Syllabus: GS2/Social Issues; Issues Related To Women
Context
- Despite decades of legislation and activism, dowry continues to claim lives, particularly among young married women.
About Dowry
- The Dowry Prohibition Act, 1961 defines dowry as ‘any property or valued security given or agreed to be given, directly or indirectly, to either partner in a marriage, to the other party’s parents, to any other person, is referred to as dowry’.
- Dowry-related violence and deaths are symptoms of deep-rooted patriarchy, and remains one of the most persistent forms of gender-based crimes in India.
- In many cases, women are subjected to mental and physical abuse, culminating in suicide or murder — often by burning, poisoning, or hanging.
Dowry Death in India: Current Statistics
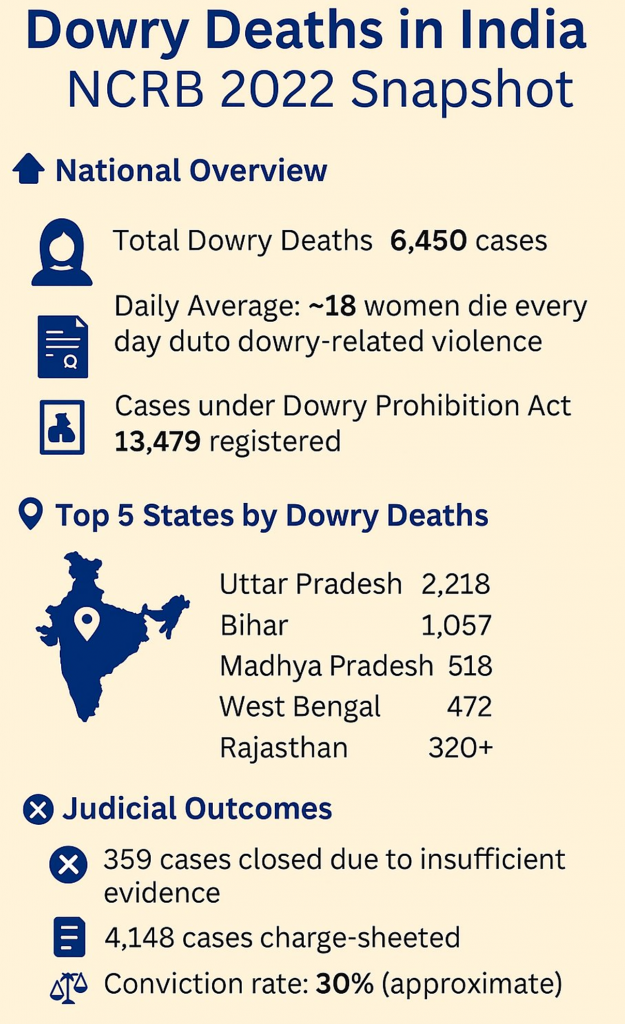
- High-Burden States: According to NCRB data for 2022, 6,450 dowry deaths were registered across India;
- Uttar Pradesh (highest), Bihar, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Rajasthan, and Haryana together contributed 80% of all dowry death cases.
- From NCW’s 2024 complaint data: 4,383 cases of dowry harassment (17% of total complaints): 292 cases of dowry deaths.
- Over 60% of dowry murders occurred in West Bengal, Odisha, and Bihar.
- Cities with Highest Cases: Delhi alone accounted for 30% of all dowry death cases among India’s 19 major cities.
- Other high-reporting cities include Kanpur, Bengaluru, Lucknow, and Patna.
Causes Behind Dowry Deaths
- Cultural Acceptance: Dowry is still seen as a customary obligation, especially in arranged marriages.
- Economic Exploitation: Dowry is often used to secure financial gain or status for the groom’s family.
- Gender Inequality: Women are viewed as financial burdens, leading to coercive demands and abuse.
- Districts with skewed sex ratios show higher dowry death rates (Sex ratio imbalance).
- Illiteracy and Lack of Awareness: Many women are unaware of their legal rights or fear retaliation (Lower levels correlate with increased vulnerability).
- Delayed Justice: Investigations are often slow, and convictions rare, weakening deterrence.
- Caste and kinship structures: Hypergamy and patrilocality intensify dowry pressures.
Key Concerns & Issues
- Policing and Investigations: Of the 7,000 yearly cases, only 4,500 were charge-sheeted.
- Many cases were dropped due to reasons like ‘insufficient evidence’, ‘false complaints’, or ‘misunderstanding’.
- By the end of 2022, 67% of pending dowry death investigations had been stalled for over six months.
- Delay in Charges and Trials: In 2022, 70% of the charge-sheets were filed after two months or more, showing procedural inefficiencies.
- From 6,500 trials initiated annually, only around 100 led to convictions.
- Over 90% of cases remain pending in courts.
- Acquittals, plea bargains, and withdrawn complaints account for a large number of unresolved cases.
Key Legal Provisions
- Dowry Prohibition Act, 1961: Criminalizes giving or receiving dowry.
- Section 113B of the Indian Evidence Act, 1872 (replaced by the Bharatiya Sakshya Adhiniyam, 2023): Presumes dowry death if it occurs within 7 years of marriage and is preceded by harassment.
- Section 80 of the BNS (formerly IPC Section 304B): It defines dowry death and mandates punishment of 7 years to life imprisonment.
- Section 85 BNS (formerly Section 498A IPC): It deals with cruelty against married women, and penalizes cruelty by husband or relatives.
Judicial Interventions: Landmark Judgments
- Sanjay Kumar Jain v. State of Delhi (2011): Supreme Court condemned dowry deaths as a ‘curse on society’.
- State of Haryana v. Satbir Singh (2021): Expanded the scope of cruelty to include indirect evidence.
- Rajesh Sharma v. State of U.P. (2017): Introduced safeguards to prevent misuse of Section 498A.
Way Forward
- Strengthen forensic and investigative protocols;
- Establish fast-track courts for dowry-related cases;
- Promote legal literacy and community vigilance;
- Encourage economic empowerment and education for women;
- Support victim protection mechanisms and whistleblower safeguards;
Previous article
Bombay High Court Flags Misuse of Matrimonial Laws
Next article
Appointment of Governors