Syllabus :GS2/Governance
In News
- Kavinder Gupta (former Deputy Chief Minister of Jammu and Kashmir) has been appointed Lieutenant Governor of Ladakh, replacing Brig. (retd.) B.D. Mishra
| Other related Appointments – Pusapati Ashok Gajapathi Raju, a senior TDP leader and former Civil Aviation Minister, has been appointed Governor of Goa, succeeding P.S. Sreedharan Pillai. – Ashim Kumar Ghosh, a senior BJP leader from West Bengal, has been appointed Governor of Haryana, replacing Bandaru Dattatreya. |
Governor: Appointment and Eligibility
- The Governor is the constitutional head of a State and acts as a link between the Union and the State governments.
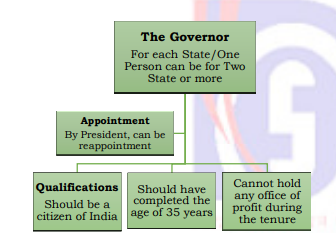
- Article 153 provides that each State shall have a Governor, and the same person can be appointed for more than one State.
- The Governor is appointed by the President (Article 155) and holds office during the President’s pleasure, though his tenure is generally five years (Article 156).
- Eligibility : To be eligible, one must be an Indian citizen aged 35 or above (Article 157), and cannot be a member of Parliament or a State Legislature, nor hold any other office of profit (Article 158).
Power and Functions
- As per Article 154, the executive powers of the State are vested in the Governor and exercised according to the Constitution.
- He/she appoints the Chief Minister, and on the Chief Minister’s advice, appoints the Council of Ministers and allocates their portfolios.
- The Governor also appoints the Advocate-General, and the Chairman and members of the State Public Service Commission.
- Additionally, the Governor appoints judges of subordinate courts and is consulted in the appointment of High Court judges by the President.
- Legislative: The Governor is an integral part of the State Legislature, holding several legislative powers.
- Governors may summon, prorogue, or dissolve the Legislature (Article 174), address or send messages to the House (Article 175), and must deliver a special address at the start of the first session each year or after general elections (Article 176).
- For any bill to become law, the Governor’s assent is essential; he/she can approve, withhold, return it for reconsideration, or reserve it for the President. During the Legislature’s recess, the Governor can issue ordinances, which must be approved within six weeks of the Assembly’s reconvening.
- Financial Powers: The Governor has key financial powers in the State: no money bill can be introduced in the Legislative Assembly without prior permission
- The annual and supplementary budgets are presented in the Governor’s name; and the Governor controls the State Contingency Fund.
- Judicial: The Governor has the power to grant pardons, reprieves, respites, remission, or to suspend, remit, or commute sentences of persons convicted under laws related to the State’s executive powers (Article 161).
Source :TH
Previous article
Dowry Deaths in India: Long Investigations, Rare Convictions
Next article
Corporate Investment Lagging Behind