Pre-Harappan Coastal Settlements in Kachchh
Syllabus: GS1/ Ancient History
Context
- The study by the researchers of the Indian Institute of Technology Gandhinagar (IITGN), has uncovered archaeological evidence that pushes back the human presence in this region by at least 5,000 years prior to the arrival of Harappans.
Findings of the study
- Early Human Settlement in Kachchh: The study suggests that early communities inhabited a mangrove-dominated landscape and relied on shell species (both bivalves like oysters and gastropods), naturally adapted to such environments, as a significant food source.
- The presence of stone tools (for cutting, scraping, and splitting) and tool-making cores indicates the existence of semi-permanent or settled communities.
- Pre-Harappan Culture with Regional Linkages: The findings suggest a cultural continuity and regional interaction among early coastal communities from:
- Las Bela and Makran regions (now in Pakistan), and
- The Oman Peninsula, indicating similar subsistence and survival strategies.
- This challenges the long-held belief that urbanisation in Kachchh emerged solely under the influence of the Sindh-based Harappan culture, suggesting instead a more complex and indigenous developmental trajectory.
Method to determine the age of the sites
- The research team used Accelerator Mass Spectrometry (AMS) dating of shell remains, a highly precise technique that measures the radioactive isotope Carbon-14 (C-14) absorbed by living organisms.
- After death, C-14 begins to decay and is reduced by half every 5,730 years.
- As atmospheric C-14 levels have varied over time, the results were calibrated using tree-ring data.
- Trees form one ring per year, and these tree-ring sequences can be matched and extended back over thousands of years, allowing scientists to construct an accurate reference timeline of atmospheric C-14.
Source: PIB
Index Cards
Syllabus: GS2/ Governance
In News
- The Election Commission has streamlined a technology-driven system to generate Index Cards and various statistical reports after the conduct of the elections.
- Earlier, this information was manually filled at the Constituency level using various statutory formats in Physical Index Cards.
About Index Cards
- It is a non-statutory, post-election Statistical Reporting Format developed as a suo moto initiative by the Election Commission of India (ECI) to promote accessibility of election-related data at the constituency level for all stakeholders.
- It is designed to disseminate data across multiple dimensions—such as candidates, electors, votes polled, votes counted, party-wise and candidate-wise vote share, gender-based voting patterns, regional variations, and performance of political parties.
Source: PIB
S Mahendra Dev Appointed New Chief of EAC-PM
Syllabus: GS2/Governance
In News
- Economist S Mahendra Dev has been appointed as Chairman of the Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister (EAC-PM), replacing current head Suman Bery.
| Do you know? – S Mahendra Dev is an expert in agriculture and rural economy and is also editor of Economic and Political Weekly and chairs the Institute for Development Studies, Andhra Pradesh. – Previously, he served as director of Indira Gandhi Institute of Development Research and held roles at Kotak Mahindra Bank. 1. Dev holds a PhD from Delhi School of Economics and completed post-doctoral research at Yale University. |
The Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister (EAC-PM)
- It is an independent body constituted to give advice on economic and related issues to the Government of India, specifically to the Prime Minister.
- Functions: It includes analyzing economic or other issues referred by the Prime Minister, addressing macroeconomic matters, providing advice, and undertaking any additional tasks requested by the Prime Minister.
- These tasks can be initiated by the Council itself or on referral.
Source :IE
Ayush Nivesh Saarthi
Syllabus:GS2/Governance
In News
- The Government of India launched the Ayush Nivesh Saarthi portal to position India as a global hub for traditional medicine and wellness.
Ayush Nivesh Saarthi
- It is a dedicated, investor-centric digital platform developed by the Ministry of Ayush in collaboration with Invest India.
- It brings together policy frameworks, incentive structures, investment-ready projects, and real-time facilitation under one unified interface.
- It is designed to support both domestic and global investors.
Importance
- It is a strategic tool that strengthens India’s standing as a global investment destination for traditional systems of medicine.
- India’s Ayush industry has emerged as one of the fastest-growing sectors in the country, recording an annual growth of 17% between 2014 and 2020.
- The Ayush sector’s relevance is also strongly reflected in its contributions to medical value travel (MVT) and the global wellness economy. Ranked among the top five health services in India, Ayush is a key driver of the country’s USD 13 billion MVT sector Globally.
- The portal is expected to drive FDI, support entrepreneurs, and promote India’s leadership in traditional health systems.
Source :PIB
United Nations Security Council Counter-Terrorism Committee
Syllabus :GS 2/IR
In News
- Pakistan’s appointment to key UN counter-terrorism bodies has caused concern in India, especially following recent terror incidents and military tensions.
Counter-Terrorism Committee (CTC)
- It was established by UN Security Council resolution 1373 (2001), which was adopted unanimously on 28 September 2001 in the wake of the 11 September terrorist attacks in the United States.
- It comprises all 15 Security Council members and it monitors countries’ implementation of measures such as criminalizing terrorism financing, freezing terrorist assets, denying support and safe haven to terrorists, and promoting international cooperation.
