Fall of Berlin Wall
Syllabus: GS1/ History
Context
- The fall of the Berlin Wall on November 9, 1989, marked a pivotal moment in world history.
Berlin Wall Construction
- Erected in 1961 by the German Democratic Republic (East Germany), the Berlin Wall physically and ideologically divided East and West Berlin.
- It was built to stop the mass exodus of East Germans to the more prosperous West, symbolizing the “Iron Curtain” that separated the Eastern Bloc and Western Europe.
Events Leading to the Fall
- Soviet Reforms: Mikhail Gorbachev’s policies of Glasnost (openness) and Perestroika (restructuring) signaled more liberal approaches, contributing to the weakening control of communist governments.
- Growing Protests: Civil unrest and widespread protests for freedom and political reform erupted across Eastern Europe throughout 1989, especially in countries like Poland and Czechoslovakia.
Significance
- End of the Cold War: The fall paved the way for German reunification, which formally took place on October 3, 1990.
- Global Impact: The event shifted the balance of global power, diminishing Soviet influence and fostering the expansion of democracy and market economies in former communist states.
Source: IE
Mount Lewotobi
Syllabus: GS 1/Physical Geography
Context
- Mount Lewotobi Erupts in Indonesia.
About: Mount Lewotobi
- Mount Lewotobi is one of Indonesia’s active volcanoes.
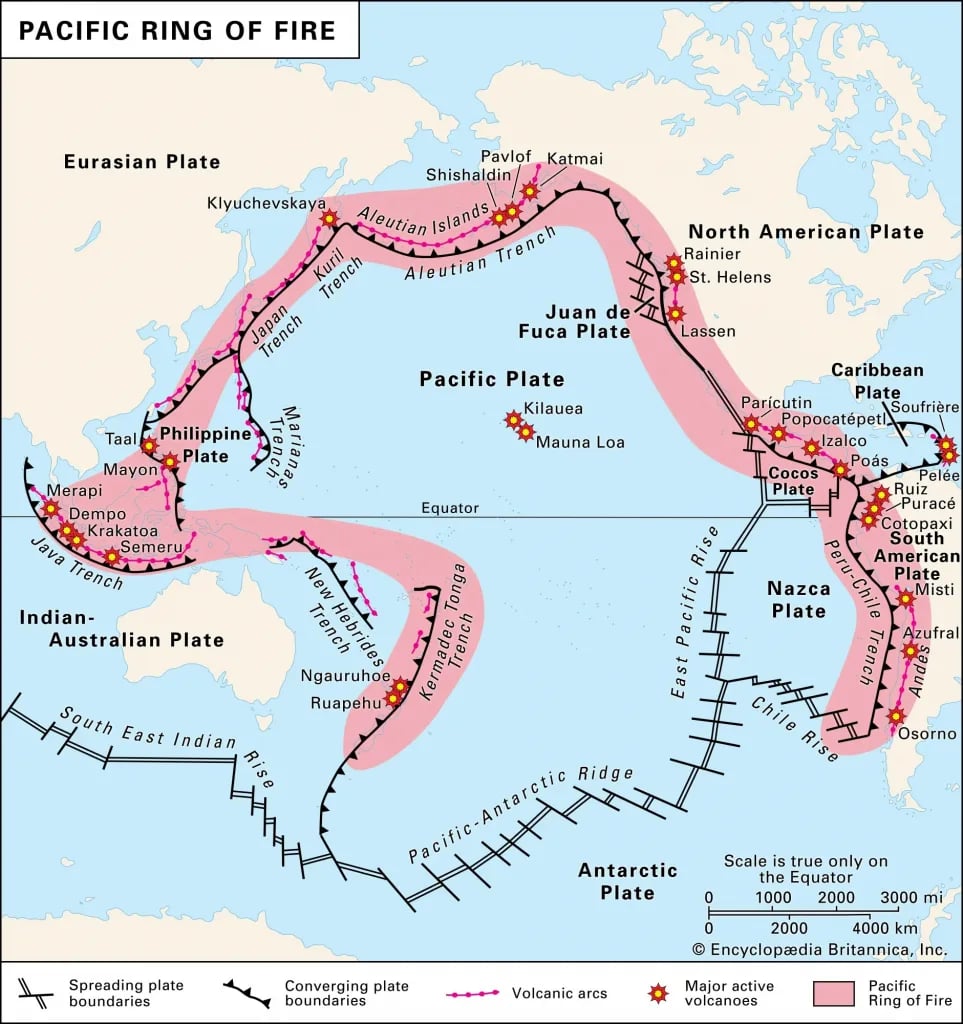
- Indonesia lies along the “Pacific Ring of Fire,” an area of high seismic activity where multiple tectonic plates meet.
