Syllabus: GS3/Environment
Context
- Delhi government has announced that it has approved a framework for carbon credit monetisation.
- The government has not released much details in the public domain regarding the framework or how and when it will be implemented.
About
- Delhi government activities such as operating electric buses, plantation drives, promoting solar energy and waste management, will be used to generate carbon credits under the new policy.
- The reduction in emissions through these initiatives will be scientifically measured, registered as carbon credits, and sold in national and international carbon markets to generate revenue.
- A specialised agency will be selected to handle documentation and registration as per international norms.
- The model is based on revenue-sharing, with no upfront cost to the government.
- All proceeds will be deposited in the Consolidated Fund of the State.
- Delhi is one of the pioneers among states to approve such a policy.
- Maharashtra has approved one such policy four-five months ago.
- This mechanism creates a direct financial incentive for the government to engage in activities which reduce carbon emissions.
Carbon Markets
- Carbon markets are trading systems in which carbon credits are sold and bought.
- Companies or individuals can use carbon markets to compensate for their greenhouse gas emissions by purchasing carbon credits from entities that remove or reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- One tradable carbon credit equals one tonne of carbon dioxide or the equivalent amount of a different greenhouse gas reduced, sequestered, or avoided.
- When a credit is used to reduce, sequester, or avoid emissions, it becomes an offset and is no longer tradable.
- There are broadly two types of carbon markets: compliance and voluntary.
- Compliance markets are created as a result of any national, regional, and/or international policy or regulatory requirement.
- Voluntary carbon markets – national and international – refer to the issuance, buying, and selling of carbon credits voluntarily.
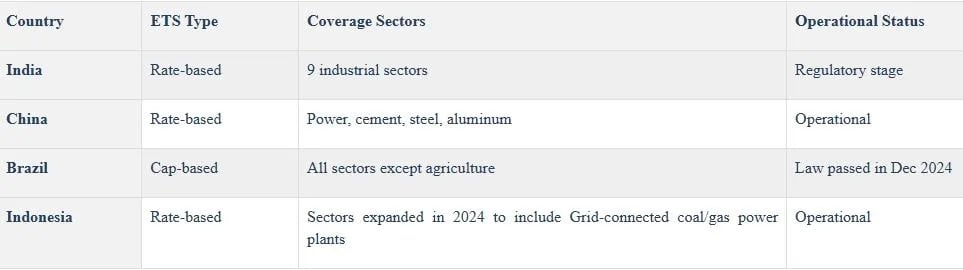
India’s Position in the Global Carbon Pricing Landscape
- India is moving towards a rate-based Emissions Trading System (ETS) with the adoption of the Carbon Credit Trading Scheme (CCTS) in 2024.
- Rate-based ETS refers to a system where total emissions are not capped, but individual entities are allocated a performance benchmark that serves as a limit on their net emissions.
- The national ETS will initially cover nine energy-intensive industrial sectors.
- The scheme focuses on emissions intensity, not absolute emissions caps.
- Credit Certificates will be issued to facilities that outperform benchmark emissions intensity levels.
| Carbon Credit Trading Scheme (CCTS) – It involves two key elements: a compliance mechanism for obligated entities (primarily industrial sectors) and an offset mechanism for voluntary participation. – The CCTS aims to incentivize and support entities in their efforts to decarbonize the Indian economy. – CCTS laid the foundation for the Indian Carbon Market (ICM) by establishing the institutional framework. |
Government Steps to Strengthen Carbon Market Readiness
- As highlighted during the COP 27, India balances its developmental needs with lower carbon emissions through Common but Differentiated Responsibilities and Respective Capabilities (CBDR-RC) principles.
- India’s efforts include:
- Mission LiFE and the Green Credit Program to promote a sustainable lifestyle.
- Creation of the National Steering Committee for the Indian Carbon Market (NSCICM) and the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) under the Ministry of Power.
- Incentives for private sector participation.
Conclusion
- As global markets evolve and instruments like CBAM create external pressures, India is aligning its policies to maintain competitiveness while achieving climate goals.
- By focusing on emissions intensity rather than absolute caps, India’s rate-based ETS offers a pragmatic and flexible path forward, particularly for an economy balancing development with decarbonization.
Source: IE
Previous article
Employment and Social Trends 2026 Report: ILO