- The Resolution 1624 (2005) expanded its scope to include criminalizing incitement to terrorism and promoting intercultural dialogue.
Source :PIB
ECINET App
Syllabus: GS2/Governance
Context
- Due to the alleged discrepancies in the voter turnout data, the Election Commission of India has introduced a new streamlined and tech-driven system to provide such data.
About
- The new one-stop platform, ECINET, will integrate and reorient over 40 of ECI’s existing mobile and web applications.
- It will have an aesthetic User Interface (UI) and a simplified User Experience (UX) by providing a singular platform for all electoral-related activities.
- The Presiding Officer of each polling station will enter the turnout figures on the new ECINET app every two hours on polling day in order to reduce the time lag.
- This will be automatically aggregated at the constituency level.
- Need for the App: Previously, voter turnout data were collected manually by Sector Officers and relayed to Returning Officers (ROs) through phone calls, SMS, or messaging apps.
- The polling percentage trends were often updated hours later due to physical records arriving late leading to delays.
- Significance of the App: Now, approximate voter turnout will be updated faster and more accurately on the Voter Turnout app.
- While Form 17C under Rule 49S remains the official record, this tech-driven process aims to improve transparency, timeliness, and public trust.
Source: TH
Chenab and Anji Rail Bridges
Syllabus: GS3/Infrastructure
Context
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the Chenab and Anji rail bridges in Jammu and Kashmir, marking a historic moment for infrastructure and connectivity in the region.
About the Chenab Rail Bridge
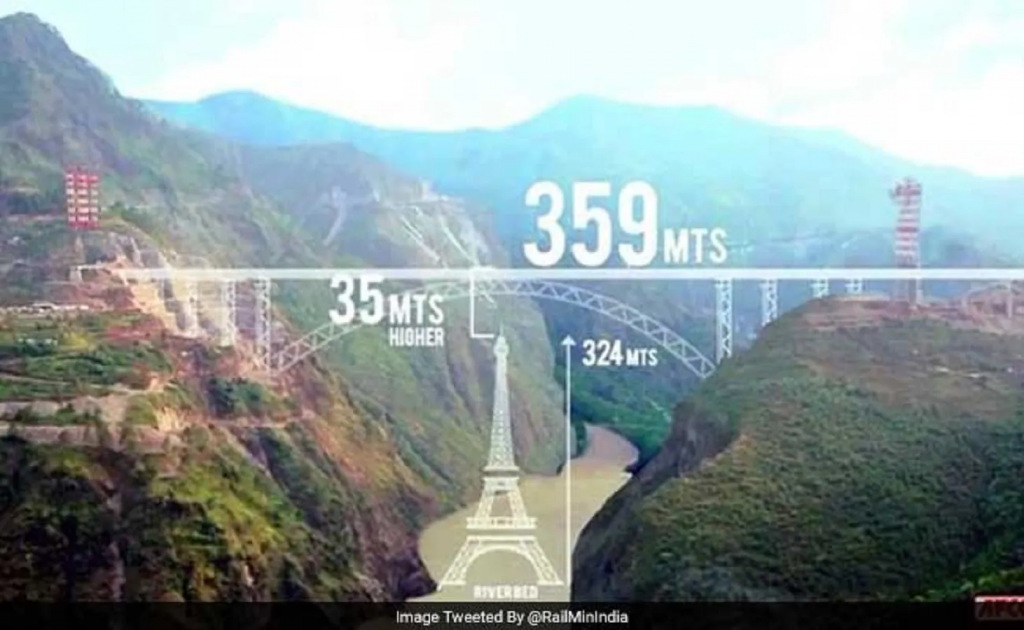
- The Chenab Rail Bridge, situated 359 meters above the Chenab River, is the world’s highest railway arch bridge.
- It is a 1,315-metre-long steel arch bridge engineered to withstand seismic and wind conditions.
- A key impact of the bridge will be in enhancing connectivity between Jammu and Srinagar. It will take just about 3 hours to travel between Katra and Srinagar.

About the Anji Rail Bridge
- The Anji Bridge, India’s first cable-stayed railway bridge, is located in the Reasi district, spanning 473 meters across the Anji River, a tributary of the Chenab.
- The bridge is part of the Udhampur-Srinagar-Baramulla Rail Link project.
- The bridge will enhance connectivity to the Kashmir Valley, playing a crucial role in improving trade, travel, and defense logistics in the area.

Source: PIB
Aravalli Green Wall Project
Syllabus: GS3/ Environment
In News
- The Prime Minister launched the Aravalli Green Wall project to combat the threat of desertification.
About Aravalli Green Wall Project
- It is a flagship initiative launched by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) to combat land degradation.
- The project aims to establish a 5-km-wide green buffer along the entire 700-km stretch of the Aravalli Range (one of the oldest in the world), which runs through Gujarat, Rajasthan, Haryana, and Delhi.
- It is an afforestation and reforestation initiative, focusing on native species, water harvesting, and community involvement.
- The project directly contributes to India’s commitments under various international conventions, including the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD), the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), and the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
Source: TH
EnviStats India 2025: Environment Statistics
Syllabus: GS3/ Environment
Context
- The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) has released the 8th edition of EnviStats India 2025, offering a detailed statistical assessment of India’s environmental landscape.
