GI Tag Push in Bodoland Territorial Region (BTR)
Syllabus: GS1/ Culture
Context
- The Assam’s Bodoland Territorial Region (BTR) government recently launched a special drive to work towards GI tag registration of cultural artefacts belonging to all 26 communities of the region.
- This move follows the recognition of 21 Bodo indigenous items with GI tags.
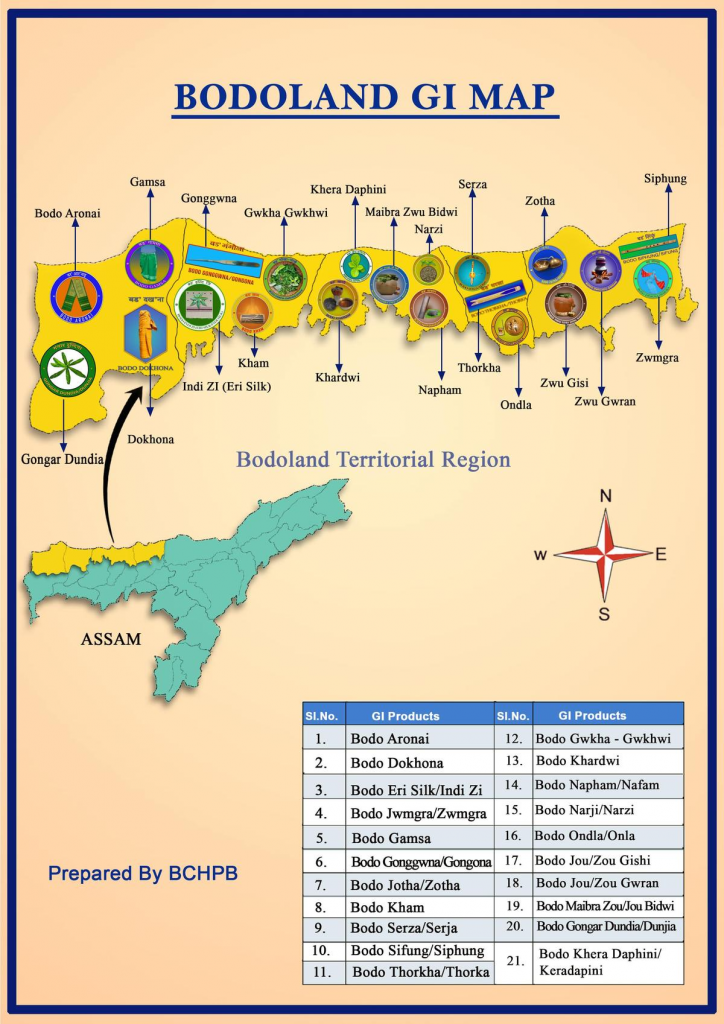
| Geographical Indication (GI) – A geographical indication (GI) is a sign used on products that have a specific geographical origin and possess qualities or a reputation that are due to that origin. – In order to function as a GI, a sign must identify a product as originating in a given place. – Geographical indications are typically used for agricultural products, foodstuffs, wine and spirit drinks, handicrafts, and industrial products. GI Tags and India – The Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act,1999 seeks to provide for the registration and better protection of geographical indications relating to goods in India. – The Act is administered by the Controller General of Patents, Designs and TradeMarks, who is the Registrar of Geographical Indications. – The registration of a geographical indication is valid for a period of 10 years. |
Source: IE
International Earth Sciences Olympiad (IESO-2025)
Syllabus: GS2/Education
Context
- The Minister for Earth Sciences felicitated student winners comprising the Indian team at “International Earth Sciences Olympiad” (IESO-2025) held in China.
About
- Team India secured a total of seven medals – 1 Gold, 4 Silver and 2 Bronze – along with a 3rd Prize in the International Geoscience Youth Movement (I-GYM) Reporter category.
- The Ministry supports students for IESO every year by conducting the Indian National Earth Science Olympiad (INESO) across 300 centres in India.
International Earth Sciences Olympiad
- It was established in 2003 by the International Geoscience Education Organization (IGEO).
- It is one of the twelve International Science Olympiads.
- It is an annual competition for secondary school students (Class IX–XII) worldwide.
- India has been participating since 2007 and hosted the 10th edition at Mysore in 2013.
- Aim: To enhance the level of geoscience education worldwide and increase public awareness of Earth Sciences.
International Geoscience Education Organization (IGEO)
- Nature: A non-governmental, non-profit international organization established in 2000.
- Purpose: Promotes geoscience education at all levels (schools, universities, and public education).
- Membership: Open to individual geoscience educators, institutions, and organizations worldwide.