Pacific Ring of Fire
- A horseshoe-shaped region around the Pacific Ocean.
- Characterized by frequent earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
- Caused by the interaction of the massive Pacific Plate with surrounding plates (Nazca, Juan de Fuca).
Source: AIR
India’s Nutraceutical Industry
Syllabus: GS2/ Health
In News
- India is emerging as a strong player in nutraceuticals, leveraging traditional knowledge like Ayurveda and biodiversity. However, India’s market share is below 2%.
About Nutraceutical Industry
- Nutraceuticals include dietary supplements, functional foods, beverages, and fortified foods that aim to support health, prevent chronic diseases, and promote well-being.
- The US, Japan, and Europe currently dominate the global nutraceutical market, accounting for over 90% of the total market share.
- India’s nutraceutical market is prepped to be a global leader at USD 4-5 billion. It is expected to grow approximately USD 18 billion by 2025.
India’s Competitive Advantages
- Traditional Knowledge: A deep-rooted legacy in health sciences, particularly Ayurveda.
- Agro Climatic Diversity: India’s 52 agroclimatic zones make it ideal for cultivating various medicinal plants.
- Rich Plant Biodiversity: Home to 1,700 medicinal plants, including curcumin, bacopa, and ashwagandha, needing further scientific validation.
- Pharmaceutical Expertise: India’s robust pharmaceutical formulation expertise sets high standards for nutraceuticals.
- Startup Ecosystem: A growing number of startups and companies in nutraceuticals drive innovation.
Challenges
- Regulatory Clarity: Lack of defined industry classification limits targeted sector support.
- Scientific Validation: Many traditional ingredients require rigorous scientific studies to meet international regulatory standards.
- Research and Development: Investing in research and development to innovate and create new products.
Source: PIB
Allulose
Syllabus: GS 2/Health and GS 3/Science and Tech
In News
- South Korea has become a top testing ground for the sweetener allulose, which is gaining popularity as a strong contender to other sugar substitutes like stevia.
About: Allulose
- Production: Also known as D-allulose and d-psicose, it is naturally present in only certain foods like wheat, raisins, figs, molasses. It is commercially produced from beet sugar or corn using specific enzymes.
- Similarity and difference: It is 70% as sweet as sugar and does not have the bitter aftertaste found in some sweeteners, like aspartame.
Benefits
- Controls blood sugar spikes, helps in weight loss and reduces health risks associated with added sugar.
| Do you know? – The World Health Organization (WHO) in 2023, issued a guideline advising against using non-sugar sweeteners for weight control purposes, citing potential undesirable long-term effects. – Also, the WHO has also classified aspartame as a “possible carcinogen” but maintained that it remains safe to consume within established intake limits. |
Source: TOI
Seaplane Service
Syllabus: GS3/ Infrastructure
In News
- Kerala to launch seaplane service to boost tourism.
About Seaplane
- Brief:
- A seaplane is a type of aircraft that can take off and land on water.
- Types of Seaplanes:
- Floatplanes: These aircraft have floats attached to the wings or fuselage, allowing them to land on water.
- Flying Boats: These have a boat-like hull that serves as the main structure of the aircraft, enabling it to take off and land on water.

- Working Principle:
- They rely on buoyancy provided by floats or a hull to take off and land. Once airborne, they function similarly to conventional aircraft.
Advantages of Seaplanes
- Access to Remote Locations: Seaplanes can access remote areas with limited land-based infrastructure.
- Versatility: They can operate from both water and land (in the case of amphibious seaplanes).
- Reduced Infrastructure Requirements: They don’t need traditional runways, making them suitable for various environments.
