Syllabus: GS3/Artificial Intelligence
Context
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi advocated that India’s AI model should promote local and indigenous content as well as regional languages.
- He also stressed that AI developed in India must be ethical, unbiased, transparent, and grounded in strong data privacy principles.
About
- The PM chaired a roundtable meeting with Indian AI start-ups, the roundtable was held ahead of the AI Impact Summit 2026, scheduled to take place in India in February.
- During the meeting, the Prime Minister highlighted the importance of artificial intelligence in driving societal transformation.
India’s Technology Sector
- India’s technology sector is expanding rapidly, with annual revenues projected to cross USD 280 billion this year.
- Over 6 million people are employed in the tech and AI ecosystem.
- India has secured the 3rd position globally in Artificial Intelligence competitiveness, according to Stanford University’s 2025 Global AI Vibrancy Tool.
- The country hosts 1,800+ Global Capability Centres, including more than 500 focused on AI.
- GCCs are mainly offshore centres established by global level firms/MNCs to provide various services to their parent organisations.
- India has around 1.8 lakh startups, and nearly 89% of new startups launched last year used AI in their products or services.
- On the NASSCOM AI Adoption Index, India scores 2.45 out of 4, showing that 87% of enterprises are actively using AI solutions.
- Leading sectors in AI adoption include industrial and automotive, consumer goods and retail, banking, financial services and insurance, and healthcare. Together they contribute around 60 percent of AI’s total value.
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) – AI is the ability of machines to perform tasks that normally require human intelligence. – It enables systems to learn from experience, adapt to new situations, and solve complex problems independently. – AI uses datasets, algorithms, and large language models to analyse information, recognise patterns, and generate responses. – Over time, these systems improve their performance, allowing them to reason, make decisions, and communicate in ways similar to humans. |
Concerns
- Bias & Discrimination: AI trained on data may develop biases and can discriminate against certain groups.
- Data Privacy: India lacks a comprehensive framework for sensitive citizen data despite the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023.
- Accountability Gap: If AI makes a wrong decision, it’s unclear who is responsible — programmer, operator, or government.
- Overdependence on Technology: Risk of ignoring human judgment, empathy, and contextual understanding.
- Cybersecurity Threats: AI systems vulnerable to hacking, manipulation, or adversarial attacks.
- Dependence on Foreign Tech Firms: Risk of “digital colonization” if India relies too much on external AI companies.
Government Initiatives
- IndiaAI Mission (2024): It has a budget of ₹10,300 crore over five years.
- A key goal is the creation of a high-end common computing facility with 18,693 GPUs.
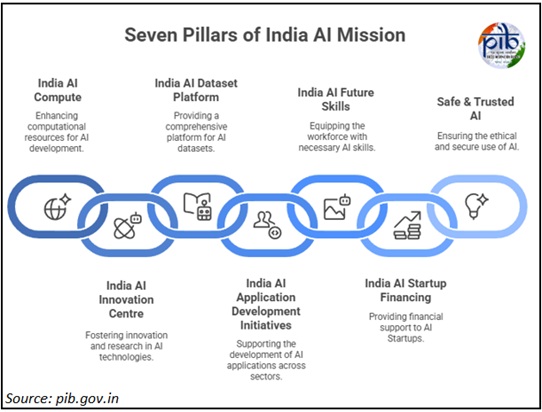
- India’s AI Models & Language Technologies: The government is facilitating the development of India’s own foundational models, including Large Language Models (LLMs) and problem-specific AI solutions tailored to Indian needs.
- BharatGen: The world’s first government-funded multimodal LLM initiative, BharatGen was launched in 2024.
- Sarvam-1 AI Model: A large language model optimised for Indian languages, Sarvam-1 has 2 billion parameters and supports ten major Indian languages.
- Hanooman’s Everest 1.0: A multilingual AI system developed by SML, Everest 1.0 supports 35 Indian languages, with plans to expand to 90.
- Bhashini is an AI-powered platform that breaks language barriers by offering translation and speech tools in multiple Indian languages.
- AI Centers of Excellence: Establishing dedicated AI hubs and innovation centers across the country to support AI startups and research.
- India’s Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI): Combines public funding with private sector innovation to drive digital transformation.
- Aadhaar, UPI, and DigiLocker serve as the foundation of India’s DPI.
- Intelligent solutions are being integrated into financial and governance platforms to enhance DPI.
- e-Courts Project: Initiated by the Supreme Court of India to modernize judicial functions through digital innovation.
- Phase III: Integrates advanced AI solutions to improve case management and administrative efficiency in courts.
Conclusion
- From expanding computing infrastructure to fostering homegrown models and supporting startups, the country is creating a robust AI ecosystem that benefits citizens and drives innovation.
- Initiatives in agriculture, healthcare, education, and governance demonstrate practical applications with real impact.
- These efforts lay a strong foundation for India to emerge as a global AI leader while advancing the vision of Viksit Bharat 2047.
Source: TH
Previous article
News In Short 09-01-2026
Next article
Digitalizing India’s Dairy Sector