Source: PIB
Universal Postal Union (UPU)
Syllabus: GS2/ International Organisation
In News
- The 28th Universal Postal Congress, the supreme decision-making body of the Universal Postal Union (UPU), opened in Dubai.
About Universal Postal Union (UPU)
- Established: 9 October 1874 (Treaty of Bern).
- UN Agency: Became a specialized UN agency in 1948.
- Purpose:
- Coordinates international postal policies and operations.
- Created a “single postal territory” for uniform international mail rates and equal treatment for domestic and foreign mail.
- Sets technical standards and rules for cross-border mail, parcels, and financial services.
- Members: 192 member countries, making it one of the oldest and largest global organizations.
- India joined UPU in 1876.
Source: AIR
Himachal Pradesh Becomes Fully Literate State
Syllabus: GS2/Governance
In News
- On International Literacy Day, Himachal Pradesh Chief Minister declared the state fully literate, achieving a 99.30% literacy rate which is higher than the national benchmark of 95%.
| Definition of literacy – According to the 2011 Census, literacy is defined as the ability to both read and write with understanding in any language for individuals aged seven and above. – Merely being able to read does not qualify as literacy. The 2011 data shows a notable rise in literacy levels across India. |
International Literacy Day (ILD)
- International Literacy Day (ILD) is observed annually on September 8 and was proclaimed by UNESCO during the 14th General Conference in October 1966, following the landmark World Conference of Ministers of Education on the Eradication of Illiteracy held in Tehran in 1965.
- It has become a global occasion recognised by nearly every country, serving as a moment to reflect on the importance of literacy, assess progress, and confront ongoing challenges.
- 2025, International Literacy Day’s theme : “Promoting Literacy in the Digital Era,” emphasizing the need to integrate digital skills with traditional literacy to bridge the digital divide.
India’s progress in literacy
- India has made significant progress in literacy, with Himachal Pradesh becoming the fourth state—after Tripura, Mizoram, and Goa—to achieve full functional literacy. Ladakh is the first fully literate Union Territory.
- The national literacy rate rose from 74% in 2011 to 80.9% in 2023–24.
- The ULLAS Nav Bharat Saaksharta Karyakram enrolled over 3 crore learners with a 90% success rate.
- India’s digital public infrastructure has played a key role, setting an example for the Global South in advancing education and inclusion.
Source :IE
Engineering Export Promotion Council (EEPC)
Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
In News
- Recently, the platinum jubilee of the Engineering Export Promotion Council (EEPC) was held.
About Engineering Export Promotion Council (EEPC)
- Established: 1955, Ministry of Commerce & Industry.
- Objectives: Boost India’s global competitiveness and raise engineering export targets.
- Acts as the interface between government and exporters, advocating policy reforms and providing technical, financial, and strategic support.
- Members: Over 12,000 companies, with around 60% SMEs (Small and Medium Enterprises).
- Head & Registered Office: Kolkata.
Source: LM
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Syllabus :GS3/Science and Technology
In News
- Many services are implementing Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) to improve security.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
- It is a cybersecurity measure that strengthens user verification by requiring two distinct forms of identity: something you know (like a password) and something you have (such as an OTP-generating app or device).
- Apps like Google Authenticator generate short, time-sensitive codes using a system called TOTP (Time-based One-Time Password), which relies on a shared secret key and the current time divided into 30-second intervals.
- Both the app and the server use this key and time counter to compute the same code via a cryptographic process involving HMAC-SHA-256—a secure hash-based method that combines the key and message using XOR operations.
- XOR (exclusive OR) is a fundamental logical operation in computer science that works on bits.
Benefits
- Enhances account security and ensures both authenticity and integrity which make it a cornerstone of digital trust across public and private sectors.
| TOTP (Time-based One-Time Password) – TOTP is a time-based variant of HMAC-based OTP systems, offering automatic synchronization and robust protection against password-only attacks. 1. HMAC stands for ‘hash-based message authentication code’. – TOTP is secure because: 1. Codes expire quickly (every 30 seconds) 2. Guessing the correct code is nearly impossible 3. The secret key is not transmitted or exposed |
Source :TH
Ghost Bat Drone
Syllabus:GS3/Defence
In News
- Australia is rapidly developing its defense capabilities with the production of MQ-28A Ghost Bat drones.
Ghost Bat Drone
- They are 38-foot-long autonomous military aircraft designed as “robot wingmen.”
- They can be operated remotely and can fly preprogrammed missions with human oversight from afar.
- They are named after a fierce native bat, they have a range of ~2,300 miles, nearly spanning Australia.