About India’s Seaplane Project
- Objective: To boost regional air connectivity and promote tourism through water-based aviation under India’s RCS-UDAN scheme.
- India’s First Seaplane Project: Launched in Gujarat, 2020, connecting the Sabarmati Riverfront in Ahmedabad to the Statue of Unity in Kevadia.
- Later the service was suspended due to high operational cost.
- Recent Development: In August 2024, the Union Minister for Civil Aviation launched guidelines for seaplane operations in India, emphasizing the country’s 7,517 km coastline and extensive network of rivers and lakes as opportunities for seaplane development. The guidelines aim to integrate seaplane operations into India’s aviation landscape.
Source: TOI
Cyanobacteria
Syllabus: GS3/ Environment
Context
- Recently, a novel strain named “Chonkus” of Cyanobacteria has been discovered noteworthy for its carbon capture potential.
About
- Cyanobacteria, often termed “blue-green algae,” are a group of photosynthetic microorganisms that play a vital role in Earth’s ecosystems.
- Cyanobacteria are unique due to their ability to photosynthesize like plants, converting sunlight and carbon dioxide (CO2) into food.
- These microorganisms can thrive in diverse and extreme environments, such as hot springs and volcanic vents, due to their remarkable resilience.
Significance of discovery
- Carbon Sequestration Projects: Its efficient CO2 absorption and ability to settle at the bottom of bodies of water could help in long-term carbon storage.
- Bioproduction: The strain’s properties could be harnessed for producing biofuels, food supplements, and other valuable commodities.
Source: Science News
Animal Cells Capable of Photosynthesis Created
Syllabus: GS3/ Science and Technology
Context
- Recently scientists have successfully engineered animal cells that are capable of photosynthesis.
About
- Photosynthesis, a process fundamental to life on Earth, has long been exclusive to plants, algae, and certain bacteria.
- This process transforms sunlight into energy, converting water and carbon dioxide into oxygen and sugars.
Animal Cells with Photosynthetic Ability
- Traditionally, when chloroplasts are forcibly introduced into animal cells, the animal’s immune response perceives them as foreign, leading to their rapid degradation.
- However, researchers have discovered a novel method where chloroplasts are introduced as “food” rather than injected, allowing them to be maintained within animal cells for a limited period (up to two days) and enabling photosynthetic activity.
Potential Applications
- Bioengineering New Life Forms: Creating organisms that can self-sustain or enhance their nutritional profiles could revolutionize food security.
- Bioactive Compounds Production: Photosynthesis in animal cells may be harnessed to produce vital compounds and medications, reducing reliance on traditional methods.
- CO2 Absorption: Engineering animal cells or symbiotic organisms capable of photosynthesis could contribute to carbon capture efforts, assisting in the reduction of greenhouse gases.
Source: Earth.com
Manas National Park
Syllabus: GS3/ Conservation
In News
- Recent studies have shown an increase in the tiger population in Manas National Park.
About Manas National Park
- Location: Situated in the Himalayan foothills in Assam, contiguous with Bhutan’s Royal Manas National Park.
- UNESCO Status: Declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site and recognized as a Project Tiger reserve, elephant reserve, and biosphere reserve.
- Etymology: Named after the Manas River, which flows through the park and is a major tributary of the Brahmaputra River.
- Significance: Known for its rare and endangered species, including the Assam roofed turtle, hispid hare, golden langur, and pygmy hog. It is also famous for a significant population of wild water buffalo.
Source: TH
Exercise AUSTRAHIND
Syllabus: GS 3/Defence
Context
- The 3rd edition of joint military Exercise AUSTRAHIND commenced at Foreign Training Node, Maharashtra (India).
About
- Started in 2022, is an annual exercise conducted alternatively in India and Australia.
- Aim of Exercise AUSTRAHIND is to promote military cooperation between India and Australia through enhancement of interoperability in conduct of joint sub conventional operations in semi-urban environments in semi-desert terrain under Chapter VII of the UN mandate.
Source: PIB
Previous article
Rainforests into Rubber Plantations Alters Soil’s Properties
Next article
5 Years of Kartarpur Sahib Corridor