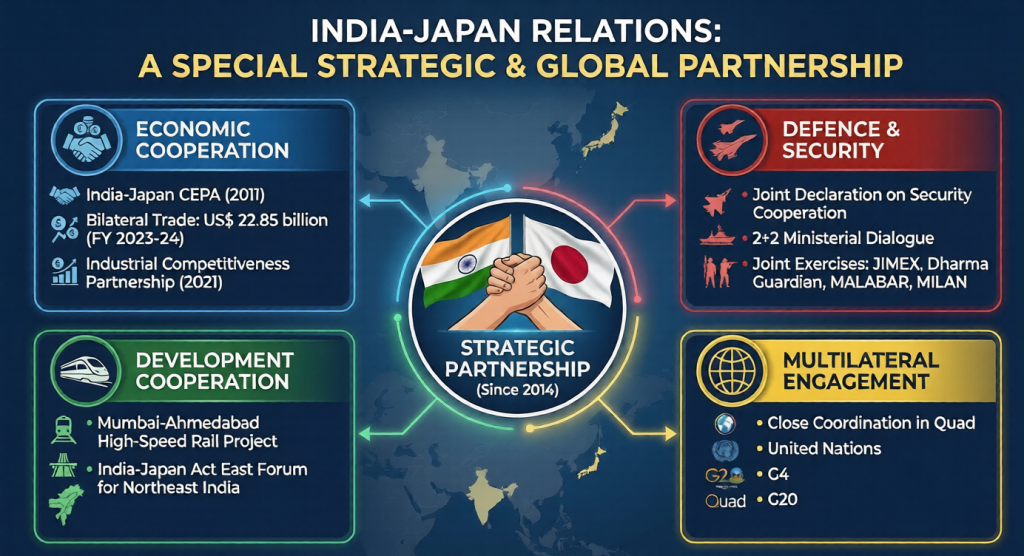
Significance of Japan for India
- Economic Partner: Key source of FDI, infrastructure financing, and high-end technology.
- Strategic Ally: Shares India’s vision of a Free, Open, and Inclusive Indo-Pacific.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Critical partner in de-risking strategies and diversification away from over-concentrated supply chains.
- Technology & Innovation: Cooperation in AI, semiconductors, clean energy, and advanced manufacturing.
- Global Governance: Supports India’s role in shaping a rules-based international order and reforms in multilateral institutions.
Challenges / Concerns
- Implementation Gap: Several dialogues and frameworks exist, but translating them into large-scale industrial and technological outcomes remains slow.
- Limited Trade Volume: Despite strong strategic ties, bilateral trade remains modest compared to potential and Japan’s trade with other major partners.
- Technology Transfer Constraints: High-end defence and semiconductor technologies face export controls, cost issues, and procedural delays.
- Discussions on UNICORN radar technology highlight progress, but such flagship projects often face lengthy negotiations.
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: Dependence on third countries for critical minerals and components continues in the short term.
Way Ahead
- Converting strategic convergence into co-production, co-innovation, and co-investment is essential to overcome these challenges.
Source: AIR
Previous article
News In Short 16-01-2026
Next article
UN High Seas Treaty Comes Into Effect