Latest Developments
- Australia has invested $650 million in partnership with Boeing to develop and manufacture the drones.
- This marks the first domestically produced aircraft in over 50 years, signaling a revival of its defense industry.
- 70% of components will be made in Australia; each drone costs ~10% of an F-35 fighter jet.
- China and the U.S. are also developing “loyal wingman” drones, reflecting a surge in unmanned systems.
Source :IE
Hilsa Fish (Tenualosa ilisha)
Syllabus: GS3/ Species in news
Context
- Bangladesh has decided to allow the export of 1,200 tonnes of hilsa fish, to India ahead of the Durga Puja festive season as a mark of “enduring Bangladesh-India friendship”.
About
- Hilsa fish, also known as Ilish, is a popular and culturally significant fish in South Asia, particularly in Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal.
- Habitat: It is found in rivers and estuaries in Bangladesh, India, Pakistan, Myanmar and the Persian Gulf area.
- It is the national fish of Bangladesh.
- Appearance: The fish has a silvery-golden color and a compressed, streamlined body.
- It is also called the “queen of fish”.
- Flavor and texture: It has an oily, rich flavor and a uniquely soft, flaky texture. Hilsa is also a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids, which are beneficial for heart health.
- Conservation status: Least Concern

Source: TH
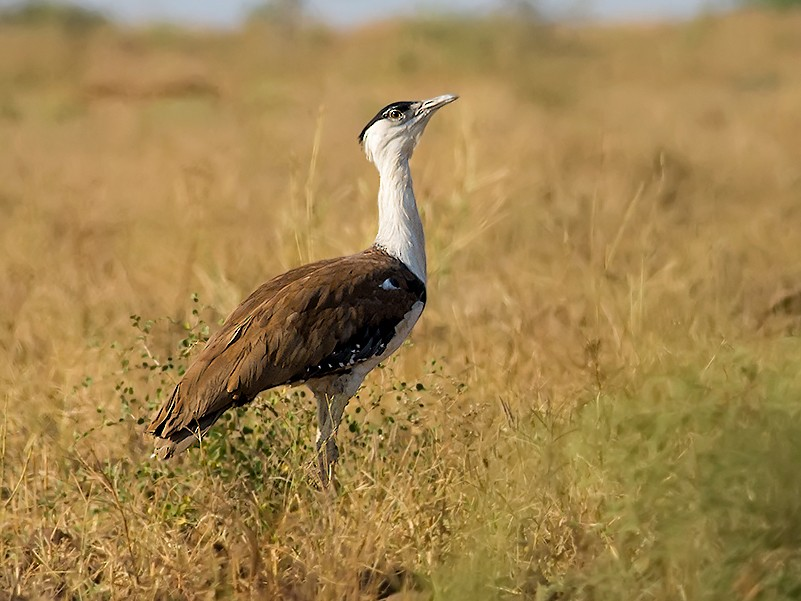
Great Indian Bustard (Ardeotis Nigriceps)
Syllabus: GS3/ Environment
Context
- The Union Environment Ministry’s Expert Appraisal Committee has approved an Environmental Impact Assessment study for the proposed 400-hectare Birmania Rock Phosphate mine in Jaisalmer, Rajasthan, which falls within the potential habitat of Great Indian Bustard (GIB).
Great Indian Bustard
- The GIB is one of the heaviest flying birds in the world.
- Diet: The great Indian bustard is an omnivore and feeds on insects, grass seeds, berries, rodents, and reptiles.
- Habitat and distribution: The Great Indian Bustard, once widespread across the Indian subcontinent and Pakistan, is now largely confined to Rajasthan with small populations in Gujarat, Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh.
- Rajasthan’s Thar Desert, particularly the Desert National Park, is the last stronghold for the species in India, holding over 90% of the remaining wild population.
- It is the state bird of Rajasthan.
- Significance: It is a key indicator of the health of its native arid and semi-arid grassland ecosystems.
- IUCN Status: Critically Endangered

Conservation Efforts
- Project Great Indian Bustard: It was launched by the Rajasthan government in 2013, the project works to construct breeding enclosures and reduce human pressure on the bustard’s habitat.
- National Bustard Recovery Plan: It is implemented by the Indian Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change (MoEFCC) and the Wildlife Institute of India (WII), focusing on habitat improvement and conservation breeding.
- Captive breeding: A conservation breeding program was established in 2019, with captive breeding centers at Sam and Ramdevra in Rajasthan.
- Mitigation of power line collisions: Following a Supreme Court order, measures are being taken to install bird diverters on existing power lines and explore undergrounding lines in critical habitats.
Source: IE
Previous article
Submarine Cables