About
- Launched in 2018, EnviStats India is an annual publication prepared by the National Statistics Office (NSO).
- It follows the UN’s Framework for the Development of Environment Statistics (FDES) 2013, ensuring global comparability and standardisation.
- A comprehensive and integrative framework developed by the United Nations.
- Offers a structured approach to collect, compile, and present environment statistics at the national level.
- The report is a critical tool for policymakers, environmentalists, and researchers, covering data across a wide spectrum of environmental domains.
Key Features of EnviStats India 2025
- Expert Consultation: An expert group was constituted with members from relevant Ministries and domain experts to;
- Expand the publication’s scope
- Identify new data sources
- Refine presentation and design
- Component-Wise Restructuring: The report is now organized in alignment with FDES’s component-wise format, improving clarity and usability.
- Indicator Concordance: A mapping exercise was conducted to align EnviStats indicators with FDES 2013. A full list of FDES indicators is included in the publication.
- New data on the population’s access to electricity, transport, and sanitation is included.
Key Highlights of the publication
- The annual mean temperature increased from 25.05°C in 2001 to 25.74°C in 2024.
- Similarly, the annual minimum and maximum temperature rose from 19.32°C to 20.24°C and 30.78°C to 31.25°C respectively, during the same period.
- The annual rainfall data from 2001 to 2024 highlights significant year-to-year variability influenced by monsoon patterns. Despite this variability, the data does not indicate any clear long-term upward or downward trend in total annual rainfall
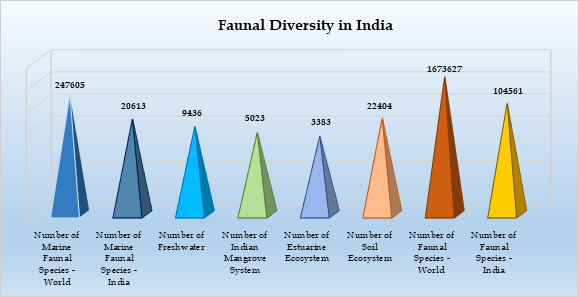
- Globally, there are 2,47,605 marine faunal species, while India accounts for 20,613.
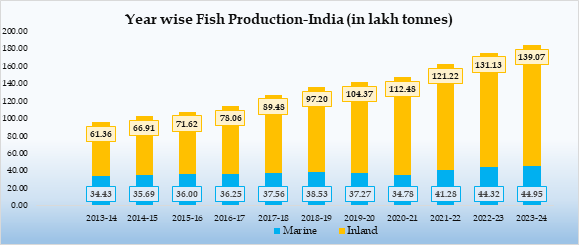
- Inland fish production has increased from 61.36 lakh tonnes in 2013-14 to 139.07 lakh tonnes in 2023–24, possibly indicating inland aquaculture and freshwater fisheries.
- The Environment Sustainability Sector shows the highest expenditure share as Rs. 2433.24 crore in 2021-22.
- The Conservation of Natural Resource Sector shows an upward trend and the Agro-Forestry Sector exhibits the lowest expenditure among the three sectors: Agro-Forestry, Conservation of Natural Resources, and Environment Sustainability.
Source: PIB
Fusarium Graminearum
Syllabus: GS3/ S&T
In News
- Two Chinese nationals had been charged in the US for allegedly smuggling an agricultural pathogen Fusarium graminearum into the United States.
About
- It is an ascomycete fungus responsible for Fusarium head blight (FHB)—a devastating disease affecting cereal crops such as wheat, barley, maize, oats, and rice. It produces Vomitoxin (Deoxynivalenol), harmful to humans and livestock.
- This pathogen not only reduces crop yields and quality but also contaminates grains with harmful mycotoxins, posing significant risks to both animal and human health.
What is agro-terrorism?
- Agro-terrorism is the intentional use of biological agents such as plant pathogens, pests, or contaminants to attack a country’s agricultural infrastructure.
- It targets food production systems with the aim of causing economic devastation, food insecurity, and public panic.
- Agro-terrorism is attractive to hostile actors because it is low-cost, difficult to detect, and capable of triggering far-reaching economic and social damage.
Global Examples
- UK Foot and Mouth Disease (2001): Cost over £8 billion; suspected bio-attack.
- Rice Blast Fungus (Asia): Could be weaponized to destroy staple crops.
- Anthrax in Cattle (Soviet Era): Tested by USSR in Cold War biowarfare labs.
Global Conventions
- Biological Weapons Convention (BWC) (1972): It bans the development, production, acquisition, transfer, stockpiling, and use of biological and toxin weapons.
- United Nations Security Council Resolution 1540: UNSCR 1540 obliges all UN member states to prevent non-state actors from acquiring nuclear, chemical, and biological weapons.
- Interpol’s Bioterrorism Prevention Program: Interpol works with member countries to enhance law enforcement capabilities in preventing and responding to bioterrorism.
Source: TH
Previous article
Should India Amend its Nuclear Energy Laws?